Jira Service Management (JSM) works well for IT teams but presents challenges for non-technical support teams like HR or customer service. Here’s why:
- Complex Setup: Configuring workflows often requires technical skills, making it hard for non-IT teams to get started.
- Confusing Interface: IT-focused terms like "incidents" and "problems" don’t align with tasks like customer inquiries or HR requests.
- Limited Reporting: Default reports focus on IT metrics, not customer-focused data like satisfaction or first-contact resolution.
- Integration Issues: Connecting JSM with non-Atlassian tools often requires significant technical effort.
While AI tools and customizations can address some of these issues, they often come with higher costs or require technical expertise. For non-technical teams seeking simplicity, alternatives like Supportbench may offer a better fit with features tailored to their needs.
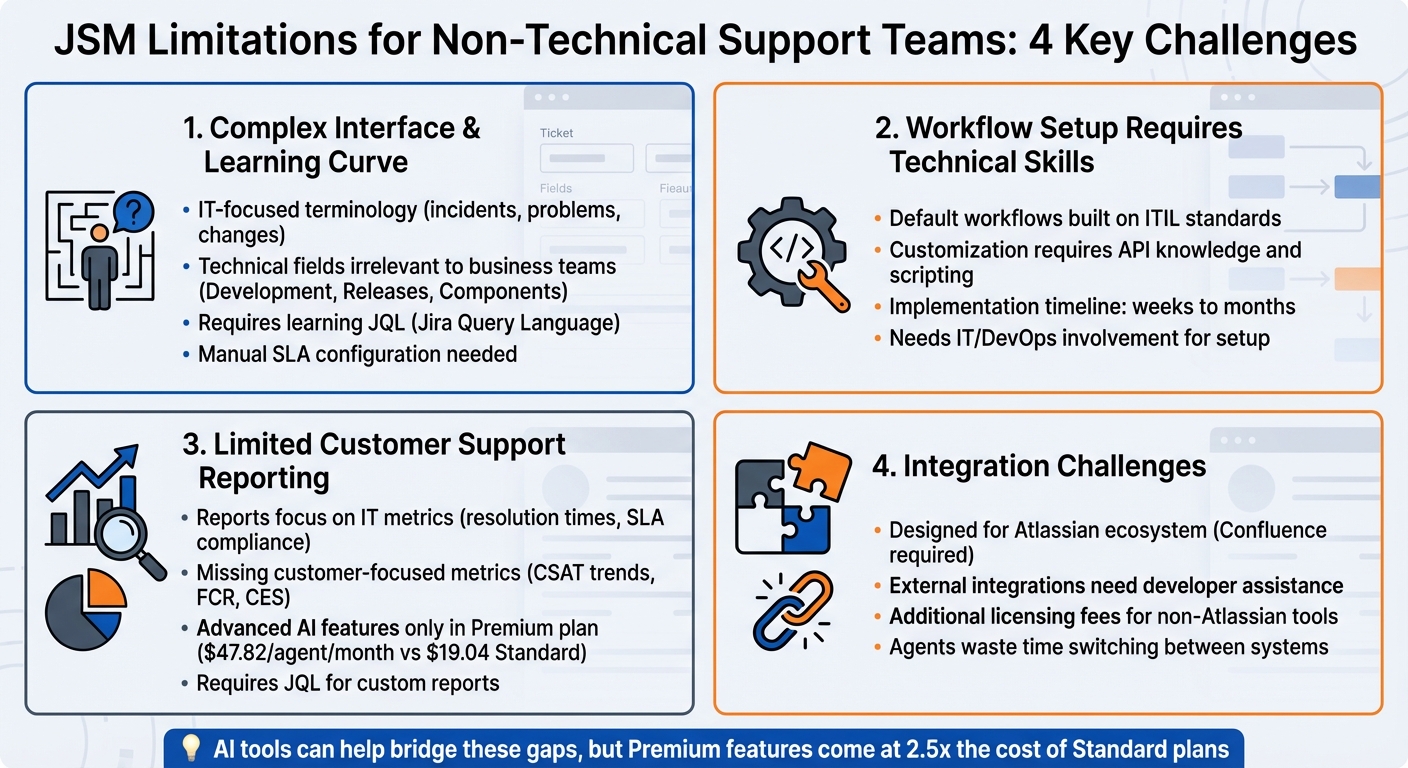
JSM Limitations for Non-Technical Support Teams: Key Challenges Overview
Jira Project Templates Explained for Every Team (Jira Tutorial 2025)
sbb-itb-e60d259
Difficult Learning Curve and Interface Problems
Jira Service Management (JSM) caters primarily to IT professionals, which makes it less suitable for teams like customer support or HR. This focus on IT creates usability challenges that add to the operational difficulties already mentioned. Non-technical teams often struggle with a system that doesn’t prioritize an intuitive, quick way to resolve tickets.
Complicated Navigation and Setup
JSM’s navigation and setup can feel overwhelming, especially for users without IT expertise. Its reliance on tools like Jira Query Language (JQL), manual configuration of SLAs, and custom form building creates steep barriers. Even minor adjustments often require admin access, leading to delays and reduced productivity.
The interface itself adds another layer of complexity. It displays technical fields such as Development, Releases, Components, and Time tracking, which are irrelevant for many business teams. For non-technical users, this clutter makes routine tasks unnecessarily complicated.
The challenge isn’t just the interface – it’s also the technical language used throughout JSM.
IT-Focused Language and Terms
JSM uses terminology like "incidents" and "service requests", which align with IT workflows but don’t resonate with other departments such as customer support, HR, or marketing. For example, a billing support agent might find it confusing to work in a system structured around IT incidents instead of customer inquiries. This mismatch can complicate even basic ticket handling.
"As JSM is designed for IT, I find it often hard to filter out relevant information for my purposes from your general product information… several functionalities – designed for a different purpose of course – are often hard / not possible to utilize for our use cases", said Soraa Kim-Pueschel, Operations at ubitricity.
Even updates and newsletters from JSM lean heavily on IT-related content, forcing non-technical users to sift through irrelevant details to find what applies to their needs.
Addressing these language and interface issues is essential to making JSM more user-friendly for non-IT teams.
Simplifying the Interface for Support Teams
There are ways to make JSM more accessible. For example, administrators can rename fields (like changing "Incident" to "Inquiry") to better match business language. Role-based permissions can also hide technical fields, streamlining the interface for different users.
For teams with simpler needs, Jira Work Management (JWM) offers an easier alternative. It comes with business-specific templates and user-friendly views such as List, Calendar, and Timeline – eliminating the need to learn JQL. Additionally, AI-powered virtual agents can simplify things even further by creating conversational interfaces. These agents handle Tier 1 support in natural language, allowing users to avoid the complexities of the Jira portal entirely. This approach has led to a 50% boost in resolution rates and a 40% increase in CSAT scores by removing technical barriers.
Workflow Setup Requires Technical Skills
Configuring workflows in JSM isn’t just a matter of clicking a few buttons – it often requires a level of technical expertise that can feel out of reach for non-technical teams. While navigating the interface and language settings presents its own challenges, the real struggle comes when teams need to adapt workflows to mirror their actual business processes. What might work smoothly for IT service management often falls short when applied to areas like customer support, HR, or facilities management, requiring significant adjustments.
Default Workflows Don’t Align with Customer Support Needs
JSM’s default workflows are built around ITIL standards, which are great for IT teams but don’t translate well for other departments. These workflows are designed for IT-centric tasks like Problem Management and Service Request Management, leaving teams dealing with customer inquiries, billing issues, or general business requests stuck with a structure that doesn’t fit their needs. As a result, non-technical teams either have to work within these rigid frameworks or invest heavily in customizing them to suit their processes.
Customization Requires Coding or Developer Expertise
Making workflows work for non-technical teams often means diving into advanced settings, which can be daunting for users without a technical background. For example, automating something as straightforward as a password reset might require API knowledge and scripting skills.
Stevia Putri, Marketing Generalist at eesel AI, notes, "Building a custom AI agent isn’t just a project; it’s a full-on engineering effort… you’d need a team with skills in Python, AI frameworks like LangChain, and a deep understanding of Jira’s APIs".
Even tasks like managing conversation data bring their own challenges, as they demand familiarity with database structures like DynamoDB to meet data residency requirements. These layers of complexity make the need for less technical solutions all the more pressing.
Reducing the Need for Technical Expertise
AI-powered features are stepping in to make workflow setup easier and less reliant on technical know-how. For example, the "Create using AI" feature suggests request types based on simple work descriptions, cutting down on manual setup. Teams can also describe automation rules in plain language – like "When a ticket is overdue, alert the manager" – and JSM’s AI builder translates these instructions into actionable triggers and workflows. Pre-built intent templates further simplify the process, offering ready-to-use workflows for common scenarios like onboarding or software access without requiring teams to design conversation flows from scratch.
To reduce risk, these workflows can even be tested in simulation mode using historical ticket data. This helps identify potential issues before they go live. Additionally, team-managed service spaces eliminate the need to map workflows to underlying Jira work types, saving time and effort. These advancements help bridge the gap for non-technical teams, making workflow customization more accessible and less intimidating.
Reporting Tools Miss Customer Support Metrics
JSM’s reporting tools present another challenge for customer support teams. Designed primarily for IT departments, JSM overlooks the unique metrics that matter to non-technical support teams. While IT teams focus on metrics like incident resolution times and SLA compliance, customer support teams need insights into areas such as customer satisfaction trends, agent performance, and first-contact resolution rates. This disconnect leaves organizations with two options: settle for incomplete data or invest time and resources in creating workarounds.
Reports Built for IT, Not Customer Service
JSM’s default reporting leans heavily toward IT-focused metrics like resolution times, ticket statuses, and SLA adherence. While these are useful for IT operations, they don’t provide much insight into the quality of customer interactions. For instance, the "Workload Report" tracks the number of tickets assigned to each agent but doesn’t consider ticket complexity or the nature of customer interactions. Similarly, the "Requests Resolved" report prioritizes volume – counting how many tickets are marked as "Done" – without addressing whether the customer’s issue was resolved during the first interaction.
Missing Customer-Focused Data
The gaps in JSM’s reporting become even more evident when customer support teams try to track KPIs centered around customer experience. For example, the built-in Customer Satisfaction report aggregates CSAT scores but lacks the flexibility to filter results by agent, organization, or request type without exporting data to external tools. To uncover deeper insights – like pinpointing underperforming agents or recurring product issues – teams often resort to using Jira Query Language (JQL) with queries like Satisfaction IS NOT EMPTY, followed by exporting the data for further analysis in tools like pivot tables. This lack of intuitive, customer-centric reporting makes it harder for non-technical teams to evaluate and improve service quality. Metrics that go beyond ticket volume, such as average response quality or time spent per customer, are notably absent from JSM’s default capabilities.
Building Better Reports with AI and Custom Views
AI features are starting to fill some of these gaps, but they usually come with a higher price tag. For example, JSM’s AI containment reporting tracks the percentage of queries resolved by virtual agents without human intervention, while real-time sentiment analysis evaluates customer comments to help prioritize tickets based on frustration levels instead of just ticket age. Predictive CSAT scoring is another valuable tool, estimating customer satisfaction even when surveys are left incomplete. These AI-powered features provide actionable insights but are typically only available with the Premium plan, which costs $47.82 per agent per month compared to the Standard plan’s $19.04 per agent per month.
For teams looking to avoid premium pricing, custom dashboards can combine multiple reports, though setting them up requires manual effort. Alternatively, modern B2B support platforms like Supportbench offer solutions tailored to customer support needs. Features such as predictive CSAT, customer effort score (CES) tracking, and first-contact resolution detection are standard, providing the insights necessary to improve service quality – not just operational efficiency. While advanced reporting is just one piece of the puzzle, it highlights the broader limitations JSM imposes on non-technical teams.
Integration Problems Create Disconnected Systems
JSM’s integration hurdles often create headaches for non-technical support teams. While the platform operates seamlessly within the Atlassian ecosystem, extending that functionality to other essential tools – like CRMs, external knowledge bases, or e-commerce platforms – can be a major challenge. Why? Because setting up these connections usually demands technical skills that many support teams lack. This leads to fragmented workflows, siloed data, and agents wasting valuable time switching between systems instead of helping customers. Let’s dive into how these technical barriers disrupt tool connectivity.
Connecting JSM to Other Business Tools
Setting up integrations with JSM is no walk in the park. As Eric Klimuk, Founder and CTO of Supportbench, explains:
"Initial setup often requires IT or DevOps involvement".
Non-technical teams frequently need developers to handle tasks like field mappings, permissions, and workflow connections. JSM is designed to work best with Atlassian tools – its knowledge base, for instance, relies on Confluence. This adds layers of complexity and extra costs for teams that rely on non-Atlassian solutions. When it comes to integrating with external systems like Salesforce or specialized CRMs, teams often face additional licensing fees, the need for technical assistance, or reliance on third-party connectors. Even JSM’s AI features are tuned primarily to work with Confluence, leaving teams using tools like Google Docs, PDFs, or internal wikis with isolated data.
How Disconnected Data Slows Teams Down
These integration challenges don’t just create technical headaches – they slow teams down. When systems fail to communicate, agents end up paying the price. They spend valuable time switching between platforms to find information, manually transferring data, or re-routing tickets. Without a seamless connection between JSM and external tools like CRMs or e-commerce platforms, agents often lack a complete view of the customer journey. This makes it harder to deliver personalized and informed responses.
Picture this: an agent needs to check an order status in Shopify, verify customer details in Salesforce, and then manually input that information into JSM – all while the customer waits. These manual processes aren’t just frustrating – they add up quickly, dragging down efficiency. Implementing workflow automation can help eliminate these bottlenecks across the entire support team.
Creating Connected Workflows
To tackle these issues, tools like Zapier can help automate some tasks and reduce manual data entry. However, these solutions often come with trade-offs, such as limited functionality or added costs. API-driven integrations and advanced AI tools can bridge the gap between different data sources, but they usually require ongoing technical support or premium pricing plans.
Supportbench sidesteps these challenges by offering native connections to commonly used business tools, providing a unified view of customer data from day one – no IT team required. This streamlined approach allows agents to work more efficiently, cutting down on time spent toggling between systems and letting them focus on what really matters: helping customers.
How AI Tools Address JSM’s Gaps
AI tools help smooth out some of JSM’s rough edges, especially for non-technical support teams. By automating tedious tasks like ticket triage and generating insights that focus on customer needs, these tools fill in the gaps left by JSM’s IT-focused design. This frees up support agents to concentrate on what they do best: assisting customers.
Automated Ticket Sorting and Assignment
Manually sorting and assigning tickets can be a huge time waster. AI-powered triage steps in by analyzing ticket content and automatically recommending – or directly assigning – the appropriate request type and fields. This is especially helpful for tickets submitted through generic channels like email, where context is often missing. Sentiment-based prioritization takes this a step further by scanning customer comments in real time, flagging emotional tones (positive, neutral, or negative). This allows agents to quickly spot frustrated customers and prioritize their tickets without having to read every message. Adding a "Sentiment" column to JSM queues can give teams an instant overview of tickets needing urgent attention or a more empathetic response.
Another feature, predictive user pickers, suggests the top five most likely assignees for a ticket with 86% accuracy. By analyzing past interactions and ticket details, this tool cuts down on guesswork. Virtual agents powered by natural language processing (NLP) also play a key role by identifying customer intent – like "password reset" or "onboarding help" – and routing tickets to the right team or workflow.
A real-world example: In February 2023, Atlassian IT introduced the JSM virtual agent to support its 10,000+ global employees. Led by Technical Program Manager Joe Flowers, the team centralized support through a single Slack channel. In just one month, the AI agent handled over 50% of incoming requests and fully resolved 10% without human help, saving 500 hours of work and earning a customer satisfaction score of 4.5 out of 5.
"The time saved in the first month was an incredible 500 hours – 20 days – in how long a service desk team would spend finding information and providing repetitive answers to tickets." – Joe Flowers, Technical Program Manager, Atlassian IT
For teams drowning in "Emailed requests", AI triage can bulk-assign tickets to specific request types, clearing up backlogs. Tools like the Rovo Service Triage Assistant can be integrated into automation rules to rewrite unclear ticket titles, adjust priority levels, and flag requests for escalation based on SLAs.
Beyond ticket management, AI also transforms resolved tickets into valuable resources for future use.
AI-Generated Knowledge Base Content
Creating and maintaining a knowledge base is often a heavy lift, especially for non-technical teams without dedicated writers. This is where AI steps in. By analyzing entire conversation histories, AI can turn resolved tickets into searchable help articles, complete with subject lines, summaries, and keywords.
AI also identifies gaps in the knowledge base by analyzing what customers search for but don’t find. Features like "AI Drafts" and "Suggested Topics" generate reports on missing content, turning these insights into actionable steps to improve support. This keeps teams ahead of recurring issues and ensures the knowledge base stays relevant.
For teams using more advanced AI setups, these systems can pull data from a wider range of sources – like Google Docs, PDFs, and past Jira tickets – rather than being limited to Confluence pages.
But AI doesn’t stop at knowledge management – it also enhances reporting with predictive insights.
Predictive Metrics and Sentiment Analysis
JSM’s reporting tools are heavily geared toward IT metrics, but AI bridges the gap by surfacing insights that focus on customers. Real-time sentiment analysis interprets the emotional tone of customer comments, helping teams track satisfaction trends before CSAT surveys are even sent. This early warning system lets support leaders prioritize tickets from unhappy customers.
AI-powered virtual agents have already shown impressive results, including a 50% increase in resolution rates and a 40% boost in CSAT scores. These agents also provide analytics that reveal which topics successfully deflect tickets and which ones require human follow-up. Additionally, AI can predict key metrics like CSAT, CES, and FCR – metrics that are often tough to track manually. For instance, agents can view a column in the case list that predicts whether a customer would have been satisfied with the resolution, even if no survey was completed.
AI also analyzes conversation data from virtual agents to uncover the specific language customers use, which can refine reporting categories and improve knowledge base content. By grouping related alerts and identifying patterns, AI reduces the manual effort required by on-call engineers to filter out critical issues from background noise.
Supportbench takes this further by offering built-in AI tools for predictive CSAT, CES, and FCR detection – no premium plan needed. These features empower non-technical teams to deliver better customer support without the complexity or cost of custom IT solutions. This makes it easier for businesses to adopt AI-driven operations while keeping expenses in check.
Conclusion: Is JSM Right for Your Support Team?
JSM stands out in IT service management but may fall short for non-technical support teams. Before diving in, consider whether its strengths align with your team’s needs or if its limitations could create unnecessary hurdles.
Main Challenges to Consider
There are four key challenges to keep in mind. First, JSM’s interface heavily relies on ITIL terminology like "incidents", "problems", "changes", "epics", and "sprints", which can confuse non-technical users. Second, setting up JSM can be a headache – configuring workflows, field mappings, and permissions often requires IT or DevOps expertise, with implementation timelines stretching to weeks or even months. Third, its reporting tools are tailored to IT metrics, not customer-focused data like CSAT or customer effort scores. Creating custom reports requires learning JQL (Jira Query Language), adding another layer of complexity. Finally, JSM’s reliance on Confluence for its knowledge base adds extra configuration steps and potential licensing costs. Advanced AI features, such as the Virtual Service Agent, are only available with Premium plans ($47.82–$49.35 per agent/month) or higher, leaving Standard-tier users without access.
These factors should play a central role in your decision-making process.
Questions to Ask Before Choosing JSM
Start by assessing whether you have technical resources available. Non-technical teams may find JSM’s setup demands overwhelming. Consider your timeline – if you need to launch within days, JSM’s setup process might slow you down. Take a close look at your knowledge management strategy and total ownership costs. For example, if your support content isn’t already in Confluence, migrating it could be a significant challenge. Pricing is another factor – Premium plans for a 10-person team can drive up costs considerably.
Modern Alternatives for B2B Support Teams
If JSM’s limitations outweigh its benefits, exploring alternative platforms designed for B2B support might be a better route. Supportbench, for instance, offers a no-code setup, built-in AI tools, and a native knowledge base, starting at $32 per agent/month. Unlike JSM, which emphasizes ITIL workflows, Supportbench focuses on relationship-driven support for long-term customer accounts. Features like email-grade communication, dynamic SLAs, customer health scoring, and AI-powered summaries are included without requiring IT involvement for configuration. For teams prioritizing fast, efficient support with minimal technical overhead, these platforms often deliver better usability, lower costs, and quicker implementation compared to adapting an IT-focused tool.
Choosing tools tailored to non-technical teams can simplify operations and improve customer satisfaction in the long run.
FAQs
When is JSM a bad fit for customer support teams?
Jira Service Management (JSM) often falls short for customer support teams that prioritize ease of use, streamlined workflows, and the ability to handle non-technical processes. Since JSM is primarily built with IT and technical teams in mind, it may demand specialized admin knowledge and additional plugins to operate efficiently. This can make it a challenging choice for non-technical support environments.
How can non-technical teams simplify JSM without IT help?
Non-technical teams can make Jira Service Management (JSM) easier to use by taking advantage of its user-friendly features and customization options. Tools like visual workflows, project templates, and various views – such as lists, boards, and calendars – help simplify how work is organized and managed.
Automation is another game-changer, handling repetitive tasks like ticket routing to save time and reduce manual effort. Plus, AI tools, including virtual agents, can step in to handle ticket triage and provide quick responses. These approaches not only simplify operations but also cut down the need for constant IT support.
What customer support KPIs are hardest to measure in JSM?
Measuring customer support KPIs in Jira Service Management (JSM) can get tricky, especially when it comes to metrics like customer satisfaction and overall service quality. These are highly subjective and often rely on personal perceptions, which makes them tough to quantify with precision. As a result, extracting clear, actionable insights from these metrics can be a real challenge.










