When setting up Jira for customer support, the goal is to create a system that ensures tickets are handled efficiently and communication with customers is clear. Here’s the essential process:
- Map Issue Types to Ticket Categories: Use customer-friendly language for ticket categories (e.g., "I can’t log in" instead of "Authentication Failure"). Group similar requests under shared workflows to simplify management.
- Design Workflows That Reflect Processes: Create workflows that mirror your support steps, from triage to resolution. Include clear escalation paths and statuses like "Waiting for Customer" to track stalled tickets.
- Simplify Statuses for Customers: Internally detailed statuses (e.g., "Waiting for Triage") can be mapped to simpler, customer-facing terms like "Waiting for Support" for better clarity.
- Automate Repetitive Tasks: Use workflow automation tools to auto-assign tickets, update statuses based on activity, and send SLA reminders. This saves time and reduces errors.
- Avoid Common Mistakes: Keep workflows simple, maintain consistency across teams, and focus on meaningful metrics like resolution quality rather than just ticket volume.
Jira Service Management Crash Course 2025
sbb-itb-e60d259
Jira Basics for Support Operations
To effectively align Jira with your support operations, it’s important to grasp the three core elements that dictate how tickets flow through your system: issue types, workflows, and statuses. Together, these elements shape how customer requests are categorized, managed, and tracked from start to finish.
In Jira Service Management, issue types act as the foundation. They define a ticket’s settings and the workflow it follows. Think of them as categories like "IT Help", "Access", "Purchase", or "Fault." These categories determine how each ticket functions behind the scenes. Each issue type connects to one workflow, but it can support multiple customer-facing request types. For example, the "Purchase" issue type might serve as the backbone for both "Request new hardware" and "Request new software" options visible to customers in the portal.
Workflows outline the journey of a ticket through a sequence of statuses and transitions. A status reflects a ticket’s current stage (like "To Do" or "In Progress"), while transitions define the actions that move it between statuses. Using a unified workflow for similar issue types helps maintain consistency across your processes.
Statuses play a dual role by providing clarity to both agents and customers. Internally, agents see detailed statuses like "Waiting for Triage" or "Waiting for Support." Meanwhile, customers view simplified labels – for instance, both internal statuses could appear as "Waiting for Support" on the customer-facing side. Jira’s ability to map internal statuses to customer-friendly terms ensures that your team can manage tickets thoroughly without overwhelming users with unnecessary details.
How to Map Jira for Customer Support
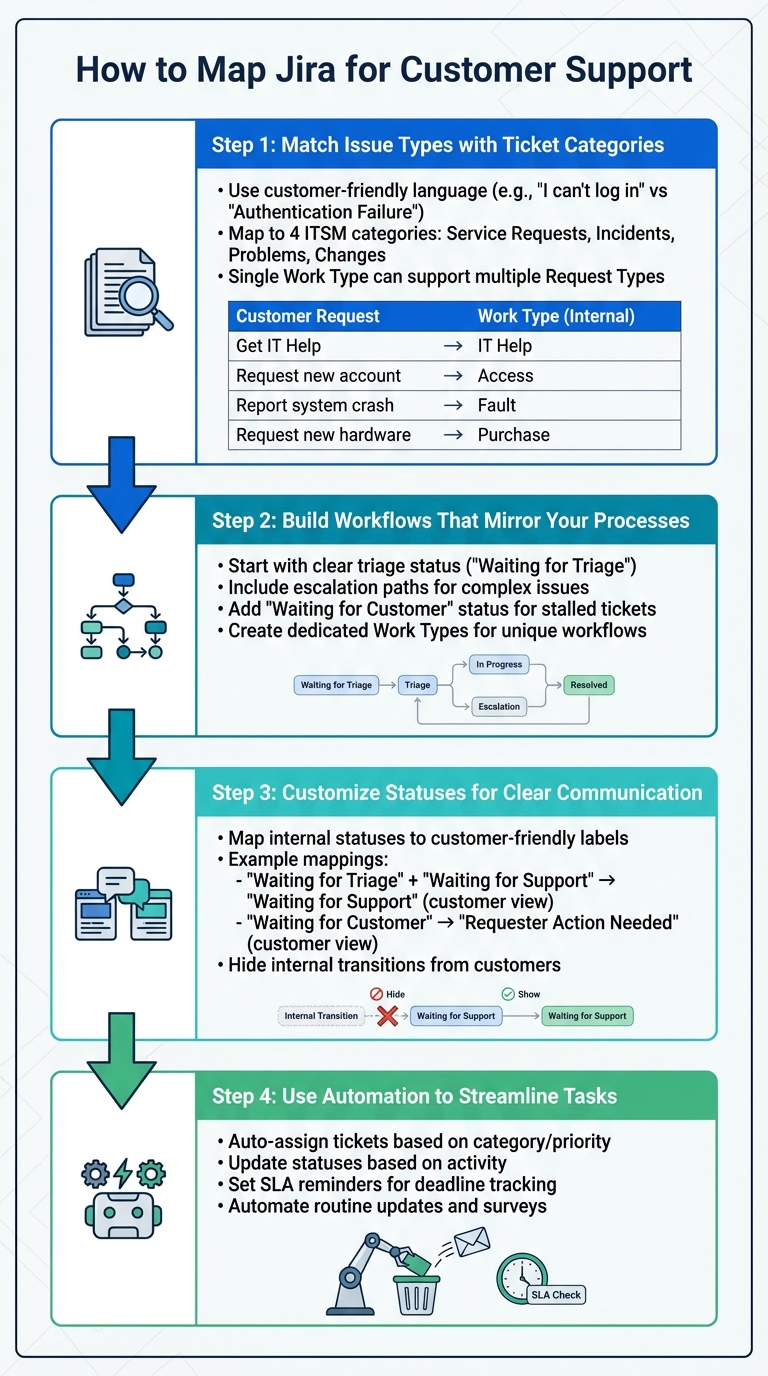
4-Step Process for Mapping Jira to Customer Support Helpdesk
Setting up Jira for customer support involves aligning your helpdesk operations with Jira’s framework. This means organizing ticket categories as issue types, creating workflows that reflect your support processes, and customizing statuses to match your helpdesk stages. The aim is to build a system where tickets move smoothly from creation to resolution.
Step 1: Match Issue Types with Ticket Categories
Jira Service Management operates on two levels: Request Types for customers and Work Types for backend operations. Request Types are what customers see – like "Get IT help" or "Request new hardware" – while Work Types handle the technical setup, such as workflows behind the scenes.
Start by identifying your key support categories. Most helpdesks fall into four ITSM categories: service requests, incidents, problems, and changes. Use customer-friendly language for Request Types. For instance, instead of "Authentication Failure", use "I can’t log in". This makes it easier for customers to select the right category.
A single Work Type can support multiple Request Types if they share the same workflow. For example, a "Purchase" Work Type could handle both "Request new hardware" and "Request new software". By consolidating workflows, you reduce the complexity of your setup.
| Customer Request Type | Internal Jira Work Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Get IT Help | IT Help | General support for IT-related issues |
| Request a new account | Access | Requesting access to internal systems |
| Report a system crash | Fault | Reporting hardware or software failures |
| Request new hardware | Purchase | Requests for procurement and fulfillment |
Simplify the customer experience by hiding unnecessary fields on the request form. For specific categories, use preset values in hidden fields to automatically assign categories or priorities without customer input. If a Request Type requires a unique workflow, create a new Work Type to avoid affecting other shared workflows.
Once your categories are mapped, you can move on to crafting workflows that align with your support processes.
Step 2: Build Workflows That Mirror Your Processes
Workflows in Jira define how tickets move through different statuses and transitions. Your workflow should reflect your actual support process, from ticket submission to resolution, including triage, assignment, escalation, and closure.
Start with a clear triage status like "Waiting for Triage" to ensure new tickets are queued for review. This helps your team prioritize work and prevents tickets from being overlooked.
For more complex issues, include escalation paths in your workflow. If your support team operates in tiers or includes specialists, add transitions that allow agents to escalate tickets to the right team. Keep these transitions simple and clearly labeled to avoid confusion.
For tickets requiring customer input, add a "Waiting for Customer" status. This helps distinguish stalled tickets from those actively being worked on. It also improves your metrics by ensuring your team focuses on actionable tickets.
When a Request Type needs a unique workflow, create a dedicated Work Type for it. This isolates changes and prevents disruptions to other workflows. It’s better to have a few extra Work Types than to risk breaking existing processes.
Step 3: Customize Statuses for Clear Communication
Tailor internal statuses with customer-friendly labels to make them easy to understand. This dual-layer approach ensures your team gets the detailed tracking they need while keeping things simple for customers.
Go to Space settings > Request management > Request types, and use the Workflow Statuses tab to enter customer-facing names. For example, you could map both "Waiting for Triage" and "Waiting for Support" to the single customer-facing status "Waiting for Support". This simplifies the experience for customers while preserving internal tracking.
To hide transitions between internal statuses, assign the same customer-facing name to both statuses. This is particularly useful for internal steps that don’t require customer visibility.
| Internal Workflow Status | Customer-Friendly Status Name | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Waiting for Triage | Waiting for Support | Queues new requests for initial review |
| Waiting for Support | Waiting for Support | Tracks assigned tickets awaiting action |
| Waiting for Customer | Requester Action Needed | Separates stalled tickets for better metrics |
| Resolved | Resolved | Marks tickets as complete for closure tracking |
Statuses like "Waiting for Customer" are especially useful for calculating metrics. They allow you to exclude time spent waiting for customer responses from your resolution time calculations, giving a clearer view of your team’s performance.
Step 4: Use Automation to Streamline Tasks
With categories, workflows, and statuses in place, automation can take your setup to the next level. Jira’s automation tools can help reduce repetitive tasks and improve efficiency.
- Auto-assign tickets: Automatically route incoming tickets to the right team or agent based on category, priority, or availability. This eliminates manual triage for straightforward requests.
- Update statuses based on activity: For example, when a customer replies to a ticket in "Waiting for Customer" status, transition it back to "Waiting for Support" automatically. This keeps tickets moving without manual updates.
- Set SLA reminders: Use custom fields like "Time to resolution" and dynamic SLA management to trigger notifications when tickets approach their deadlines. These reminders can escalate tickets or notify managers before SLA breaches.
- Automate routine updates: Send satisfaction surveys or close tickets automatically after resolution. Small automations like these can save significant time across your team.
Common Challenges and How to Avoid Them
Once you’ve mapped Jira’s components to your support processes, it’s crucial to steer clear of common missteps that can disrupt system efficiency. Poor configuration can derail your operations, leading to issues like overcomplicated workflows, inconsistent practices across teams, and misaligned metrics. These problems tend to grow over time, making your system harder to manage and more costly to fix. By focusing on simplicity, consistency, and meaningful metrics, you can avoid these pitfalls and keep your Jira setup running smoothly.
Keep Workflows Simple
One of the most frequent mistakes is making workflows overly complex. Teams often assume that adding more statuses and transitions provides better control, but this can actually obscure bottlenecks and confuse users. Instead of trying to account for every possible scenario, focus on the core, repeatable flow of work.
"Mature processes are usually simple, clear, and enforce the right questions at the right time, not complicated diagrams that nobody truly follows." – Anahit Sukiasyan, Atlassian Community Champion
Stick to generic status names like "In Progress" that can be reused across workflows and projects. This approach keeps your instance organized and simplifies reporting. Before introducing automation, ensure your manual processes are effective. Automating a flawed process only hides the chaos. Implementing ticket routing automation can further streamline these workflows once they are optimized. A simple workflow makes your Jira setup easier to maintain and use.
Maintain Consistency Across Teams
Consistency is just as important as simplicity. When teams use different naming conventions or workflows, it hampers collaboration and complicates reporting. This issue is particularly challenging in Jira, where workflows and work types are often shared across projects. If one team alters a shared workflow, it can unintentionally affect every project using that workflow.
To avoid this, use workflow schemes to link multiple projects to a single, standardized process. Collaborate with end-users and stakeholders to map workflows before building anything. Many problems arise from disagreements over field definitions or data ownership. Establishing consistent practices across teams strengthens your overall support strategy and prevents unnecessary disruptions.
Configure Metrics and Reporting
Metrics are your guide to improving support operations. While many teams focus on ticket volume, this metric alone doesn’t reveal much about customer satisfaction or team performance. In fact, 93% of consumers are more likely to make repeat purchases from companies that deliver excellent customer experiences. Tracking meaningful metrics like resolution quality and customer satisfaction is far more valuable.
For accurate resolution tracking, Jira Service Management uses a custom field called "Time to resolution", stored in JSON format. Ensure that work items include the "Viewport Origin" field, which identifies requests created via the Customer Portal and links them to the correct Request Type. Without this field, your support reporting may break.
Use statuses like "Waiting for Customer" to exclude time spent waiting on responses from your resolution time calculations. This provides a clearer picture of your team’s actual performance. Additionally, when modifying workflows or work types, map old statuses to new ones carefully to preserve historical data. Properly configured metrics enable you to measure and improve your support operations effectively.
| Mistake | Impact | How to Avoid It |
|---|---|---|
| Over-customization | Makes Jira fragile; users forget key fields | Focus on standardizing core workflows, not exceptions |
| Status Duplication | Clutters the system; hinders reporting | Reuse existing statuses; only create new ones if necessary |
| Isolated Design | Poor adoption; workflows don’t fit reality | Involve agents and stakeholders during the design phase |
| Measuring Volume Only | Misleads leadership; overlooks customer value | Build reports around meaningful metrics like resolution quality |
Using AI to Improve Support Operations
Once you’ve set up your Jira workflows, AI can take your support operations to the next level by automating tasks and uncovering insights you might otherwise miss. This isn’t just about basic automation – AI can analyze customer sentiment to predict issues, intelligently route tickets, and keep your knowledge base current. These features build on your existing workflows, making your support system even more efficient.
AI Automation for Ticket Routing and Prioritization
AI shines when it comes to organizing and managing support tickets. It can classify, prioritize, and route tickets to the right teams or experts based on the content of each request. Instead of relying on complex JQL queries, you can use natural language to create automation rules. For instance, a simple instruction like, "When a high-priority bug is reported, assign it to the development team lead", is all it takes for Jira to generate an actionable automation rule.
AI also keeps an eye on customer interactions, monitoring comment threads for negative sentiment or signs of frustration. This allows the system to escalate tickets before the customer even files a formal complaint. As Rodolfo Bortolin, an Atlassian Expert, puts it:
"The idea of this solution is to escalate the ticket even before the user needs to take this action… generating more satisfaction in the service".
This kind of automation can drastically cut down on manual ticket management. For example, AI can reduce the time spent on categorizing tickets from around 2.5 hours per queue to just 10 minutes. It goes further by pulling in data from external tools like Slack, Google Docs, or Notion to enrich ticket details, ensuring they are routed with greater accuracy. Machine learning models add another layer by predicting potential SLA breaches and alerting teams to address urgent tickets before deadlines are missed.
AI-Generated Case Summaries and Knowledge Base Articles
AI also simplifies communication and context-sharing. By generating concise summaries of ticket histories, AI helps agents quickly understand the background of a ticket, especially when it’s handed off between teams or revisited after a break. This is a game-changer for streamlining workflows. Generative AI even scans knowledge bases to provide clear and concise responses to customer queries. Martin Brignall, Developer Tooling Specialist at OVO, highlights its impact:
"Atlassian Intelligence has helped bring our DevOps practices into Slack to reduce context-switching. Alongside AI answers and issue summaries, harnessing Atlassian Intelligence has led to a boost in our developer experience".
But the effectiveness of these AI-driven responses depends on the quality of your knowledge base. To make the most of it, ensure you are building a knowledge base with articles that are up-to-date, well-structured, and written in a way that resonates with your audience. Use everyday terms like "laptop" or "keyboard" instead of overly technical jargon. Avoid duplicating content across articles, as this can lead to conflicting or outdated information. Regularly auditing your knowledge base ensures it stays accurate and helpful.
Predictive Insights for Better Decisions
AI doesn’t just react – it anticipates. By analyzing customer sentiment and comment patterns, it can predict when an issue might escalate, giving managers the chance to step in before a complaint arises. Real-time sentiment tracking – whether positive, neutral, or negative – provides a clear picture of which tickets might need senior-level attention.
Jira’s predictive tools simplify resource allocation, too. For example, predictive user pickers can identify the top five most likely assignees for a task with 86% accuracy. AI also learns from past behavior and current context to recommend the best agents for specific tickets, ensuring tasks are assigned efficiently. Features like the "Similar Requests" panel help agents spot patterns, such as whether a ticket is part of a larger incident. This makes it easier to group resources and resolve issues faster.
These predictive insights transform Jira from a passive tracking tool into an active partner in decision-making. By helping you allocate resources wisely and address potential dissatisfaction early, AI ensures your support operations run smoothly while keeping customers happy.
Conclusion
Setting up Jira issue types, workflows, and statuses for your customer support operations goes beyond just technical adjustments – it’s about designing a system that benefits both your team and your customers. By aligning issue types with ticket categories, crafting workflows that reflect real support processes, and customizing statuses for better clarity, you create a foundation that streamlines operations. Add automation to handle repetitive tasks, and you’ll see improvements in prioritization, consistency, and reporting. This approach helps you track SLAs and resolution times across various projects with ease.
The real game-changer? Integrating Jira with built-in AI tools. For example, a major airline achieved significant efficiency gains through AI integration. Atlassian’s own Wayne Tombo shared even more striking results: after implementing an AI-powered agent, his team reduced ticket resolution time from 8 days to just 9 minutes, while boosting CSAT scores by 6 points. These kinds of outcomes don’t just improve performance – they directly contribute to your bottom line.
Customer experience is also at the heart of this strategy. According to research, 80% of customers value the experience you provide as much as the products and services themselves. By thoughtfully configuring Jira and leveraging AI for tasks like predictive insights, automated ticket routing, and intelligent case summaries, you not only handle tickets more effectively but also enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Keeping workflows straightforward, ensuring consistency across teams, and automating manual tasks are critical to achieving these results.
To sustain these benefits, make sure your Jira setup evolves alongside your growing support needs. Conduct regular audits of workflows, update your AI-driven knowledge base, and tweak configurations based on performance metrics. When done well, this combination of structured processes and smart automation can transform Jira into a tool that actively drives exceptional customer support.
FAQs
How many issue types do we really need?
When setting up issue types for your support processes, simplicity is key. Aim for 3 to 7 well-defined types that align directly with your workflow. This keeps things straightforward and avoids unnecessary confusion. Prioritize categories that support critical tasks like triage, escalation, and resolution tracking. A streamlined approach ensures your team stays efficient and focused on what matters most.
What customer statuses should we show?
In a Jira-based helpdesk, ticket statuses play a crucial role in tracking the lifecycle of support requests. They provide clarity on where each ticket stands and ensure everyone involved stays on the same page.
Here are some common statuses you might use:
- New/Open: Marks tickets that have just been submitted and are awaiting action.
- In Progress: Indicates that work on the ticket is actively underway.
- Waiting for Customer/Pending: Used when additional input or information is needed from the requester.
- Escalated: Signals that the ticket has been forwarded to a higher support level or specialized team.
- Resolved/Closed: Represents tickets that have been successfully addressed and completed.
To make these statuses work best for your team, consider tailoring them to fit your specific workflows. For instance, you might add statuses like On Hold for paused tasks or Awaiting Approval for cases requiring managerial sign-off. Customization ensures your helpdesk reflects the unique needs of your support process.
How do we track SLAs fairly?
To ensure fair SLA tracking, it’s crucial to establish clear guidelines for when SLA timers should start, pause, and stop. These conditions can depend on factors such as the ticket’s priority level or the type of request. Using tools like JQL allows you to create specific goals tailored to different levels of urgency.
Regularly reviewing SLA metrics is equally important. This helps you refine criteria over time, keeping them aligned with customer expectations, avoiding bias, and ensuring smooth operations. Automation plays a key role here, as it guarantees consistent and precise tracking without manual errors.
Related Blog Posts
- How do you map Salesforce Case fields, Record Types, and Statuses to a new helpdesk?
- How do you migrate Freshdesk automations (rules, triggers, SLAs) to a new platform?
- How do you map Kayako statuses, priorities, and custom fields to a new helpdesk?
- How do you map HappyFox categories, custom fields, and statuses to a new system?










