Managing support for customers with multiple locations can be challenging due to scattered data, inconsistent workflows, and siloed communication. Here’s how you can streamline operations:
- Centralize Customer Data: Create a unified customer record to eliminate redundancy and provide a complete view of interactions across locations.
- AI-Driven Automation: Use AI to route tickets, predict escalations, and generate real-time insights, reducing response times and improving efficiency.
- Standardize Workflows and SLAs: Balance global standards with location-specific needs through tiered SLA policies and role-based access controls.
- Monitor Performance by Location: Use dashboards to track key metrics (e.g., First Response Time, CSAT) and identify regional trends.
- Leverage AI for Knowledge Management: Automate the creation of knowledge base articles and maintain a centralized repository for consistent support.
The Secret to Managing Multiple Locations Efficiently
Common Challenges in Multi-Subsidiary Support
Multi-Subsidiary Support Models: Centralization vs Decentralization vs Hub & Spoke
When a single customer interacts with multiple subsidiaries, support teams often face a set of recurring hurdles. These aren’t just technical glitches – they directly affect how teams communicate, share data, and maintain consistent service quality. Tackling these issues is crucial for successfully implementing AI-based solutions for multi-location support.
Communication Silos Between Locations
Disconnected communication tools can lead to fragmented conversations, forcing customers to repeat themselves multiple times. For instance, one subsidiary might rely on email, another on Slack, and a third on chat. This lack of synchronization causes agents to lose context, slowing down resolutions. On average, B2B buyers use 10 different channels throughout their journey.
"The worst time to try and figure out the right person to contact in another department is when a customer’s waiting on your answer." – Abhi Basu, Product Marketing Director, Zendesk
Agents often find it challenging to identify the right contact within another subsidiary, especially without a coordinated "follow-the-sun" support schedule. This results in coverage gaps and delayed responses.
Scattered Data and Customer Insights
Another major obstacle is fragmented customer data. When customer information is stored in separate regional systems, support teams lack a complete view of the customer. This forces them to rely on guesswork, leading to redundant efforts, inconsistent solutions, and failed handoffs during transitions between regions. Although contact centers generate valuable insights about customer demographics, buying patterns, and common issues, these insights often go unused when locked in isolated systems.
Additionally, scattered data makes it difficult for headquarters to monitor performance metrics across locations in a unified, actionable dashboard. Without a centralized customer record, teams struggle to deliver the personalized experiences that 80% of consumers say influence their buying decisions.
Inconsistent Workflows and SLAs
When each subsidiary operates with its own processes, even small differences can create significant service inconsistencies. For example, one location might treat a particular issue as routine, while another considers it a high-priority escalation. This misalignment can lead to confusion, delays, and even mistrust among teams. Agents may hesitate to hand off cases if they doubt the next team can maintain the same service standards.
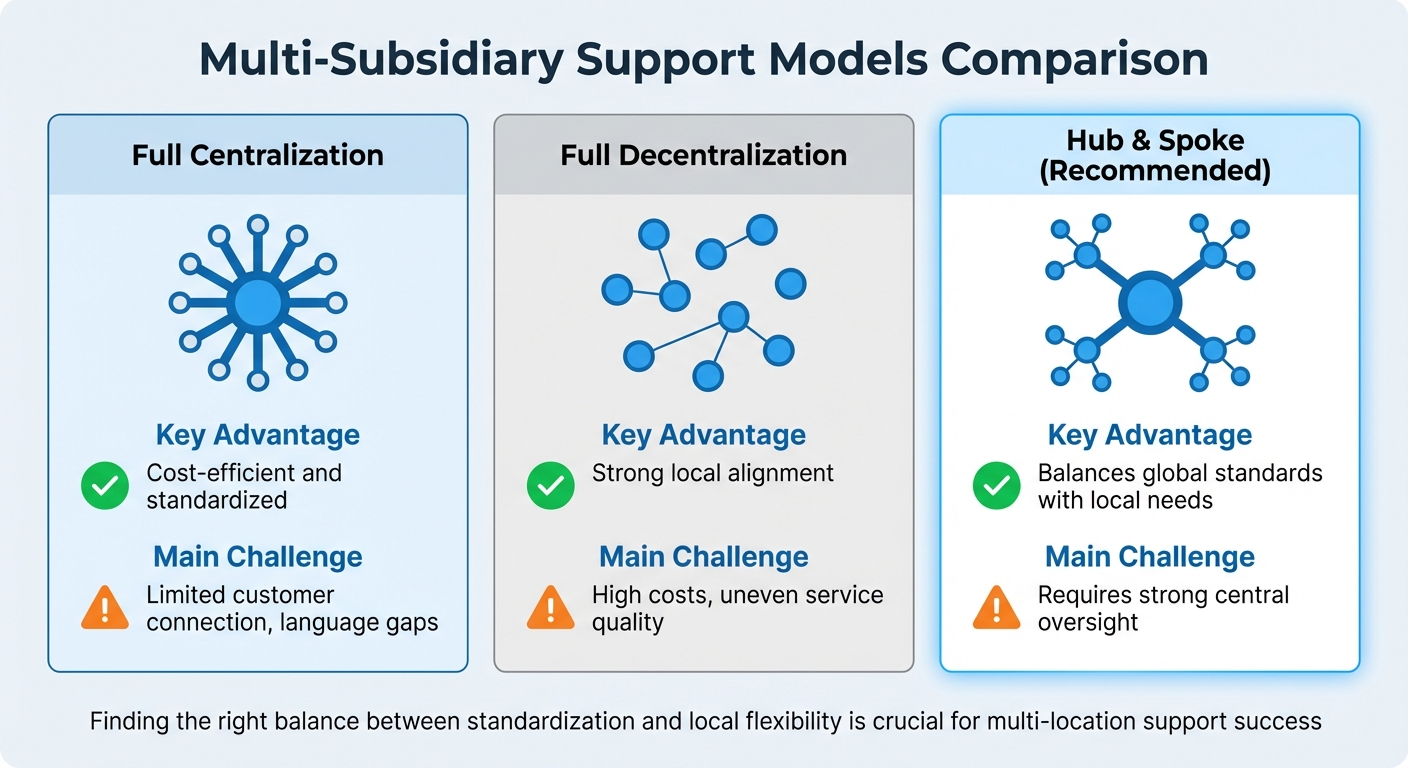
| Model Type | Key Advantage | Main Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Full Centralization | Cost-efficient and standardized | Limited customer connection, language gaps |
| Full Decentralization | Strong local alignment | High costs, uneven service quality |
| Hub & Spoke | Balances global standards with local needs | Requires strong central oversight |
Finding the right balance between standardization and local flexibility is crucial. While regional teams may need to adjust their tone or language to suit local markets, core workflows and SLAs must remain consistent to avoid a fragmented customer experience. Centralized data management and standardized processes can help address these challenges, which we’ll dive into in the next section.
Centralizing Data and Case Management
To tackle the challenges of supporting multiple locations, the first step is consolidating scattered customer data. When customer information is siloed, support teams often lack the full picture, leading to inefficiencies and frustration. Centralizing this data provides a complete, reliable view of all customer interactions, regardless of which location handled them. This eliminates repetitive tasks, prevents customers from having to repeat themselves, and gives headquarters the clarity needed to uphold consistent service standards.
Creating a Single Customer Record Across Subsidiaries
Building a unified customer record means pulling together data from various sources. This involves merging what’s often called "foundation data" entities – things like company names, aliases, support staff profiles, end-users, support groups, and site associations. The tricky part? Support staff or customers might appear in different systems under different identifiers. Before consolidating, you’ll need to reconcile these entities by migrating, merging, or renaming them to avoid conflicts.
Once these entities are mapped, historical data (like tickets, incidents, and rules) must be updated to link to the new unique identifiers. For example, an agent in Boston should be able to view a customer’s complete history, even if previous cases were handled by teams in Austin or Denver.
| Entity Type | Consolidation Challenge | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| People | Duplicated login IDs or permissions across systems | Migrate unique records; reconcile attributes (e.g., email, phone) for duplicates |
| Support Groups | Same name used for different entities | Rename groups with location identifiers or merge if they serve the same function |
| Sites | Inconsistent addresses or phone numbers | Standardize site names and link them to the parent company |
| Tickets | References to outdated system IDs | Update foreign keys to point to the new centralized foundation data |
Platforms like Supportbench help maintain security within centralized systems by using role-based access and location permissions. For example, an agent who had full access to data in a smaller subsidiary may not automatically gain the same level of access in a global system. This ensures that centralization doesn’t compromise privacy or regulatory compliance.
Once unified records are in place, the next move is to leverage AI-driven tools to keep this data current and extract meaningful insights.
Using AI to Consolidate Data and Generate Insights
Manually consolidating data is not only slow but also prone to errors. AI-powered entity detection simplifies this by identifying unique details – like account IDs, product lines, or regional tags – within tickets and automatically populating custom fields. This approach keeps your centralized system accurate without requiring constant IT intervention.
In July 2025, ezCater adopted AI-powered real-time assist tools to help newer team members during peak hours. The result? A 13% drop in overall call handling time and a 23% reduction in hold times, with 94% of calls answered within 30 seconds. The AI analyzed case histories across locations, providing instant, relevant answers to agents.
AI also enables real-time sentiment analysis and intent tagging across all interactions. Instead of waiting for survey results, you can calculate satisfaction scores (iCSAT) for every customer interaction. For example, a multinational design firm used AI to monitor support conversations, identifying patterns that led to unnecessary refunds. By training agents on AI-recommended de-escalation techniques, the firm saved over $30 million in the first year and boosted customer satisfaction scores by 47%.
"Automation is only as good as the knowledge it sits on." – Enjo.ai
The foundation for effective automation is a single source of truth for support knowledge – covering scripts, FAQs, and workflows – so every team operates with the same playbook. AI platforms that connect tools like Confluence, SharePoint, Notion, and Google Drive into a unified, permission-aware layer eliminate the need for manual data migration. This "no-migration" approach lets you centralize insights without disrupting existing workflows or forcing teams to abandon familiar tools.
Balancing Standard Workflows with Location-Specific Needs
Centralizing data is only part of the equation; workflows also need to strike a balance between standardization and adaptability. A rigid, one-size-fits-all system ignores critical factors like local regulations, time zones, team sizes, and customer expectations. The key is to create a framework that standardizes core processes – such as escalation paths and reporting – while allowing flexibility for local teams to tailor workflows to their specific needs.
Research shows that 84% of parent companies require approval at the corporate level for certain subsidiary actions or spending. This highlights the need for clear governance structures and a well-defined division of decision-making responsibilities between central and local levels.
"Subsidiaries across group structures serve a variety of purposes, and therefore need to be managed accordingly" – Andy Casey, Head of Corporate Secretarial Services at Konexo.
Setting Up Role-Based Access and Location Permissions
Role-based access control (RBAC) is a cornerstone for managing visibility and security effectively. Instead of granting unrestricted access to all customer data, permissions should be tailored to specific roles, regions, or departments. For instance, agents in Austin should not have access to sensitive customer information from a subsidiary in Europe, especially if it falls under GDPR regulations.
To manage this, group users by company or region. This approach allows you to create custom routing rules and access policies for each location, simplifying management and reducing the risk of errors. Use "Department Spaces" to ensure agents only handle tickets relevant to their assigned subsidiaries. Regular reviews of agent group memberships and brand assignments – particularly after organizational changes – are essential to maintaining accuracy. Automating processes like email domain mapping can also help direct new customers to the right subsidiary team without delays.
Once role-based access is in place, align service level agreements (SLAs) to support these policies across different locations.
Aligning SLAs and Escalation Paths Across Locations
A single global SLA policy often falls short in multi-location setups due to differences in time zones, staffing levels, and recurring challenges. Instead, implement multiple SLA policies that cater to the specific needs of each location. For example, one office might aim for a 2-hour response time during business hours, while another might set a 4-hour target based on its resources and local conditions.
A tiered SLA approach can help balance local and global priorities. Local policies should take precedence, but global standards can act as a fallback when no specific rules apply. Use trigger conditions – like Department, Location, or Customer Type – to enforce these distinct SLA targets while maintaining overall consistency.
Escalation paths also need to be adaptable. Create several levels of escalation – typically three to four for issue resolution and one for initial responses – to ensure clarity for complex cases. Macros can standardize the information passed along during escalations, ensuring that when a ticket moves from a local subsidiary to the global team, all relevant context is included. To avoid losing tickets during handoffs, designate a specific transfer status and require the receiving team to claim the ticket within a set timeframe, such as 2–4 hours. This structure keeps the process smooth and ensures accountability.
sbb-itb-e60d259
Automating Multi-Location Support with AI
Managing support across multiple subsidiaries can quickly become chaotic when relying on manual routing and prioritization. Agents often waste valuable time figuring out who should handle a ticket, leading to delays and repeated reassignments – especially for urgent issues. AI-driven automation steps in to smooth these inefficiencies, analyzing each request and assigning it to the right person or team instantly.
By using Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning, AI understands the intent behind a request, even when the phrasing isn’t standard. For instance, if a customer writes, "our system is completely down" instead of explicitly saying "outage", AI can still detect the urgency and route the ticket appropriately. This ability to interpret context works seamlessly across different regions, eliminating the need to create separate rule sets for every location.
AI doesn’t stop there. It takes case routing to the next level by dynamically matching tickets with the most qualified agents.
AI-Powered Case Routing and Prioritization
Effective case routing is essential when managing support for multiple subsidiaries. AI-based systems evaluate a range of factors simultaneously, such as required skills, language proficiency, workload, time zones, and location-specific expertise. Unlike static queues or round-robin systems, AI determines which agent is best equipped to resolve the issue on the first attempt.
Prioritization follows a similar approach. AI analyzes data like customer tier (from CRM records), sentiment (e.g., frustration or urgency), and interaction patterns (like rapid follow-ups) to identify critical cases. This ensures high-value customers don’t get stuck behind routine issues, even if they didn’t explicitly mark their ticket as "urgent."
Coveo is a great example of this in action. In 2024, under the leadership of Patrick Martin, VP of Technical Support, the company implemented AI-driven case assignment. By matching tickets to agents based on their skills and expertise, Coveo cut its Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) by over 50%, dropping from four days to just two.
"Our management team uses SupportLogic as our eyes everywhere. SupportLogic SX case assignment detects who the best and most qualified people are." – Patrick Martin, VP of Technical Support, Coveo
To get started, define a skills ontology – a structured list of technical areas, product modules, and specialized skills like language or environment expertise. Use virtual teams to group agents by region or subsidiary, simplifying management without the need for complex individual rules. Begin with AI-generated routing recommendations, validate them, and gradually move toward full auto-assignment.
While optimized routing ensures tickets are handled efficiently, AI also tackles potential delays with proactive escalation prediction.
Predicting Escalations and Managing SLAs with AI
AI doesn’t just route tickets – it also predicts which cases are likely to escalate. By analyzing factors like sentiment changes, response delays, product context, and historical trends, AI flags at-risk tickets early. This allows you to take action, whether it’s assigning the case to a senior agent, adjusting the SLA, or offering a remediation plan.
Dynamic SLA management takes this a step further. AI adjusts ticket priority and targets based on urgency, customer tier, and issue criticality – tailored to each subsidiary’s needs. For instance, if a ticket shows "Very Negative" sentiment and comes from a customer nearing renewal, the system can elevate the SLA and route it to a specialized retention team – all without manual intervention.
Companies using AI for escalation prediction have reported impressive results: an 86% reduction in manual analysis time, a 32% drop in escalation rates, and 28% faster Mean Time to Resolution. High-risk tickets handled with AI insights also saw an 18% boost in CSAT scores.
To make this work, combine ticket features with entitlement and SLA data to create a unified risk score. Set high intent confidence thresholds so AI only acts when it’s certain of the ticket’s intent. Maintain a small group of tickets that bypass AI for manual handling – this "holdout" group helps measure the ROI and impact of your AI tools. Finally, retrain your AI models monthly by feeding in the outcomes of past interventions, reducing false positives over time.
| Feature | Rule-Based Systems | AI-Powered Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Logic | Rigid IF-THEN keywords | Contextual NLP and Sentiment Analysis |
| Urgency | Based on user-selected fields | Based on emotion, keywords, and customer tier |
| Routing | Static queues/Round-robin | Dynamic matching (Skills, Capacity, Time Zone) |
| Maintenance | High (rules break over time) | Low (learns from historical outcomes) |
| Scalability | Limited | Scales across multiple subsidiaries/locations |
Tracking Performance by Location
Once routing and escalation processes are automated, the next step is gaining clear visibility into performance. With AI-powered tools in place, dashboards become essential for monitoring subsidiary performance while maintaining a unified account view. Start by creating a core dashboard with universal KPIs like First Response Time (FRT), Average Resolution Time (ART), and CSAT. Then, replicate this dashboard for each subsidiary, using filters such as "Requester Organization", "Ticket Group", or "Business Unit" to break down performance by location. For organizations managing multiple accounts, data syncing tools like Snowflake or BigQuery can centralize information, while SQL UNION queries consolidate identical schemas into a single reporting table. This creates a unified view, serving as the foundation for detailed location-based analysis.
Building Dashboards for Multi-Subsidiary Reporting
Start with "Card" visuals to display core metrics – Total Tickets, FRT, ART, and CSAT – for a quick overview. Add line and bar charts to track trends and compare performance across locations.
Interactive filtering is a must. Use charts like pie or bar graphs that double as visual filters. For example, clicking a specific location updates all dashboard components to show metrics for that location. Save commonly used views, such as "North America Subsidiary" or "Global View", using the "Bookmarks" feature. This allows stakeholders to toggle between consolidated and location-specific data seamlessly.
AI-enriched data adds deeper insights. For instance, tracking sentiment and intent by location can highlight unique challenges that aren’t immediately visible in standard metrics. If one subsidiary shows "Very Negative" sentiment for a specific product module, addressing the issue early can prevent larger disruptions.
| Dashboard Component | Purpose for Multi-Subsidiary Support | Key Metrics to Include |
|---|---|---|
| Scorecards (Cards) | Summarize overall health for each location | Total Tickets, Avg. CSAT, FRT Median |
| Line/Area Charts | Monitor trends over time | Tickets Created vs. Tickets Solved |
| Bar/Column Charts | Compare performance across locations | Tickets by Channel or Location, Tickets by Intent |
| Slicers/Filters | Segment data in real time | Location Name, Business Unit, Date Range |
| Agent Leaderboards | Evaluate individual agent performance | Solved Tickets per Agent, CSAT per Agent |
Dashboards should let users drill down from high-level KPIs to specific ticket data. This helps managers identify and address issues impacting performance at any subsidiary.
Using KPI Scorecards to Monitor Service Quality
KPI scorecards are essential for assessing whether subsidiaries meet service quality standards. Key metrics include FRT, First Contact Resolution (FCR), ART, CSAT, and Ticket Reopen Rate. Segment these metrics by location using custom fields like "Business Unit" or "Location" to dive deeper into site-specific data.
AI-powered insights enhance scorecards by pinpointing trends and identifying contributing factors. For instance, if one subsidiary has a high Ticket Reopen Rate, AI can determine whether the issue stems from inadequate training, product defects, or prioritizing speed over quality. Modern platforms also support natural language queries, making it easy to ask questions like, "Which subsidiary had the longest FRT this month?" and get instant answers.
"For years, brands have relied on dashboards as the backbone of performance reporting. While they provide… prompt-driven analytics deliver AI-powered insights." – Mozhdeh Rastegar-Panah, Senior Director, Product Marketing, Zendesk
To make scorecards actionable, configure AI-driven triggers. For example, automatically escalate tickets with low CSAT ratings to regional managers for immediate follow-up. Analyze "one-touch" resolutions at specific locations – high rates may indicate that common issues could be addressed through a centralized knowledge base. Use heatmaps to identify if certain subsidiaries face challenges during specific hours or time zones.
| KPI Category | Specific Metric | AI Application |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | First Response Time (FRT) | Predict surges and adjust staffing accordingly |
| Quality | CSAT / NPS | Analyze sentiment to uncover regional pain points |
| Resolution | Full Resolution Time | Reduce time by up to 50% via automated routing |
| Volume | Tickets by Channel or Location | Auto-classify tickets into the correct queues |
| Consistency | Ticket Reopen Rate | Identify if speed is prioritized over quality |
Standardizing ticket fields and tags across subsidiaries ensures accurate reporting. Without this, teams might spend more time cleaning data than analyzing it. These practices ensure support teams can maintain both detailed and consolidated views of customer interactions. Platforms like Supportbench enable this balance, combining operational consistency with AI-driven insights to optimize performance across all subsidiaries.
Using AI Insights for Consistent Support
AI takes the insights from dashboards and KPI scorecards a step further, helping businesses deliver consistent support across all locations. By turning raw case data into actionable intelligence, AI equips teams to resolve issues faster, predict customer satisfaction levels, and build a knowledge base to reduce future inquiries. This ensures that support quality remains steady, regardless of team size or regional differences.
AI Case Summaries for Faster Resolution
AI-generated case summaries give agents a complete picture of customer issues, even when cases span multiple interactions or involve several teams. These summaries include the issue’s background, actions already taken, and next steps, making it easy for any agent to step in and keep things moving smoothly. Administrators can also customize prompts to ensure summaries match the company’s preferred tone and style. Plus, modern AI tools consolidate insights from emails, chats, meetings, and CRM systems, creating a unified view of customer interactions.
Predicting CSAT and CES Scores
AI can predict Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) and Customer Effort Scores (CES) by analyzing sentiment, emotion, and the complexity of cases – even before surveys are sent out. Features like Dynamic Detection, which updates a ticket’s sentiment score with every customer reply, help ensure predictions stay accurate in real time. Advanced models that combine factors like sentiment changes, response times, and customer history can pinpoint at-risk interactions. For example, these models have driven an 18% boost in CSAT for high-risk tickets and cut escalation rates by 32%. Additionally, AI can assess tickets for empathy and tone, assigning quality-assurance scores that correlate with expected CSAT levels.
"AI predicts which support tickets are likely to escalate by learning from historical patterns, customer profiles, sentiment, and agent workload." – Pedowitz Group
Creating Knowledge Base Articles from Resolved Cases
With modern platforms, agents can turn resolved tickets into knowledge base (KB) articles with a single click. AI handles the heavy lifting by organizing, summarizing, and tagging the content. This process ensures that successful solutions are quickly shared across the organization. AI can also identify common unresolved queries or "no results" searches and draft articles to address these gaps, keeping the KB aligned with customer needs.
To maintain uniformity, AI-generated articles should follow a set structure, including action-focused titles, concise summaries, clear prerequisites, and step-by-step instructions. AI models can analyze up to 1 million past cases to suggest effective solutions for new articles. A robust knowledge base can cut Assisted Handle Time by 20–30% and enable AI agents to resolve over 40% of repetitive IT issues directly within tools like Slack or Teams.
"Automation is only as good as the knowledge it sits on." – Enjo
AI tools also streamline knowledge management by integrating data from platforms like Confluence, SharePoint, and Notion into a single, permission-aware system. This ensures every location accesses the same reliable information. To keep content fresh, high-impact articles (the top 20% by usage) should be reviewed quarterly by subject matter experts. By combining AI-driven case summaries, predictive satisfaction scoring, and automated KB creation, platforms like Supportbench help businesses deliver consistent, cost-effective support across all subsidiaries.
Conclusion
Supporting multiple subsidiaries or locations doesn’t have to be a logistical headache. The secret lies in centralization, standardization, and AI-powered automation – a trio that can transform scattered operations into a streamlined, cost-effective system. By consolidating customer data, workflows, and knowledge into a single platform, organizations can eliminate communication gaps and cut down manual ticket triage by as much as 80%.
Platforms like Supportbench, designed with AI at their core, handle repetitive tasks that would otherwise require additional staff. Companies using AI-driven support systems report a 73% reduction in customer service costs and automate up to 96% of customer inquiries. This kind of automation makes scaling support across multiple locations both smooth and efficient, while also laying the groundwork for standardized workflows.
On top of automation, standardized workflows and SLAs ensure consistent support quality no matter the location. AI tools add another layer by predicting escalations in real time, evaluating customer satisfaction, and even converting resolved cases into knowledge base articles – making proactive support a reality.
Switching from outdated, fragmented systems to AI-native platforms is more than just a tech upgrade; it’s a strategic move. Former IBM CEO Ginni Rometty summed it up perfectly:
"Some people call this artificial intelligence, but the reality is this technology will enhance us. So instead of artificial intelligence, I think we’ll augment our intelligence."
With these advancements, support teams can scale personalized, high-quality assistance while keeping the focus squarely on the customer experience.
FAQs
How does AI enhance customer support for businesses with multiple locations or subsidiaries?
AI helps businesses with multiple locations deliver better customer support by simplifying complex processes and ensuring uniformity across all branches. It takes care of repetitive tasks, like answering frequently asked questions, directs tickets to the appropriate teams, and even anticipates potential escalations to speed up issue resolution.
On top of that, AI enables multilingual communication, consolidates knowledge bases to ensure consistent service, and offers actionable insights through advanced reporting tools. These capabilities allow businesses to provide top-notch support while boosting efficiency and cutting down on operational expenses.
What are the advantages of centralizing customer data for multi-location support?
Centralizing customer data from various locations creates a single, unified view of each customer. This ensures that no matter where or how interactions occur, support teams can provide consistent and tailored assistance. With access to complete customer histories, preferences, and past issues, teams can resolve problems more quickly and accurately.
Having a centralized system also enhances communication and teamwork. By working from a shared source of information, silos are minimized, and all teams stay aligned. It also makes tracking and reporting much easier, allowing businesses to identify patterns, evaluate performance, and fine-tune their support strategies.
On top of that, centralization opens the door to leveraging AI and automation tools. These tools can handle tasks like ticket routing and escalation, cutting down on manual work and boosting efficiency. This means teams can focus on delivering proactive and scalable support, no matter the location.
How can standardized workflows improve support across multiple locations?
Standardized workflows bring consistency, efficiency, and clarity to support teams, regardless of where they are located. By sticking to the same procedures, scripts, and policies, teams can deliver a consistent customer experience, maintain a unified brand voice, and minimize confusion for both agents and customers. This uniformity also makes training and onboarding much smoother, enabling new agents to get up to speed quickly and helping operations grow without unnecessary complications.
Another key advantage is the ability to track and report issues across different locations more effectively. Standardized processes allow managers to spot recurring problems or bottlenecks with greater ease. Clear escalation paths and smoother task handoffs further improve communication and teamwork, cutting down on delays. Pairing these workflows with AI-powered tools – like automated ticket routing and prioritization – takes things a step further, ensuring support remains consistent and cost-efficient across all locations.
Related Blog Posts
- How to Manage Customer Support Across Multiple Products with Different Complexity Levels
- What’s the best helpdesk for multi-tier support?
- How do you handle support for multiple products, tiers, or service levels in one help desk?
- How do you handle support for “mission-critical” customers without building a VIP mess?