Managing support for various products, customer tiers, and service levels can be challenging. Here’s a straightforward approach to streamline your help desk:
- Organize Support Tiers:
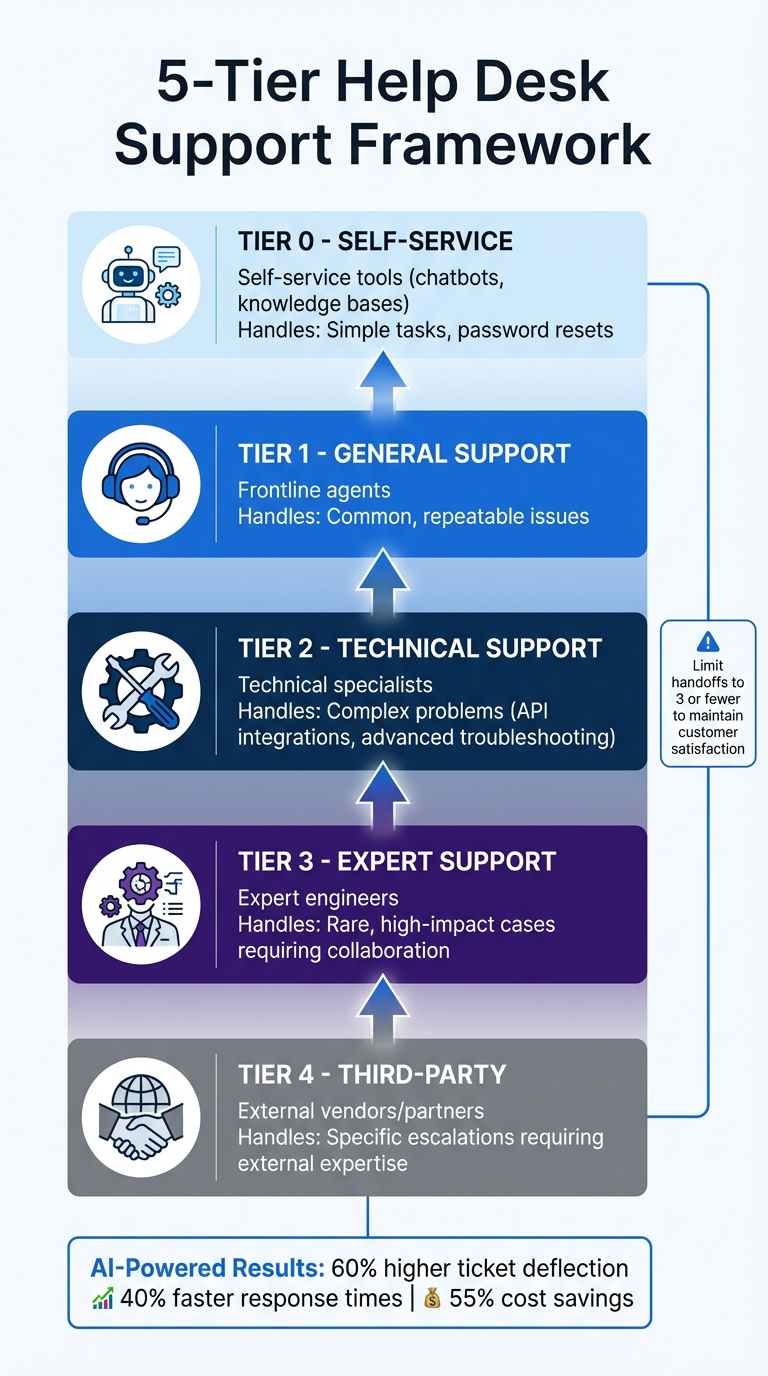
- Tier 0: Self-service tools like chatbots and knowledge bases handle simple tasks.
- Tier 1: Frontline agents address common, repeatable issues.
- Tier 2: Specialists resolve complex technical problems.
- Tier 3: Experts collaborate on rare, high-impact cases.
- Tier 4: External vendors manage specific escalations.
- Automate Ticket Routing:
- Use AI to analyze ticket content, intent, and sentiment.
- Automatically assign tickets to the right team based on expertise, urgency, and customer type.
- Dynamic SLAs:
- Adjust service-level agreements by customer tier, product, or issue type.
- Set alerts to prevent SLA breaches and prioritize critical cases.
- Specialized Teams:
- Group agents by skills, product knowledge, or customer type.
- Use fallback systems to handle overflow and avoid bottlenecks.
- AI-Powered Tools:
- Automate categorization, tagging, and prioritization.
- Use AI to assist agents with ticket summaries, suggested solutions, and missing details.
- Knowledge Base:
- Create tier-specific content to address customer needs effectively.
- Use AI to generate and maintain articles based on ticket trends.
- Track Performance:
- Monitor metrics like resolution time, customer satisfaction (CSAT), and escalation rates.
- Use dashboards to identify bottlenecks and optimize workflows.
Five-Tier Help Desk Support Structure: From Self-Service to Expert Escalation
The 5 Levels of Help Desk Support (And Why You Need Them)
Assess Your Support Structure and Requirements
Before diving into optimizing your help desk for multiple products and tiers, it’s crucial to get a clear picture of your current support system. Start by analyzing recent ticket data. Instead of sorting by customer type, categorize tickets based on complexity and resolution paths. Look for patterns – where do tickets tend to get delayed? Which issues require the most expertise? These insights will help you outline the natural divisions for your support tiers. This groundwork is essential for building an effective tiered support system.
Take Wolseley Canada as an example. In 2025, their small customer service team was overwhelmed, managing 7,000–8,000 emails every month without structured workflows. Eilis Byrnes, their Customer Service and Process Improvement Manager, tackled the issue by introducing automated ticket routing based on case type and client profiles. This change brought centralized ticket management, gave better visibility into agent performance, and resolved long-standing support challenges that had been missed due to manual processes.
"The ticketing system assisted us in resolving instances that were long overdue and in providing the staff with a smooth platform experience." – Eilis Byrnes, Customer Service and Process Improvement Manager, Wolseley Canada
When assessing your support needs, consider ticket volume alongside complexity. For instance, a team managing 50 tickets daily with just two agents might need three distinct tiers. Also, with many companies spending $100 or more per hour on customer support, understanding your resource limits is key to balancing costs.
Map Products, Tiers, and Customer Segments
Once you’ve reviewed your ticket data, it’s time to organize your operations. A five-tier framework is a practical way to categorize issues based on their complexity:
- Tier 0 (Self-Service): Use tools like knowledge bases and chatbots to handle repetitive tasks, such as password resets.
- Tier 1 (General Support): Focus on straightforward, repeatable questions that can be addressed by frontline agents.
- Tier 2 (Technical Support): Tackle more complex issues like API integrations or advanced troubleshooting, requiring specialized skills.
- Tier 3 (Expert Support): Handle rare, high-impact problems that might involve collaboration with engineering teams.
- Tier 4 (Third-Party): Work with external vendors or partners when necessary.
"Customer service tiers solve this by routing issues based on complexity and technical depth. Simple questions are handled through self-service or frontline agents, while advanced problems move directly to specialists." – BetterDocs
Customer segmentation should go beyond contract size. Instead, group customers by business value and complexity. For example, low-touch customers might only need basic setup help, while enterprise clients often demand more advanced support for integrations and performance tuning. Tools like custom drop-down fields in ticket forms or dedicated email addresses (e.g., productname@company.com) can help automatically tag and route tickets to the right teams. Clearly define escalation triggers and issue boundaries to avoid misrouting tickets.
Define Dynamic SLAs for Service Tiers
Static SLAs often fall short in complex support setups. Instead, opt for dynamic service-level agreements that adapt based on tiers, products, or specific customer needs. Start by ensuring every ticket has a priority assigned in the system’s default Priority field, as this is essential for applying SLA rules correctly.
Choose SLA metrics that align with the goals of each support tier. For example:
- First Reply Time: Measures how quickly the initial response is sent.
- Periodic Update: Tracks how often updates are provided during the ticket lifecycle.
- Requester Wait Time: Calculates the time a ticket spends in an active, non-pending status.
Order your SLA policies carefully, placing the most restrictive or high-priority rules at the top, as the system applies the first matching policy it encounters. Leverage AI-powered tools for intelligent triage – these can identify ticket intent (e.g., billing issues) and automatically adjust SLA priorities. Automating these adjustments ensures that urgent matters are addressed without delay.
To stay ahead of potential SLA breaches, set up business rules or automations. For example, if a ticket is nearing its resolution deadline, trigger an alert to notify a manager or add a tag for immediate attention. This proactive approach can help prevent dissatisfied customers from spreading negative feedback, which 81% of them are likely to do after a poor resolution experience.
Streamline Ticket Triage and Routing
Once you’ve mapped your products and support tiers, the next step is to ensure every ticket reaches the right agent quickly. Relying on manual triage can lead to slowdowns – especially during busy periods or when requests pour in from multiple channels. That’s where intelligent automation comes in. It can categorize, prioritize, and route tickets based on factors like product, tier, and urgency.
Modern routing systems leverage AI to analyze ticket intent, assess customer sentiment, and even identify the language used. For example, a frustrated VIP customer with a billing issue can be instantly routed to a senior specialist, while a straightforward password reset lands with Tier 1 support. By skipping manual ticket reviews, intelligent triage can save 30–60 seconds per ticket.
The real magic lies in matching tickets to the right agents in real time. Automated routing assigns tickets based on agent availability, workload, and expertise. If your team handles multiple products, agents certified in specific product lines can take on relevant tickets. And if an agent is unavailable or at capacity, fallback systems redirect tickets to secondary queues, ensuring nothing gets stuck.
Start small by automating high-impact areas like VIP escalations or common product inquiries. For better accuracy, use product-specific email addresses or custom drop-down fields in contact forms to help the system tag and route tickets correctly from the start. Keep an eye on reassignment rates in your dashboards – frequent reassignments might signal that your AI or routing rules need some fine-tuning.
Use AI for Ticket Categorization and Prioritization
AI-driven categorization goes beyond basic keyword matching. It can interpret ticket content to understand intent, gauge sentiment, and pinpoint details like product names or model numbers. This allows the system to automate tagging and prioritization.
For instance, if a ticket includes the word "refund" and has a negative tone, AI can flag it as urgent, route it to a retention specialist, and even attach internal notes with links to relevant knowledge base articles or escalation guidelines. If critical details like a purchase order number are missing, AI can prompt the customer for that information before the case reaches an agent.
Sentiment-based prioritization is especially helpful in multi-tier support environments. For example, AI can recognize an "unhappy VIP" and escalate their ticket immediately, ensuring high-value customers are taken care of without delay.
| AI Technique | Function | Benefit for Multi-Tier Support |
|---|---|---|
| Intent Detection | Identifies the purpose of the ticket | Ensures tickets go to specialized teams (e.g., Billing vs. Tech) |
| Sentiment Analysis | Detects customer emotions | Prioritizes frustrated VIP customers |
| Language Detection | Recognizes the ticket’s language | Routes to agents fluent in the same language |
| Entity Recognition | Extracts product names/IDs | Ensures expertise for specific products |
| Workload Balancing | Tracks agent availability | Prevents burnout by limiting ticket assignments |
Set up triggers for specific intents. For example, if AI detects a "return order" request, program the system to immediately ask for an invoice number. This keeps the ticket moving and reduces the number of interactions needed to resolve it.
Set Up Role-Based Queues and Specialized Teams
Organizing your support team into specialized queues ensures tickets reach agents with the right expertise. You can structure these queues by topic (e.g., billing or tech support), product line, or customer tier (VIP or standard). For larger teams, appoint a Queue Manager to oversee the main queue, assign tickets to specialists, and track trends like outages or recurring issues.
Clearly define agent skills by considering attributes like seniority, product knowledge, channel expertise (e.g., chat or email), and language fluency. This allows the routing engine to match tickets with the best-suited agent, improving first-response accuracy and minimizing reassignments.
Set up primary and secondary groups for each queue. If the primary group is at capacity, tickets can flow to a secondary team with broader expertise, ensuring customers still get timely responses.
To prevent burnout, establish capacity rules that cap the number of tickets an agent can handle at once. For example, live chat agents might be limited to one conversation at a time, while email agents could manage multiple open tickets. If an agent goes offline, triggers can automatically reassign their tickets to other team members.
For teams handling multiple products, streamline routing by creating product-specific entry points. Use unique email addresses for each product line or add custom fields to contact forms so customers can identify their issue upfront. This helps the system tag and route tickets to the correct queue.
"Automated ticket routing isn’t just about saving time – it’s about getting every customer the right help, at the right moment." – Nooshin Alibhai, Founder and CEO, Supportbench
Track queue performance using metrics like average time in queue, reassignment rates, and first-contact resolution. High reassignment rates could indicate issues with your routing logic, such as outdated skill profiles or inaccurate AI intent detection. By combining these strategies with automated escalation workflows, you’ll create a seamless multi-tier support system.
Build Tiered Escalation Workflows
An effective escalation workflow builds on a streamlined routing system to ensure issues are addressed at the right support level. A tiered approach advances complex cases based on urgency, expertise, and customer priority, typically using a four-tier structure: Tier 0 (self-service and AI), Tier 1 (frontline human support), Tier 2 (technical issues requiring deeper expertise), and Tier 3 (specialized or expert-level support).
Escalations can be triggered by the need for specific expertise, management intervention, automated processes, or the business impact of an issue. However, it’s crucial to limit the number of handoffs – too many transfers (more than three) can harm customer satisfaction and resolution quality. To maintain a smooth process, use contextual handoffs that include all relevant details – like order numbers, product IDs, or account history – so customers aren’t forced to repeat themselves as their case moves between tiers.
Automate Escalation Paths with AI
AI can streamline escalation by predicting when a ticket needs to move up the chain. It analyzes factors like intent, sentiment, and interaction patterns to gather critical context before escalating. For example, if a customer uses phrases like "this is unacceptable" or "I want to speak to a manager", sentiment analysis can flag the case for immediate attention.
Automated triggers can also escalate tickets based on specific conditions. For instance, if a ticket has been open for more than five exchanges, it might indicate the issue is too complex for the current tier. For teams managing multiple products or services, AI can ensure availability-aware handoffs. If no agents are available outside regular hours, the system can create an email ticket or schedule a callback.
Service Level Agreement (SLA)-based escalations are another essential tool. For example, if a ticket from a VIP customer is nearing an SLA breach, AI can prioritize it and assign it to a senior agent to ensure timely resolution.
| Escalation Method | Best Use Case | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Forward to Agent | Urgent, high-impact messaging queries | Ensures immediate human intervention |
| Send an Email | Complex issues outside operating hours | Provides a follow-up record for specialists |
| Custom Escalation | Workflow tagging and analytics | Tracks trends without altering ticket endpoints |
| Webhook Forwarding | Issues needing external teams | Automatically routes data to external systems |
To implement this effectively, allow your AI to collect data over a couple of weeks to identify patterns in intent and sentiment. Once you’ve established a baseline, set triggers – like flagging tickets with high-priority keywords and negative sentiment – to ensure complex cases are routed directly to the right specialist.
Track Escalations and De-Escalations Across Tiers
After setting up automated escalation pathways, tracking these flows is key to maintaining efficiency. For instance, if a significant number of tickets escalate from Tier 1 to Tier 2 for the same issue, it might indicate a need for better documentation or additional training for frontline agents.
Use tags and custom fields to monitor escalation status at every stage. Labels like "escalated_customer" or "3touch_or_more" can help you filter and analyze patterns in reporting dashboards. Frequent group transfers may reveal inefficiencies, such as unclear ticket ownership.
Keep an eye on metrics like the number of interactions per ticket and SLA violations. If tickets often require more than five touches, set up automated internal notes to alert agents that the case might need escalation or senior involvement. Similarly, if SLA breaches are common at a specific tier, it might point to understaffing or a lack of expertise.
De-escalations also deserve attention. These occur when a ticket is resolved at a higher tier and returned to a lower one. For example, if a Tier 3 engineer resolves a technical issue and sends the ticket back to Tier 1 for customer communication, make sure these tickets are prioritized upon return. Use custom queues or tags to ensure they don’t get overlooked.
sbb-itb-e60d259
Optimize Knowledge Management for Products and Tiers
When paired with automated ticket triage, a well-organized knowledge base can greatly improve self-service options and support efficiency. A structured system helps users and agents avoid irrelevant content. Without proper segmentation, users might stumble upon articles that don’t apply to them. For instance, segmenting by customer attributes, tags, or organizations ensures that someone on an Enterprise plan doesn’t see content intended for Starter users. If you manage multiple product lines, creating separate help centers can further refine search results.
Organize your knowledge base hierarchically with categories and sections. For complex product portfolios, deeper nesting – up to six levels for enterprise plans – can help arrange technical documentation without overwhelming the top-level navigation. Keeping each article tightly focused on a single topic not only makes it easier for users to understand but also improves the accuracy of AI-driven responses. Additionally, aligning your knowledge base structure with tier-specific needs enhances its effectiveness.
Here’s how you can implement tier-specific knowledge bases and leverage AI for content creation.
Create Tier-Specific Knowledge Bases
Segmenting content by service tiers ensures users only see articles relevant to their plan. Use ticket data to identify the specific needs of each tier. For example, if premium customers frequently report issues with API integrations, this indicates a need for detailed API documentation. On the other hand, if basic-tier customers often ask about billing, creating targeted FAQs for that group can address their concerns.
You can also audit commonly used macros and convert them into tier-specific knowledge base articles. Meeting self-service expectations is critical – 73% of consumers prefer resolving issues independently, and 90% expect access to a self-service portal.
Use AI to Generate Knowledge Base Content
AI can significantly reduce the effort required to build and maintain a knowledge base. By analyzing recent support tickets – usually from the past 30 days – AI tools can identify recurring issues and automatically generate structured content. These tools can produce up to 40 articles, complete with titles, summaries, and keywords, based on common customer queries. Importantly, AI also ensures customer data remains secure by automatically redacting any personally identifiable information (PII).
The results speak for themselves. For example, one organization achieved a 57% automated resolution rate and reduced full resolution time by 19%. Another saw a 30% drop in daily ticket volume.
To get the most out of AI-generated content, save drafts for human review before publishing. Agents and administrators should refine these drafts to ensure accuracy and maintain the brand’s tone. AI can also assist in expanding content – agents can start with bullet points or quick notes, and AI tools can turn them into polished, professional paragraphs. This is especially helpful when documenting new product features or tier-specific processes that need to be published quickly.
For best results, format articles with clear titles, structured subheadings, and bullet points. Since AI systems primarily rely on text, this structure ensures automated responses based on your knowledge base are accurate and helpful. This approach not only supports customer service agents but also enhances the effectiveness of AI-powered responses.
Track Performance with Tiered Analytics and KPIs
Tracking performance helps uncover whether premium tiers experience faster resolutions and highlights product line bottlenecks. Relying solely on averages can hide critical issues. To get a clearer picture, segment key performance indicators (KPIs) like resolution times, CSAT scores, and first-contact resolution rates by product and service level. This breakdown helps identify where resources need to be reallocated.
For example, analyzing "Group Stations" can reveal frequent tier escalations, which may point to training gaps. Similarly, monitoring the percentage of reopened tickets per tier can expose where quick fixes are failing, potentially signaling gaps in technical expertise or inaccuracies in the knowledge base. If Tier 1 agents struggle with one-touch resolutions for a specific product, it might indicate they lack the right tools or documentation. These insights not only inform dashboard design but also feed AI-driven proactive strategies.
Customize Dashboards for Tier and Product Performance
Once you’ve gathered these insights, design dashboards that separate customer experience metrics (like SLAs and CSAT) from operational metrics (such as agent workload and net flow) using interactive filters for product name, request type, or brand. Unique tags can also be used to refine reporting.
To set realistic benchmarks, consider using the 90th percentile for resolution times. Track metrics like "delayed" requests (tickets stuck in the same status for seven or more days) and "bounced back" tickets (those returning from a resolved status) to identify friction points in specific workflows.
For instance, in August 2025, Pair Eyewear leveraged omnichannel routing to monitor agent availability and capacity in real time. This approach automatically directed inquiries to the best-suited agents, cutting their first reply time by 83%. Similarly, CARET, a software provider, implemented skills-based omnichannel routing in 2025. This allowed them to maintain a steady CSAT score of 91% by ensuring tickets were routed to agents with the right expertise.
Use AI Predictions for Proactive Improvements
AI-driven analytics take things a step further by identifying trends and sentiment in support conversations, which helps managers address potential issues before they escalate. For instance, if AI detects a spike in "order is late" complaints, managers can review week-over-week performance and reallocate resources as needed.
Predictive analytics can also forecast metrics like CSAT, CES, and QA, enabling teams to make preemptive adjustments to agent workload and routing. Sentiment-based routing, for example, prioritizes tickets with negative sentiment, ensuring frustrated customers are addressed quickly to prevent SLA breaches. Automated prompts for missing information further streamline resolution times.
In 2025, Liberty London adopted AI to analyze customer sentiment and language across its support channels. This allowed Ian Hunt, Director of Customer Services, to route issues intelligently to specialized teams. As Hunt explained:
"Liberty is all about delivering a personal service. I see AI enhancing that personal service because now our customers will be interacting with a human who’s being put in front of them at the right time with the right information."
Integrate AI for Multi-Tier Automation
In multi-tier environments, AI takes over tasks like sorting, tagging, and routing tickets, which saves agents time and minimizes errors. AI-driven systems ensure tickets are routed to the right agent with the appropriate priority level – all without constant manual input, even in high-volume situations.
Speed and consistency are critical here. Intelligent triage systems can automatically detect factors like intent, language, and sentiment. For example, AI can flag urgent issues, adjust SLA targets, and route tickets to specialized teams. This eliminates the 30-60 seconds agents typically spend manually categorizing each ticket, freeing them to focus on more critical tasks. By handling these initial steps, automation sets the stage for more advanced support functions.
Use AI-Powered Copilot for Agents
An AI-powered copilot works as a real-time assistant, summarizing ticket histories, suggesting relevant knowledge base articles, and even drafting responses based on past interactions.
It goes a step further by identifying missing details – like an order number or shipping address – and automatically reaching out to customers to collect that information before the ticket is assigned to an agent. This ensures agents have all the context they need to resolve issues on the first try, boosting first-contact resolution rates across all tiers. In more complex cases, AI can flag tickets with internal notes, such as special handling instructions or troubleshooting resources, when a ticket exceeds a certain number of replies.
Eilis Byrnes, Customer Service and Process Improvement Manager at Wolseley Canada, highlighted the benefits of such automation:
"The ticketing system assisted us in resolving instances that were long overdue and in providing the staff with a smooth platform experience."
Beyond assisting agents in real time, AI also enhances workflows by dynamically tagging and prioritizing tickets.
Automate Tagging, Prioritization, and SLA Adjustments
Manual tagging often slows things down, especially for businesses with diverse product lines. AI steps in by analyzing ticket content to apply tags automatically, enabling more precise organization. It also evaluates ticket data – like sentiment, urgency, and customer tier – to adjust priority levels dynamically.
For instance, if a VIP customer submits a ticket with negative sentiment, AI can escalate it to a high-priority queue and shorten the SLA response time. Sentiment analysis further improves routing accuracy, cutting down on misassignments. These adjustments happen instantly, ensuring top-tier customers receive faster responses without any manual effort.
AI also tracks patterns like frequent ticket reassignments or shifts in sentiment, which could signal potential escalations. It can then add internal notes or transfer cases directly to managers. This level of automation reduces reassignment rates and prevents tickets from getting stuck in the wrong queue, an issue commonly seen with rigid rule-based systems. As Nooshin Alibhai, Founder and CEO of Supportbench, explains:
"Automated ticket routing isn’t just about saving time – it’s about getting every customer the right help, at the right moment."
Conclusion
Supporting multiple products, tiers, and service levels doesn’t have to mean juggling fragmented systems or expanding your team. The solution lies in creating a cohesive strategy driven by intelligent automation, tier-specific workflows, and smart routing. From aligning products to implementing dynamic SLAs, each step builds toward a flexible, efficient support system.
The benefits of AI-first platforms are hard to ignore: 60% higher ticket deflection, 40% faster response times, and up to 55% cost savings. Some teams have even slashed first response times from 15 minutes to just 23 seconds – a staggering 97% improvement. These results showcase what’s possible when organizations shift from manual, rule-heavy processes to AI-powered systems designed for scalability.
Adopting AI-based support doesn’t just boost efficiency – it creates a competitive edge. With 73% of CX leaders recognizing AI as critical to their future success and early adopters being 128% more likely to report high ROI, the divide between AI-driven companies and those falling behind is becoming more pronounced. On top of that, 70% of consumers notice a clear difference between companies using AI and those that aren’t. These numbers highlight the growing importance of leveraging AI to stay ahead.
FAQs
How does AI enhance ticket routing and prioritization in a multi-tier support system?
AI improves ticket management by analyzing details like intent, language, and sentiment to automatically route tickets to the right teams or agents. This ensures quicker, more precise resolutions.
It also helps prioritize tickets by urgency, context, or set business rules, allowing support teams to tackle critical issues first. As a result, workflows become more efficient, response times drop, and service quality improves – even in complex, multi-tier setups.
What are the advantages of using dynamic SLAs for different customer tiers?
Dynamic SLAs let you tailor response and resolution times to match the unique needs of different customer tiers. By syncing service levels with what customers expect, you can boost satisfaction, strengthen trust, and highlight the value you bring to your clients.
This method also helps you allocate resources more effectively. High-priority customers get the focus they deserve, while still delivering reliable service to everyone else. It’s a smart way to combine operational efficiency with a more personalized touch.
How can AI improve knowledge bases for multi-tier customer support?
AI can play a big role in improving knowledge bases for multi-tier support by creating precise, context-driven content tailored to the unique requirements of each support level. This leads to quicker ticket resolutions, uniform responses, and a closer match to what customers expect.
With AI, tasks like updating articles, spotting missing documentation, and customizing content for various audiences can be automated. This not only simplifies processes but also cuts down on manual work, allowing your team to dedicate more time to solving complex problems while ensuring top-notch support across all levels.










