In the high-stakes world of B2B customer support, where balancing operational efficiency with superior customer experiences is essential, understanding and utilizing support data analytics can be a game-changer. For service leaders grappling with rising customer expectations and the need to stay ahead of escalations, support analytics offers the tools to transform reactive processes into proactive, strategic solutions.
This article explores how support leaders can harness the power of support data analytics to prevent escalations, improve processes, and create long-term value for their organizations. Drawing from a discussion on leveraging analytics in support operations, we’ll delve into actionable strategies, insights, and transformative approaches tailored to the needs of growing and mature B2B companies.
The Shift from Reactive to Proactive Support
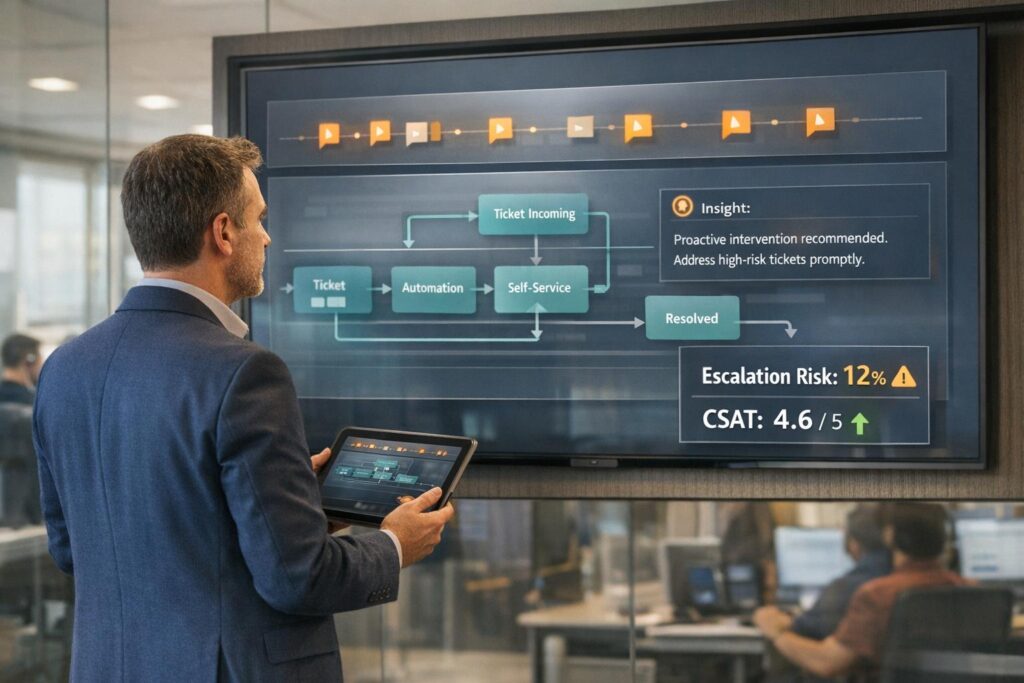
Traditionally, customer support has operated in a reactive state: waiting for customers to flag issues and responding to these as quickly as possible. While modern AI tools have enhanced this process by detecting at-risk cases faster, the ultimate goal is to move beyond reacting to problems and instead prevent them from occurring in the first place.
Support analytics enables this proactive shift by identifying patterns in customer interactions and extracting actionable insights from both structured and unstructured data. Structured data refers to metadata like case creation time, assigned agent, product, and priority, while unstructured data includes the actual communication and voice of the customer. By analyzing the intersection of these data types, organizations can uncover systemic drivers of issues and implement changes to address them at their root.
sbb-itb-e60d259
Understanding the Power of Signals in Support Analytics
One of the most transformative aspects of support analytics is the detection of "signals" within customer interactions. Signals are insights derived from unstructured data that highlight customer emotions, intents, or behaviors. Examples include:
- Frustration: An indicator of dissatisfaction likely to correlate with negative customer satisfaction (CSAT) scores.
- Confusion: Signals gaps in usability, unclear agent responses, or suboptimal documentation.
- Escalation Requests: Direct customer requests to escalate an issue.
- Likelihood of Churn: Predictive signals suggesting a customer may leave.
- Call Requests: Requests for phone support, often driven by urgency or complex issues.
Analyzing these signals at scale not only helps resolve individual cases more effectively but also reveals trends that can inform broader strategic decisions.
Holistic Analysis: The Key to Strategic Impact
Support leaders must look beyond individual cases to analyze signal trends across their entire operation. By aggregating data and identifying clusters of signals around specific products, regions, or support teams, organizations can uncover systemic issues. Here’s how this data can be leveraged:
- Identifying Product Issues: Frustration or confusion signals clustered around specific product features may indicate usability challenges or the need for clearer documentation. Sharing these insights with product and engineering teams enables targeted improvements.
- Improving Agent Training: If signals like frustration or escalation requests consistently cluster around certain teams or agents, it may point to training gaps. Proactive upskilling can reduce the recurrence of these issues.
- Enhancing Self-Service Resources: Confusion signals related to documentation can guide updates to FAQs, guides, or knowledge base articles, empowering customers to resolve issues independently.
- Optimizing Processes: For example, if call requests spike on the fourth day of a case’s lifecycle, organizations can proactively offer calls on the third day to reduce frustration and improve resolution times.
Real-World Scenarios: Turning Data Into Action
Scenario 1: Preventing Escalations
Support analytics can identify cases likely to escalate by analyzing signals such as frustration, confusion, and direct escalation requests. By looking at how these signals cluster around specific product features or support tiers, leaders can implement changes like targeted training or process adjustments to reduce the risk of escalations altogether.
Scenario 2: Addressing Customer Confusion
Confusion signals often arise from unclear product usability, insufficient agent responses, or gaps in documentation. Aggregating these signals helps pinpoint specific problem areas, enabling organizations to improve product design, train agents on clearer communication, or update self-service resources.
Scenario 3: Proactive Call Management
By analyzing when customers are most likely to request calls during a case’s lifecycle, support teams can proactively offer phone support before frustration sets in. This not only improves customer experiences but also reduces the volume of reactive requests, streamlining resources.
Scenario 4: Driving Upsell Opportunities
Positive signals – like a customer expressing satisfaction – can highlight opportunities for upselling or cross-selling additional services. Support teams can pass these insights to sales or customer success teams, turning excellent service into revenue opportunities.
Scenario 5: Enhancing Customer Content
Signal trends can reveal areas where customers struggle to find answers independently. For instance, repeated confusion signals around a particular feature may indicate the need for clearer guides or tutorials, reducing reliance on support teams.
Key Takeaways
- Adopt a Proactive Mindset: Shift from reactive case management to proactive problem prevention by analyzing support analytics at scale.
- Leverage Signal Insights: Use signals like frustration, confusion, and escalation requests to identify trends and address systemic issues.
- Prioritize Holistic Analysis: Examine data clusters across products, regions, and teams to uncover root causes of recurring challenges.
- Collaborate Across Departments: Share insights with product, engineering, and sales teams to drive improvements and revenue growth.
- Optimize Processes Based on Data: Use analytics to fine-tune support workflows, such as offering calls earlier in the case lifecycle.
- Invest in Training: Use signal trends to identify training gaps and upskill agents for better customer interactions.
- Enhance Self-Service Options: Address confusion signals by improving documentation and self-help resources.
- Use Positive Signals Strategically: Leverage customer satisfaction to create upsell opportunities or secure testimonials and reviews.
Conclusion
Support analytics is not just about resolving individual cases more efficiently – it’s a pathway to transforming customer experience and driving business growth. By analyzing structured and unstructured data, identifying actionable signals, and implementing data-driven changes, B2B organizations can prevent escalations, improve retention, and deliver strategic value across departments.
For B2B support leaders, embracing this proactive approach is no longer optional. It’s the key to scaling operations, enhancing customer loyalty, and proving ROI in an increasingly competitive landscape. Start with the data you already have, listen to the voice of your customers, and turn insights into action. The future of support is not just responsive – it’s transformative.
Source: "B2B Customer Support Analytics: Getting Truly Proactive" – SupportLogic, YouTube, Jun 13, 2025 – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BnCoHgPtLaE