Messy ticket categorization leads to unreliable dashboards and poor decision-making. If your tickets are labeled inconsistently – like "General Inquiry" or "Miscellaneous" – you lose critical insights, making it harder to identify trends, improve response times, or fairly evaluate agent performance.
Here’s how to fix it:
- Audit existing categories: Identify redundant, vague, or underused tags.
- Simplify your structure: Use 30–50 clear tags organized into 6 top-level categories with subcategories.
- Automate with AI: Let AI tools auto-tag tickets to ensure consistency and save time.
- Train your team: Provide clear guidelines and regular training to keep tagging accurate.
- Monitor and refine: Regularly review metrics like recategorization rates and ticket trends to adjust your system.
For example, companies like James Villas and Gousto achieved faster response times and better insights by standardizing tags and leveraging AI. Start by cleaning up your categories, and you’ll see improvements in efficiency, reporting, and customer satisfaction.
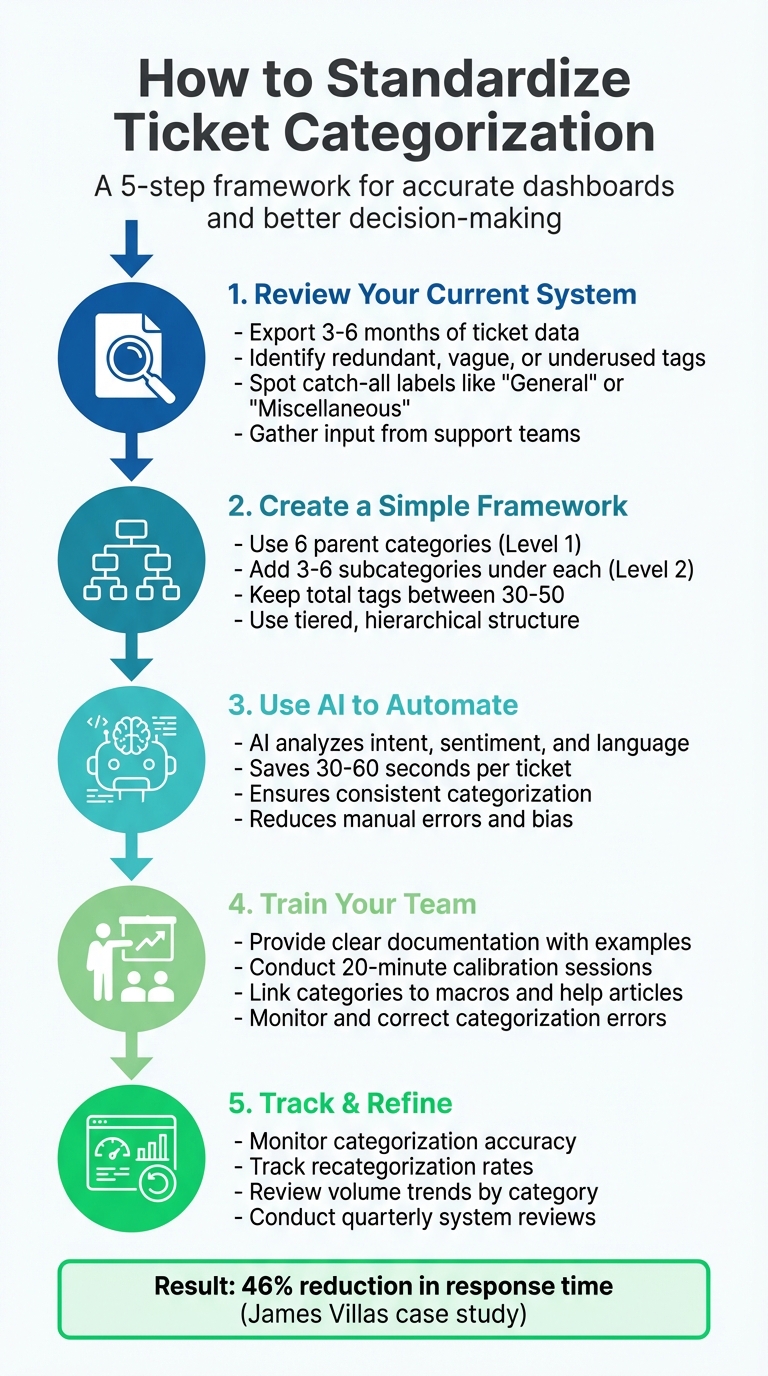
5-Step Process to Standardize Ticket Categorization for Accurate Dashboards
Ticketing System Guide for IT Support with Hands-on Ticket Labs
Step 1: Review Your Current Categorization System
Start by taking a close look at your existing category setup. Export ticket data from the past three to six months and sort it by category volume. This approach helps pinpoint inefficiencies – like underused categories, overlapping labels, or vague terms that obscure the actual issues customers are reporting. This step lays the groundwork for a more streamlined and effective taxonomy.
Spot Redundant or Rarely Used Categories
Many support teams deal with an overwhelming number of tags – sometimes 400 to 500 – leaving agents with only a few seconds to pick one. This often results in agents selecting the first option they see instead of the most accurate one.
To address this, examine ticket volumes and remove categories that are rarely used on a quarterly basis. Also, look for duplicates, such as "FTLI" and "First Time Login Issue". A streamlined system typically includes about 30 to 50 tags, organized into six Level 1 categories and around 30 Level 2 subcategories.
Address Misused or Catch-All Labels
High-volume categories like "General" or "Miscellaneous" are often overused, signaling that agents are relying on these vague labels as default options. This practice can obscure the actual customer issues.
Think carefully about your tagging structure; you need to strike a balance between being too generic and overly specific.
Investigate why agents lean on these catch-all labels and create more precise alternatives that better reflect the customer experience.
Gather Input from Support Teams
Combine your data analysis with feedback from your support team to get a complete picture of the current system’s challenges.
Your agents are the ones interacting with the categories daily, so their input is invaluable. Organize focused discussions to identify confusing or redundant categories.
"I typically start by talking to other teams to understand what needs to be measured outside of what I/my team want to measure. I learned early on that if I just measure what I want, I don’t have access to data that other teams need".
A hands-on exercise can help: print out a random sample of past tickets and have team members jot down what details they think should be captured. Compare their notes to your existing categories. If multiple agents classify the same ticket differently, it’s a clear sign your hierarchy needs simplification.
Step 2: Create a Simple and Scalable Categorization Framework
Once you’ve identified inefficiencies, the next step is to refine your system into a clear and scalable structure. A well-thought-out taxonomy provides both high-level strategic insights and detailed operational data. The goal is to create a framework that agents can use quickly and consistently while maintaining the accuracy needed for reliable dashboards.
Use Tiered Categories
A hierarchical taxonomy organizes categories into distinct layers, making it easier to navigate and analyze. Start with broad parent categories at Level 1 – think "Account", "Billing", "Product Usage", or "Bugs." Then, add more specific subcategories at Level 2 to capture precise issue details. For instance, under "Billing", you might include subcategories like "Payment_Failed_Paypal" or "Invoice_Missing." This layered approach enables both strategic insights and targeted troubleshooting.
"I get very specific and create High Level Tags + Specific Reason Tags… This helps me see how many total of one type of issue + breaking it down into smaller chunks." – Jenny Dempsey, CX Manager, Apeel
Most teams find that starting with around 6 parent categories and 3 to 6 subcategories under each strikes the right balance between usability and detail. This setup not only simplifies reporting but also makes it easier to integrate AI tools down the line.
Keep Your Category Count Manageable
On average, support agents spend just three seconds picking a category. If your system includes hundreds of tags, they’ll likely choose the first relevant option rather than the most accurate one. To avoid this, aim to keep your total tag count between 30 and 50. This range provides enough coverage for common issues without overwhelming agents.
"We typically streamline their taxonomy down to 30-50 tags which cover the main problems, questions and feedback in enough detail to be useful." – Sharad Khandelwal, Founder & CEO, SentiSum
Start with a smaller set of categories and add new ones only when an existing category consistently receives high ticket volumes. Conduct monthly reviews to consolidate duplicates and eliminate underused tags, ensuring your system stays clean and efficient. Use standardized naming conventions – put the most important topic first, like "Size_Small" instead of "Small_Size" – to make tags easier to locate.
Now, let’s consider how to choose the right taxonomy structure based on your ticket volume.
Hierarchical vs. Flat Categorization Structures
Your choice between a flat or hierarchical taxonomy depends on the volume of tickets your team handles. Flat taxonomies work best for smaller teams managing hundreds of tickets per month, where simplicity is key. In contrast, hierarchical taxonomies are ideal for teams processing thousands of tickets monthly, as they support detailed reporting and trend analysis.
| Feature | Flat Taxonomy | Hierarchical Taxonomy |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single-layered list | Multi-layered (Category > Subcategory) |
| Best For | Low volume (hundreds/month) | High volume (thousands/month) |
| Setup Effort | Low; easy to build initially | High; requires deliberate planning |
| Reporting | Broad; manual deep dives needed | Granular; flexible at each level |
| Scalability | Limited; prone to duplication | High; integrates new tags under parent categories |
| Agent Accuracy | High for short lists; low for long ones | High if well-organized; facilitates detailed categorization |
For most B2B support teams, a hierarchical structure offers the flexibility needed to grow with your product and customer base. To make categorization more actionable, assign each category a specific owner, a saved reply, and a relevant knowledge base article. This ensures that categorization contributes directly to resolution, not just reporting.
Step 3: Use AI to Automate Categorization
Once you’ve established a streamlined framework of 30–50 tags, AI can step in to ensure consistent application of these categories. Manual categorization often leads to inconsistencies, as agents may interpret and prioritize tickets differently. AI, however, applies the same logic across all tickets, removing subjective bias and ensuring your dashboards present accurate and reliable trends. Let’s break down how AI auto-tagging can revolutionize your categorization process.
How AI Auto-Tagging Works
AI-powered tools analyze the content of support tickets to automatically assign appropriate tags. These tools go beyond basic categorization by identifying the ticket’s intent (what the issue is about), sentiment (whether the customer is frustrated or satisfied), and language. This multi-dimensional analysis enhances traditional methods of categorization.
For instance, Supportbench can evaluate urgency, customer tier, and emotional tone to not only categorize tickets but also route them to the right agents. This approach can even predict metrics like First Contact Resolution (FCR), Customer Satisfaction (CSAT), and Customer Effort Scores (CES) based on the ticket’s initial content – providing actionable insights before surveys are sent out.
The time savings are impressive. AI-driven triage can cut down ticket handling time by 30 to 60 seconds per ticket, as agents no longer need to manually read and classify each one. Additionally, AI can score customer frustration on a scale from 1 to 5, helping identify and address potential churn risks early.
Add AI to Your Workflow
Start by defining 30–50 categories and use detailed prompts to capture both the nature of the issue and its priority. When deploying AI for categorization, it’s important to set up default queues for tickets that don’t clearly fit into existing categories.
A real-world example of this in action is Wolseley Canada. In June 2025, under the leadership of Eilis Byrnes, their Customer Service and Process Improvement Manager, the company implemented Supportbench to handle 7,000 to 8,000 monthly support emails. By automating ticket routing based on case type and client profile, they not only sped up resolution times but also improved operational visibility.
"The ticketing system assisted us in resolving instances that were long overdue and in providing the staff with a smooth platform experience."
- Eilis Byrnes, Customer Service and Process Improvement Manager, Wolseley Canada
To further optimize performance, monitor how often agents override AI-generated tags. This recategorization data can help fine-tune the system’s accuracy over time. By integrating AI into your workflow, you create a foundation for ongoing improvements in your support operations.
sbb-itb-e60d259
Step 4: Train Your Team and Enforce Guidelines
Once your taxonomy is streamlined and AI automation is in place, the next step is getting your team up to speed. Even with AI handling much of the heavy lifting, your team needs to fully understand the purpose and application of each category. Without clear training and consistent enforcement, there’s a risk that agents might take shortcuts – like overusing a generic label like "Other" or defaulting to the first tag they see. These habits can quickly erode the consistency and accuracy of your system, undermining the work you’ve put into refining your framework.
Provide Clear Documentation and Examples
A well-documented knowledge base is key. Each category should be clearly defined, with explanations of when and why it should be used. To make things easier for your team, link categories to their owners, quick-reply macros, and relevant help articles. Avoid using confusing acronyms – opt for descriptive names like "Payment_failed_paypal" instead. A one-page cheat sheet outlining "Do and Don’t" rules for each subcategory can be a game-changer. Additionally, a synonyms table (e.g., mapping "SSO" to "Single Sign On") can help agents quickly locate the correct category.
"Make sure yours [knowledge base] clearly says what each category means, where it’s supposed to be applied and why it’s important."
- Sharad Khandelwal, Founder & CEO, SentiSum
Conduct Regular Training Sessions
Short, focused training sessions can go a long way in reinforcing proper categorization. Consider holding 20-minute daily calibration meetings in a sandbox environment where agents can practice. Including team members from product, operations, and customer experience ensures everyone sees how accurate categorization benefits the entire organization. Reviewing random ticket samples as a group helps reinforce the system. After the initial rollout, monthly governance reviews can help you spot and address issues like duplicate or underused subcategories.
Monitor and Correct Categorization Errors
Keep an eye on manual adjustments to AI-generated tags and assign ownership of each top-level category to a specific individual who can handle change requests. If you notice frequent recategorization, it could signal unclear tags or system flaws. To address this, create a simple feedback loop – like a quick internal form – so agents can suggest new tags or flag issues. Periodically auditing a small sample of tickets against expert judgment can help ensure the system stays accurate and aligned with your goals.
Step 5: Track Performance and Make Adjustments
With your framework in place and your team trained, it’s time to focus on measuring how well your categorization system is performing. Monitoring key metrics is essential to ensure everything runs smoothly and to identify areas that need improvement. Start by assessing categorization accuracy – regularly audit a sample of tickets to compare AI or agent-assigned categories with the judgment of human experts. Another critical metric is the recategorization rate, which reflects how often agents manually change an automatically assigned category. A high rate here could indicate unclear category definitions or insufficient AI training.
Monitor Key Performance Metrics
In addition to accuracy, track metrics that reveal broader trends and bottlenecks. For example:
- Volume and trends by category: If a specific category sees a sudden spike, it could signal a system-wide issue or an emerging need.
- Resolution time by category: This helps pinpoint which issues are taking the longest to resolve or are getting stuck in the backlog.
- CSAT and reopen rates by category: These metrics give insight into the quality of support being provided.
- Priority-level distribution: Make sure resources are allocated effectively between high-priority and low-priority tickets.
Using this data, you can identify patterns and make informed adjustments to your categorization process.
Refine Categories Based on Data
Once you’ve gathered insights from your performance metrics, use that data to refine your categorization system. Schedule quarterly reviews to keep your system optimized. During these reviews, you can:
- Merge duplicate categories.
- Retire labels that are rarely used.
- Rename categories that seem confusing or ambiguous [16, 4].
If certain categories are being overused or underused, adjust them to better reflect the ticket trends. Standardize tag prefixes (e.g., billing/refund or bug/login) to make reporting more predictable. Additionally, link each category to specific resources, like internal macros or knowledge base articles, to maintain consistency and speed up ticket resolutions.
"A well-thought-out tag taxonomy, consistently applied by agents, will allow you to track worrying trends as they unfold and unearth valuable insights that drive product improvement."
- Ben Goodey, Customer Service Researcher, SentiSum
Before and After Implementation Comparison
To measure the impact of your efforts, compare key metrics from before and after implementing your standardized system. Here’s what you can expect:
| Metric | Before | After |
|---|---|---|
| Tagging Consistency | Inconsistent; varies by agent | High; guided by clear definitions/AI |
| Routing Accuracy | High manual triage; frequent misroutes | Automated; tickets reach the right team first |
| Recategorization Rate | High (agents frequently fix labels) | Low (initial categorization is accurate) |
| Average Resolution Time | Slower due to manual sorting and bottlenecks | Faster due to automated prioritization |
| Reporting Clarity | "General" category hides root causes | Granular insights into specific product issues |
Take James Villas, for example – a global holiday rental company. They introduced auto-categorization for urgent topics, which allowed them to route these tickets into a priority queue. The result? A 46% reduction in overall response time. This kind of improvement demonstrates how better categorization can lead to quicker resolutions, clearer insights, and smarter use of resources.
Conclusion
Standardizing ticket categorization isn’t just a technical tweak – it’s the backbone of effective customer support. Without a consistent system in place, dashboards lose their reliability, reports mislead decision-making, and teams end up wasting time on avoidable problems.
"Building a best practice help desk ticket categorization process is the lynchpin of your customer service analytics success. It’s your foundation."
- Sharad Khandelwal, Founder & CEO, SentiSum
To create a reliable categorization process, follow these key steps:
- Audit your current setup to remove redundant or overly broad labels.
- Design a scalable framework with 5 to 8 core categories.
- Implement AI-powered auto-tagging to minimize manual errors.
- Train your team with clear guidelines and ongoing support.
- Track performance through regular reviews and data-driven adjustments.
Each step builds on the previous one, creating a system that not only adapts to your business needs but also improves dashboard accuracy and operational efficiency. This leads to faster ticket routing, shorter resolution times, and better resource allocation. Considering that 90% of users expect their issues to be resolved within 10 minutes, accurate categorization ensures tickets reach the right team members quickly.
That said, automation isn’t a cure-all. Automating flawed data can lead to even bigger challenges down the road.
"You cannot fix bad data by automating it. Phase 0 must come first: clean data annotation before any model touches production."
- Faris Khasawneh, Senior IT Pro
The takeaway? Start with clean, well-defined categories. Enforce these through locked fields and oversight from governance teams. Only then should you bring automation into the mix to scale your efforts effectively.
FAQs
How does AI help ensure accurate ticket categorization?
AI improves ticket categorization by examining details like intent, language, and sentiment. This ensures tickets are routed and grouped accurately, minimizing manual mistakes and creating consistent reporting.
With automated categorization, AI simplifies workflows, saves time, and delivers dependable data for better decision-making, even in challenging customer support scenarios.
What are the advantages of using a hierarchical structure for ticket categorization?
A hierarchical ticket categorization system creates a clear and structured way to manage support tickets, which plays a big role in getting tickets to the right teams quickly. With this setup, tickets are routed more accurately, cutting down on delays and helping resolve issues faster.
This system also boosts reporting and analytics by providing a uniform structure for tracking patterns, spotting recurring problems, and managing resources effectively. It gives leaders the tools they need to make informed decisions and maintain reliable dashboards.
As ticket volumes increase, a hierarchical system ensures your support processes stay organized and scalable. It prevents chaos and keeps operations running smoothly – a smart move for businesses looking to streamline their support systems and deliver better results.
How often should you review and update ticket categories to keep them accurate?
To keep your ticket categorization accurate and useful, make it a habit to review and update your categories every 3 to 6 months. This helps ensure they stay aligned with changing customer needs, shifting business goals, and new support trends.
Frequent updates can prevent confusion, improve the accuracy of your reports, and streamline workflows. If you start noticing recurring problems, outdated labels, or inefficiencies in how tickets are routed, it might be a good idea to revisit your categories even sooner.
Related Blog Posts
- Best SaaS helpdesk for growing support teams
- How do you standardize ticket categorization so reporting is accurate (and consistent)?
- How do you handle support for multiple products, tiers, or service levels in one help desk?
- How do you identify the top ticket drivers and turn them into a Product backlog?










