Duplicate tickets and fragmented threads are a common problem in customer support, especially in B2B environments. They waste time, confuse agents, and inflate metrics, making it harder to allocate resources effectively. Merging threads while keeping context intact is critical to avoid losing important details, maintain trust, and ensure operational accuracy. Here’s what you need to know:
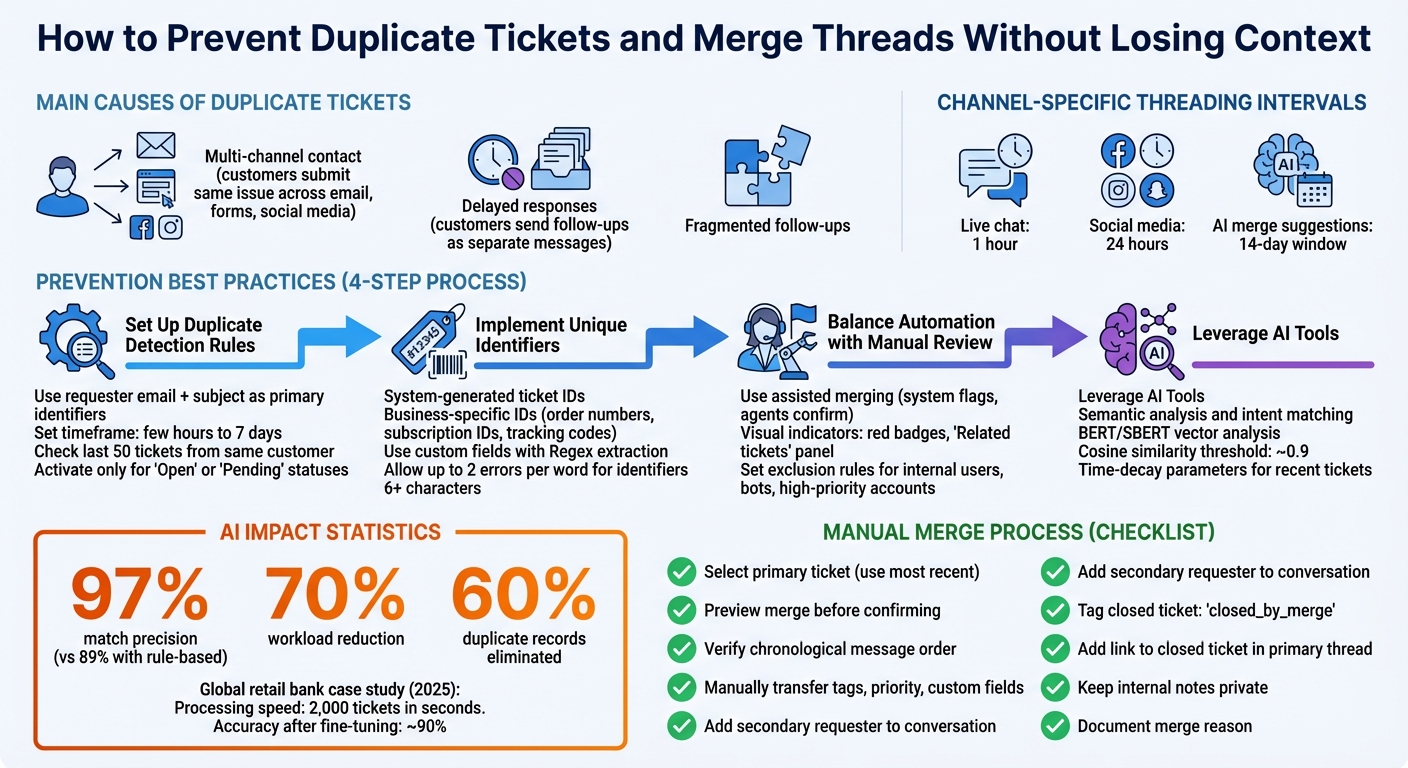
- Causes of Duplicate Tickets: Multi-channel contact, delayed responses, and fragmented follow-ups are the main culprits. Customers often submit the same issue across email, forms, and social media, or send follow-ups as separate messages.
- Why Context Matters: Merging without losing context ensures agents have a complete history, avoids duplicated work, and maintains an audit trail for compliance and SLA tracking.
- Best Practices for Prevention:
- Use duplicate detection rules based on requester email and subject.
- Implement unique ticket identifiers like order numbers or tracking codes.
- Leverage AI tools to identify duplicates using semantic analysis and intent matching.
- Balance automation with manual review to ensure accuracy.
- How to Merge Threads Correctly:
- Select a primary ticket and consolidate all information.
- Check for proper transfer of fields like tags and priority.
- Maintain transparency with clear documentation and private notes.
- AI’s Role: AI can process thousands of tickets quickly, using advanced tools like semantic analysis and cosine similarity to detect duplicates and propose merges while preserving context.
Complete Guide to Preventing and Merging Duplicate Support Tickets
How to Prevent Duplicate Tickets
Avoiding duplicate tickets requires a mix of automation, proper configuration, and human oversight to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
Setting Up Duplicate Detection Rules
Start by defining matching criteria that align with customer behavior. A reliable method is to use the requester’s email address along with the ticket subject as primary identifiers. This approach helps catch obvious duplicates, like when a customer sends the same query twice after not receiving an immediate response.
For more nuanced cases, leverage AI-powered tools that detect logical similarities. These tools can identify duplicates even when questions are rephrased or contain typos, outperforming rigid keyword-based rules that fail when wording changes.
Set a timeframe for duplicate checks – ranging from a few hours to up to 7 days. Some platforms offer additional flexibility by checking against the last 50 tickets from the same customer, which can help spot patterns that fall outside a strict time window.
To refine detection, tailor rules for specific channels like email, chat, phone, or web forms. Ensure these rules only activate for relevant ticket statuses, such as "Open" or "Pending", to avoid merging new issues into resolved tickets unless your system is configured to reopen them automatically.
Once these rules are in place, enhance accuracy by integrating unique identifiers.
Implementing Unique Ticket Identifiers
Assigning a system-generated ID to each ticket is a critical step. Beyond that, include business-specific identifiers like order numbers, subscription IDs, or tracking codes as a second layer of defense.
Use custom fields to store these identifiers and configure your system to extract them automatically from ticket subjects or body text using Regular Expressions (Regex). This ensures that duplicate detection rules can check if an open ticket already exists for a specific order before creating a new one.
For systems equipped with AI-driven entity detection, enable features that account for misspellings. For instance, many systems allow up to two errors per word while maintaining accuracy for identifiers with at least six characters. Adding synonyms for product names or categories, such as recognizing that "Premium Plan" and "Pro Subscription" refer to the same thing, further improves detection.
This setup ensures that tickets are merged efficiently and accurately.
Finding the Right Balance Between Automation and Manual Review
Even with well-optimized detection rules, human involvement is essential to maintain accuracy. Fully automated merging can be risky since merges are permanent and could erase critical context or disrupt your audit trail. On the other hand, relying solely on manual detection is slow and prone to errors, especially during high-volume periods.
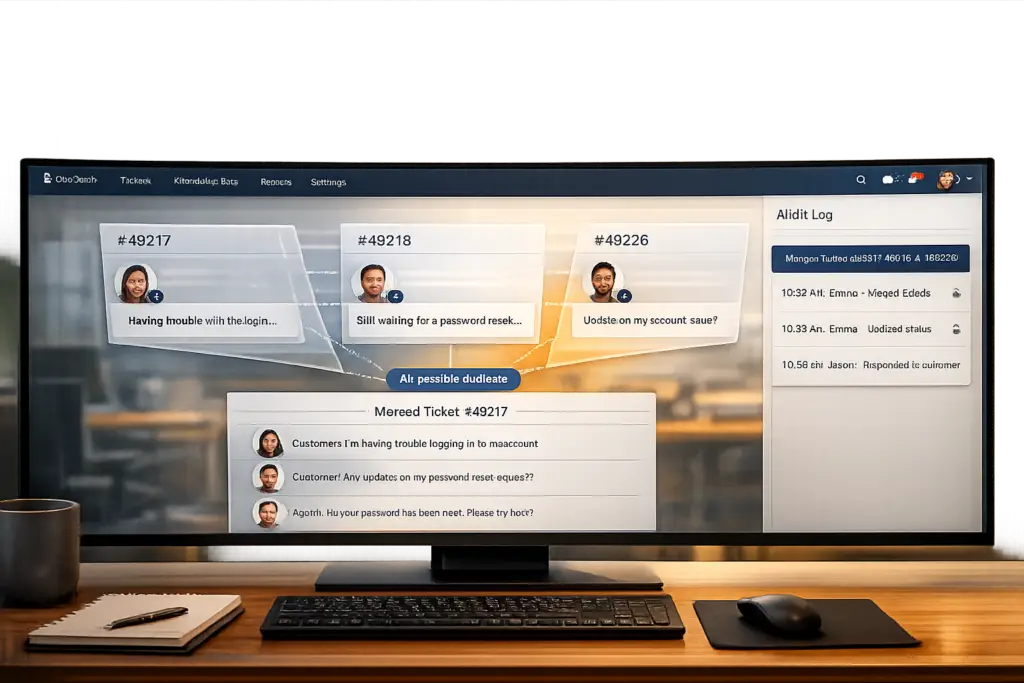
The best approach is assisted merging. Here, the system flags potential duplicates using visual indicators – like a red badge or a "Related tickets" panel – and agents confirm merges as part of their workflow. This method keeps the ticket queue organized without compromising accuracy.
"Assisted ticket merging is the safest and most scalable approach." – Lentil Labs
To reduce false positives, establish exclusion rules. For instance, prevent automation from flagging tickets from internal users, bots, or high-priority accounts. You can also fine-tune detection by ignoring generic terms that could trigger incorrect matches, such as "Inspections" when used as a verb rather than a product name. Exact match settings or noun-specific detection help refine these rules.
AI further enhances the process by identifying duplicates based on sentiment and intent rather than just keywords, which is far more reliable than traditional "IF-THEN" logic. However, AI still requires human oversight for edge cases. The goal isn’t to remove agent involvement entirely but to ensure their time is spent on meaningful decisions, rather than manually hunting for duplicates that an optimized system can handle.
How to Merge Threads Without Losing Information
When dealing with duplicate tickets, merging them correctly is crucial to keep all the necessary context intact. Since merges are final, it’s essential to handle this process carefully to avoid losing any important details.
Manual Thread Merging Steps
Start by selecting one ticket to serve as the primary record where all information will be consolidated. A good rule of thumb is to use the most recent ticket as the primary, especially if it contains updates from the customer or if the issue has already been addressed.
Typically, the process involves opening the ticket you intend to close, locating the merge option (via a menu or shortcut), and searching for the target ticket by its ID, content, or the requester’s name. Always preview the merge to ensure accuracy before confirming.
Once the tickets are merged, messages from the secondary ticket are usually arranged in chronological order within the primary thread. However, some fields – like tags or priority – may not transfer automatically. Agents should double-check and manually update any critical custom field data after the merge.
If the tickets involve different requesters, make sure the requester from the closed ticket is added to the conversation. Adjust cross-user merge settings accordingly to maintain communication with all involved parties.
Finally, document every step of the merge process to ensure transparency and accountability within your team.
Recording Merge Actions for Transparency
Clear documentation is key for both internal accountability and customer understanding. Many platforms automatically tag the secondary ticket with labels like "closed_by_merge" to support reporting and create an audit trail. Additionally, a link to the closed ticket is often added to the primary thread’s comments, making it easy to review any details that weren’t directly transferred.
Before finalizing the merge, check comment visibility settings. To avoid customer confusion, ensure that internal notes, like merge details, remain private by unchecking options like “Requester can see this comment.” This keeps administrative notes internal while maintaining clarity for your team.
In more complex cases involving multiple stakeholders, edit the default merge text to specify why the action was taken. This helps future agents quickly understand the situation without digging through closed tickets. Additionally, if merging threads with multiple participants, confirm that combining them complies with any privacy rules your organization follows.
After the merge, review private notes from the secondary tickets. If any of these notes are important for the customer’s understanding, change them to public. This ensures that the full history of the issue remains accessible, even after the merge, helping to streamline future resolutions.
Using AI to Detect and Merge Duplicate Tickets
Handling duplicate tickets manually is a daunting task, especially in high-volume environments. AI offers a way to process thousands of tickets in seconds, identifying duplicates even when customers use different phrasing. By augmenting manual efforts, AI transforms how teams manage ticket queues.
How AI Identifies Duplicate Tickets
Modern AI systems use semantic analysis to understand the intent and context of tickets. Instead of matching identical phrases, tools like BERT and SBERT convert tickets into dense vectors – unique mathematical representations that capture their meaning. For example, if one customer writes, "My screen is broken", and another says, "Display is cracked", the AI understands these as the same issue despite the varied wording.
To measure similarity, the system calculates cosine similarity between ticket vectors. A score close to 1 indicates nearly identical issues. Typically, tickets with scores above a threshold – often around 0.9 – are flagged for merging or agent review. For instance, in 2025, a global retail bank adopted AI for deduplication and saw 97% match precision, a significant improvement from their earlier rule-based system’s 89%. This upgrade reduced their workload by 70% and eliminated 60% of duplicate records.
The AI doesn’t stop at intent analysis; it also evaluates key entities to avoid merging tickets that sound similar but address different products or issues.
"The algorithm can handle 2,000 tickets within seconds… [achieving] a high accuracy of searching, around 90%, after fine-tuning of the model" – Arthur Shaikhatarov, Software Developer at Luxoft
AI-Powered Thread Merging
Once duplicates are identified, AI can merge them while maintaining the full context of each ticket. It designates one as the primary ticket and organizes messages from secondary tickets in chronological order. Additionally, platforms can generate abstractive summaries of the merged thread, offering a clear overview.
For cases with higher uncertainty, a human-in-the-loop approach ensures reliability. The AI proposes merges and explains its reasoning, but agents make the final call. This collaborative process not only minimizes errors but also improves the AI’s performance over time. Some systems even feature simulation modes that allow teams to test the merging logic on historical data before applying it to live tickets. This helps fine-tune similarity thresholds without affecting ongoing operations.
AI also uses time-decay parameters to focus on recent tickets, ensuring its recommendations stay relevant to current issues rather than pulling in outdated ones. By integrating these tools, businesses can streamline their support operations, combining speed and accuracy to handle complex ticketing challenges effectively.
sbb-itb-e60d259
Managing Duplicates Across Multiple Channels and Workflows
Building on earlier deduplication methods, managing duplicate tickets across various communication channels requires tailored solutions. Customer interactions via email, chat, and social media often result in overlapping or redundant tickets. Each channel generates its own record, and without proper configurations, agents may end up dealing with conflicting or repetitive responses.
Handling Duplicates from Different Channels
The key to managing duplicates across channels lies in configuring threading intervals. These intervals determine whether a customer reply reopens an existing ticket or creates a new one. For instance, you might set a 1-hour interval for live chat, where immediate responses are expected, but extend this to 24 hours for social media platforms like Facebook or Instagram, where conversations tend to unfold over longer periods.
Modern platforms leverage AI-powered merge suggestions to identify similar active tickets from the same requester, typically within a 14-day window. This process uses entity detection to spot specific details like order numbers, product names, or serial numbers within ticket text. By doing so, the system avoids mistakenly merging unrelated issues, such as a billing inquiry with a technical support request.
Another effective strategy is using webhooks to track the latest ticket activity. By storing the ID of a requester’s most recent ticket in their user profile, the system can trigger a check whenever a new ticket arrives. If the entities match, the new ticket is automatically merged into the active one, ensuring smooth ticket management.
These techniques lay the groundwork for managing more complex scenarios, such as cases where multiple tickets are intentionally required.
Configuring Systems for Intentional Multi-Ticket Cases
While automation helps streamline accidental duplicates, it’s equally important to handle situations where customers need multiple tickets open at the same time. For example, a customer might have one ticket for billing, another for technical support, and a third for a product return.
In these cases, assisted merging is a safer approach than full automation since merges cannot be undone. Systems should flag potential duplicates for agent review, ensuring the AI suggests merges only when the ticket intents align. For instance, two tickets about refunds can be merged, but a refund request and a technical support query should remain separate.
Custom field matching rules can also help maintain distinct tickets when necessary. For example, if one ticket is tagged "Hardware" and another is tagged "Software", the system will treat them as separate cases. As mentioned earlier, simulation modes can test these configurations against historical data to ensure accuracy.
When merges do occur, maintaining transparency is crucial. Automatically add private notes to the primary ticket, including a link to the closed secondary ticket, to create a clear audit trail. This ensures that all actions are documented and easy to track.
Conclusion
Streamline ticket management and maintain context by blending intelligent detection rules, AI-driven analysis, and clear workflows. While older systems depended on rigid keyword matching, modern AI taps into Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand the true intent behind customer interactions.
These advancements aren’t just theoretical – they bring tangible results. For example, in June 2025, Wolseley Canada handled 7,000–8,000 support emails per month using automated routing tailored to case types and client profiles. This helped resolve overdue requests and simplified operations.
"The ticketing system assisted us in resolving instances that were long overdue and in providing the staff with a smooth platform experience." – Eilis Byrnes, Customer Service and Process Improvement Manager at Wolseley Canada
Platforms like Supportbench, designed with AI at their core, provide tools such as 360° customer views, AI-powered summaries, and predictive scoring. These features allow agents to fully understand the context both before and after merging threads. The result? Reduced redundant ticket handling, less agent fatigue, and a consistent experience for high-value customers.
"AI routes the ticket to the best-equipped available agent or queue the first time. This minimizes internal transfers (‘ticket tennis’), reduces delays, and ensures customers connect with someone who can actually solve their problem faster." – Nooshin Alibhai, Founder and CEO of Supportbench
FAQs
How does AI help identify duplicate tickets and keep conversations organized?
AI uses natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms to spot duplicate support tickets by analyzing their content. These tools dig deeper than basic keyword matching, understanding the context, meaning, and even slight differences in phrasing to accurately detect duplicates. For example, AI can identify two tickets addressing the same issue, even if they’re worded differently.
It also leverages clustering techniques and entity detection to group related tickets and flag duplicates in real time. This not only cuts down on manual work but also ensures that no important details are overlooked when threads are merged. The result? Clearer, more organized conversations and smoother workflows that boost efficiency and improve the customer support experience.
How can I merge duplicate tickets without losing important context?
To combine duplicate tickets while preserving all essential details, start by thoroughly reviewing the tickets in question. Ensure they genuinely refer to the same issue or are closely related. This step is crucial to avoid merging unrelated threads and missing any critical information.
When proceeding with the merge, leverage tools or AI-powered features that can accurately identify duplicates. These tools help merge tickets while keeping key elements intact, such as conversation history, comments, and metadata. The goal is to consolidate tickets without losing any relevant details.
After completing the merge, take a moment to review the unified ticket. Confirm that all important information has been retained and that the context remains clear. This ensures a smooth experience for both your team and customers, preserving a complete history for any future interactions.
Why is it important to combine automation with manual oversight in ticket management?
Striking a balance between automation and manual oversight in ticket management is key to keeping things accurate and ensuring customer context isn’t lost. Leaning too heavily on automation can lead to mistakes – like merging unrelated tickets or overlooking duplicates – that can hurt both customer satisfaction and your team’s workflow.
By integrating manual reviews when needed, especially for complex situations or cases involving multiple stakeholders, you can catch those critical details that automation might miss. This approach allows you to combine the efficiency of automation with the human touch, creating a smoother and more reliable experience for your customers.
Related Blog Posts
- AI Prompts for Customer Support: 25 Copy-Paste Prompts for Faster Replies
- How do you convert solved tickets into knowledge base articles at scale?
- How do you prevent duplicate tickets and “email thread chaos” in customer support?
- How do you structure support for partners/resellers (and avoid double-ticketing)?