Want fewer customer escalations? Start with clear, actionable support policies.
Here’s the deal: poorly defined policies confuse customers and frustrate agents, leading to unnecessary escalations. But with the right framework, you can reduce escalations to a manageable 10-20% range, empower your team, and keep customers happy.
Key Takeaways:
- Set clear expectations: Define response times, resolution processes, and refund rules upfront to avoid customer confusion.
- Empower agents: Equip frontline staff with pre-approved guidelines for common issues like refunds and cancellations.
- Use escalation triggers: Automate when and how issues move up the chain (e.g., unresolved critical tickets after 30 minutes).
- Communicate regularly: Update customers on progress every 2-4 hours for urgent cases, even if there’s no resolution yet.
- Leverage AI tools: Automate ticket routing, sentiment analysis, and SLA adjustments to speed up resolutions.
Pro Tip: Regularly review escalation trends and update your policies to address recurring issues. Even small tweaks can have a big impact on efficiency and satisfaction.
Keep reading for step-by-step guidance, templates, and practical examples to build support policies that work.
Why Escalations Happen and How Policies Prevent Them
What Causes Escalations
Escalations usually stem from a few predictable scenarios. For instance, technical challenges beyond the expertise of frontline agents often prompt escalation. A Tier 1 agent handling basic account inquiries, for example, isn’t equipped to resolve a complex API integration issue, so the ticket is passed along to the engineering team.
Another common trigger is time-related delays. Tickets that remain unresolved for over two hours or are on the verge of breaching SLA commitments are automatically escalated. Severity and scope also play a major role – critical outages, security breaches, or issues impacting a large number of users demand immediate attention and escalation.
Then, there are customer-driven triggers, such as when a client explicitly asks to speak with a manager or when automated sentiment analysis flags negative language in their messages. In B2B settings, business impact often takes center stage. For example, problems affecting high-value accounts or creating revenue roadblocks, like delays in completing a sale or renewing a contract, are escalated immediately, even if the technical complexity is low.
A healthy escalation rate typically ranges between 10% and 20%. If your rate exceeds this, it could signal that frontline agents lack the training, authority, or clear guidelines needed to handle issues effectively.
These patterns highlight the importance of having strong policies in place to address potential problems before they escalate.
How Preventative Policies Reduce Escalations
Knowing the triggers behind escalations helps in designing policies that minimize them. Effective policies empower agents while setting clear expectations for customers.
When you establish and share clear SLAs, customers know what to expect. Automated escalation triggers and well-defined timelines help prevent SLA breaches and reduce the need for customers to follow up.
Policies also streamline processes for agents. With defined steps for issue routing, agents can handle tickets more efficiently. For instance, a policy requiring updates every two hours on urgent cases helps maintain trust during lengthy resolutions. Internally, "Group SLAs" ensure smooth collaboration across teams, like support and engineering, by addressing common bottlenecks during handoffs.
Managers who monitor customer behavior and sentiment for just 20 minutes twice a day can reduce escalation rates by 30-40%. Additionally, modern AI tools can instantly assess ticket urgency, sentiment, and complexity, ensuring issues are routed correctly without manual delays. By setting clear expectations and empowering agents to act decisively, well-crafted policies transform your support process from reactive issue management to proactive problem-solving.
Managing Customer Escalations Effectively
What Makes a Support Policy Effective
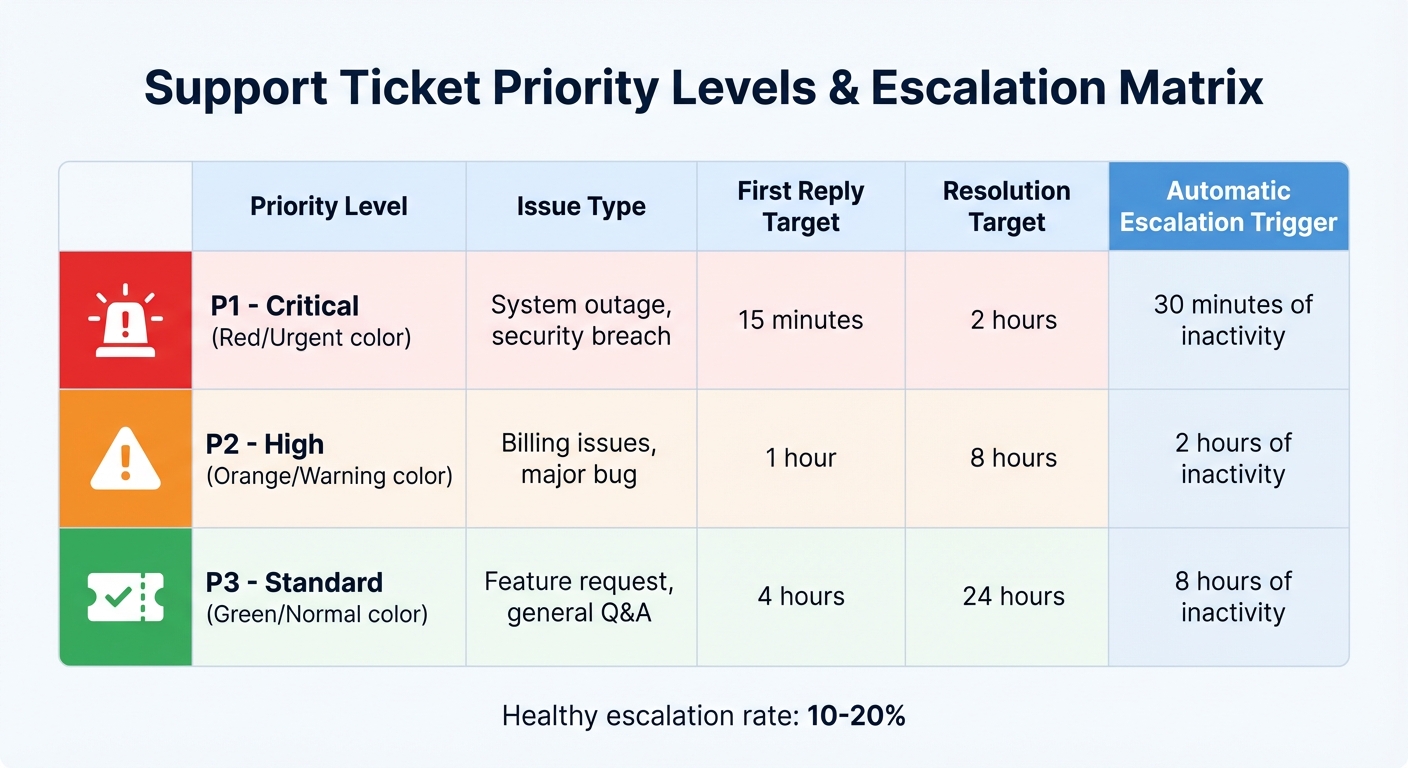
Support Ticket Priority Levels and Escalation Triggers Matrix
A well-structured support policy ensures issues are routed correctly and sets clear expectations for both customers and support agents. When done right, it reduces confusion and minimizes unnecessary escalations. Here’s how to make it work.
Issue Classification and Escalation Levels
The first step is to define priority levels based on the actual business impact of an issue – not just how urgent it feels to the customer. For instance, a P1 (Critical) issue could be a system outage affecting multiple users, while a P3 (Standard) issue might be a feature request with no immediate operational impact. Each priority should align with specific escalation tiers:
- Level 1: Frontline agents handle basic troubleshooting.
- Level 2: Specialists or supervisors step in for more complex problems.
- Level 3: Expert engineers or management address the most critical issues.
Set measurable triggers for escalation. For example, automatically escalate any unresolved P1 ticket after 30 minutes of inactivity. This ensures that issues don’t linger and helps maintain low escalation rates.
Here’s a sample table to help map priorities to escalation targets:
| Priority Level | Issue Type | First Reply Target | Resolution Target | Automatic Escalation Trigger |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 – Critical | System outage, security breach | 15 minutes | 2 hours | 30 minutes of inactivity |
| P2 – High | Billing issues, major bug | 1 hour | 8 hours | 2 hours of inactivity |
| P3 – Standard | Feature request, general Q&A | 4 hours | 24 hours | 8 hours of inactivity |
Once priorities are defined, pair them with response times and SLAs to ensure consistency.
Response Times and Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
SLAs (Service Level Agreements) are promises to your customers about response and resolution times. According to Supportbench’s CTO, dynamic SLAs can significantly enhance customer experiences. Start with realistic targets based on your team’s current performance, then tighten them as capabilities improve.
To stay ahead of deadlines, alert agents when 75% of the SLA time has passed. This proactive buffer helps prevent breaches and has been shown to reduce support costs by 25% in some companies. Also, be clear about whether SLAs operate on business hours (e.g., 9:00 AM–5:00 PM ET) or calendar hours (24/7) to avoid misunderstandings about when the clock is ticking.
Strong SLAs also set the stage for effective communication with customers.
Communication Protocols and Customer Touchpoints
Keeping customers informed is just as important as resolving their issues. For P1 issues, send updates every 2–4 hours, even if there’s no resolution yet. This approach aligns with research showing that 72% of customers prefer waiting longer for a complete solution rather than receiving a rushed, incomplete response.
Use standardized templates for common scenarios like SLA breaches, progress updates, and escalation notifications. However, train agents to personalize at least one part of the message to avoid sounding robotic. Every communication should include a specific promise, such as “next update by [time],” to reduce customer anxiety and prevent follow-up inquiries.
When tickets are handed off between teams, require agents to document summaries of interactions and troubleshooting steps already taken. This prevents customers from having to repeat their concerns, which can be a major frustration.
How to Create Customer-Facing Support Policies (Step-by-Step)
Building effective support policies isn’t about grabbing a template off the internet. It’s about understanding your team’s strengths, identifying where things go wrong, and creating policies that directly address those pain points. Here’s how to do it.
Step 1: Analyze Escalation Trends and Common Pain Points
Start by reviewing your recent support activity. Look at support tickets, incident reports, and team conversations from the past 3–6 months. The goal? Spot recurring issues. Are billing problems causing headaches? Are technical issues leading to frequent escalations? Use a priority system (such as P1 for critical issues, P2 for high-priority, and P3 for standard inquiries) to rank these problems by their impact on your business.
Next, dig into patterns of handoffs. Are tickets bouncing between agents? Ask frontline staff where information gets lost and why the first agent couldn’t resolve the issue. These "handoff vulnerabilities" can highlight gaps in your process.
It’s also important to track key metrics regularly. Keep an eye on your escalation rate, time to escalation, and repeat escalation rate to see if initial fixes are working. To catch early signs of customer friction, filter tickets for phrases like "following up", "can you clarify", or "unacceptable."
"An escalation isn’t a failure; it’s a learning opportunity. Each escalated ticket contains valuable data about a gap in your process, a training need, or a product flaw." – DocsBot AI
Use this data to create policies that address these issues head-on.
Step 2: Write Policies Using Clear and Simple Language
Once you’ve pinpointed the problems, write policies that are easy to understand. Avoid jargon and keep the language simple. Use active voice and direct phrasing. For instance, instead of saying, "Refunds will be processed within 5–7 business days", say, "You’ll receive your refund within 5–7 business days."
Organize your rules by category and tailor them to the communication channel. For example, a chat response can be casual, while emails might need a more formal tone. Avoid overly apologetic language for fixed policies; stick to neutral, factual explanations. Include examples of good and bad responses to guide agents, and set formatting standards like always including cents in currency or using "#" before order IDs.
Finally, define clear, measurable triggers for when to escalate or de-escalate issues.
Step 3: Define Escalation Triggers and De-escalation Tactics
Rely on measurable triggers instead of gut instinct when deciding to escalate. These could include time-based criteria (e.g., unresolved after two hours), impact thresholds (affecting more than 10% of users), or direct customer requests for a manager. Set up "breach-risk" triggers that automatically escalate tickets when they’re nearing 75% of the SLA target. This proactive approach helps prevent missed deadlines.
Differentiate between transferring an issue to a specialist and escalating it for higher authority. Tier 1 agents should have the tools to resolve many problems themselves – like offering refunds, discounts, or exceptions – before escalation becomes necessary.
For de-escalation, train agents to acknowledge customer frustrations before diving into solutions. During active escalations, provide updates every two to four hours, even if there’s no new information, and include a "next update by" time to reduce customer anxiety.
Step 4: Review, Test, and Improve Policies
Support policies aren’t static – they should grow with your team and business. Test new policies internally by simulating real escalation scenarios. Ask agents to flag anything confusing or unrealistic. Roll out changes gradually, perhaps starting with one product line or support channel, and gather feedback along the way.
Review high-priority cases every month to identify recurring training gaps, product flaws, or documentation issues. Track how often the same problem leads to escalations, and prioritize addressing those root causes. Update your policies based on these findings and clearly communicate any changes to both your team and your customers.
Set a formal review schedule – at least quarterly – to keep your policies aligned with your evolving needs. As your team becomes more skilled, refine escalation thresholds and adjust SLA targets. The goal is to keep improving, not to get everything perfect from the start.
sbb-itb-e60d259
Support Policy Templates You Can Customize
Building on earlier discussions about proactive support, these templates provide practical tools to help reduce escalations. You can tailor them to fit your team’s size, workload, and customer expectations.
Here are some actionable templates to streamline your support policies:
Template 1: Response Time SLA Policy
This template outlines how quickly your team should respond to and resolve issues based on their priority level. Start with a two-week baseline to set achievable goals – it’s better to have a manageable target for lower-priority issues (P3) than one that’s overly ambitious.
| Priority Level | First Response Target | Next-Response Cadence | Resolution Target | Assigned Owner |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 – Urgent | 1 Hour | Every 2 Hours | Same Business Day | On-call / Manager |
| P2 – High | 4 Hours | Twice Daily | 2 Business Days | Team Lead / Tier 2 |
| P3 – Normal | Same Business Day | Daily | 5 Business Days | Assignee / Tier 1 |
Tips for customization:
- For top-tier clients, consider tighter SLAs, like a 30-minute first response for P1 issues.
- If you support multiple products, prioritize flagship offerings with faster response times compared to older ones.
- Always include a "next update by [time]" statement in customer communications to set expectations and reduce follow-up questions.
Template 2: Escalation Matrix
This matrix explains when and how issues should be escalated between support tiers. It ensures clear boundaries and triggers for escalation based on specific timeframes or impact levels.
| Escalation Tier | Role/Responsibility | Escalation Trigger | Handoff Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 (L1) | Front-line Support | Handles initial tickets | Document troubleshooting steps taken |
| Tier 2 (L2) | Technical Specialists | Unresolved after 2 hours or requires advanced expertise | Full case history, attempted solutions |
| Tier 3 (L3) | Expert Engineers/Management | System-wide failures, impacts >10% of users, or customer requests manager | Complete timeline, business impact assessment |
Tips for customization:
- Assign specific roles (e.g., "On-Call Engineer" or "Customer Success Manager") instead of vague departments to avoid confusion.
- Automate escalation triggers in your help desk software. For instance, auto-escalate P1 issues if unresolved after 30 minutes.
- Define what "resolved" means for your team. For IT, it might mean restoring systems, while for Customer Success, it could mean resolving client concerns.
This structured approach ensures clear role assignments and escalation triggers before moving to customer relationship tactics.
Template 3: De-escalation Guidelines
De-escalation focuses on managing relationships to prevent further escalations. Use this template to guide agents in handling frustrated customers effectively.
1. Acknowledge the specific problem
Show the customer that you understand their issue. For example:
"Your account was charged twice on February 1, 2026, and the issue has remained unresolved for three days."
2. Provide a clear next step and timeline
Offer a specific action plan with a timeframe. For example:
"I’m escalating this to our billing team right now. You’ll receive a refund within 24 hours, and I’ll send you a confirmation email by 3:00 PM today."
3. Set a follow-up schedule
For escalated or high-conflict tickets, commit to regular updates – at least every 24 hours – even if the issue isn’t resolved yet. This reassures the customer that they’re not being ignored.
When to involve a manager:
Escalate to a manager when:
- A customer explicitly requests it.
- AI sentiment analysis flags "negative sentiment."
- The issue involves a high-value client.
Tips for customization:
- Train agents to use empathetic yet neutral language. For instance, instead of saying, "I’m so sorry, but our refund policy doesn’t allow that," say, "Our refund policy covers purchases made within 30 days. Since your purchase was 45 days ago, I can offer you store credit instead." This approach avoids defensiveness while still addressing the issue.
These de-escalation strategies help maintain trust and prevent minor frustrations from escalating into larger problems.
How AI Improves Support Policies
AI transforms static support policies into flexible systems that adapt to real-time needs. Instead of relying on manual reviews or reactive updates, AI tools analyze ticket patterns, customer sentiment, and agent performance on an ongoing basis. This approach shifts support strategies from being purely reactive to proactive and responsive.
Modern AI goes beyond simple automation. It anticipates potential escalations, adjusts service level agreements (SLAs), and even creates knowledge base content from solved cases. For instance, in early 2025, cybersecurity firm Cynet introduced generative AI and intelligent triage for their B2B support. The results? A 14-point increase in customer satisfaction (from 79 to 93), a 47% ticket deflection rate, and a 50% reduction in resolution times. Impressively, nearly half of Tier 1 tickets were resolved without human involvement.
Looking ahead, experts predict that by 2029, AI agents could handle up to 80% of common issues, often resolving them before customers even notice a problem. For support leaders, this means crafting policies that harness AI’s capabilities while ensuring human escalation paths remain clear for complex or emotionally charged cases.
AI for Ticket Triage and Dynamic SLAs
AI enhances ticket triage and SLA management by analyzing ticket intent, language, and sentiment. This allows cases to be routed to the right agents without the need for complex manual rules. By matching tickets with specialized agents from the start, unnecessary transfers – one of the main triggers of escalations – are minimized.
Dynamic SLAs take this a step further by adjusting response targets in real time based on ticket content, customer sentiment, and priority. For example, if a ticket involves a high-value client or sentiment analysis detects "high frustration", the system can tighten SLAs to ensure faster resolution. Platforms like Supportbench even offer AI-powered autoresponses that meet SLA metrics instantly, freeing agents to focus on more challenging issues.
To prevent sensitive or complex issues from spiraling, organizations can set automation thresholds – limiting the number of bot interactions before a human handoff is required.
AI-Generated Case Summaries and Knowledge Base Content
AI tools streamline workflows by automatically generating case summaries when tickets are opened or closed. This gives agents immediate context without wading through lengthy email threads. This is especially beneficial for B2B support, where cases often span weeks and involve multiple agents.
More importantly, AI identifies recurring issues from resolved tickets and creates knowledge base articles to support self-service. With 70% of customers expecting self-service options on company websites, maintaining a robust knowledge base is essential. Companies using AI-driven knowledge base tools have reported a 25% reduction in support costs.
To make AI-generated content effective, knowledge base articles should be concise, well-structured, and focused on answering specific questions. Including the question within the article ensures AI systems can retrieve the right information quickly, whether for customer-facing bots or internal agent tools.
Predictive Analytics for Escalation Risk Management
AI continuously monitors active tickets, assigning escalation risk scores based on factors like sentiment changes, response delays, past severity, and customer history. When a high-risk ticket is flagged, the system can trigger expert routing, schedule callbacks, or add internal notes for special handling.
Organizations leveraging AI for escalation management have seen significant results: a 32% drop in escalation rates, 28% faster Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR), and an 18% improvement in customer satisfaction for high-risk tickets. Additionally, AI reduces the time spent on manual escalation analysis from 9–13 hours to just 1–2 hours – a time savings of 86%.
By combining AI-detected intent with sentiment analysis, teams can identify tickets likely to escalate, such as those showing "Strongly Negative" sentiment in specific categories. For example, a ticket flagged as "Software Error" with five agent replies might automatically trigger internal notes or proactive interventions like goodwill credits. Tracking these interventions and linking them to outcomes allows models to be retrained regularly for better accuracy.
This predictive approach aligns with the proactive support strategies discussed earlier.
"AI predicts which support tickets are likely to escalate by learning from historical patterns, customer profiles, sentiment, and agent workload." – The Pedowitz Group
Supportbench takes this a step further by integrating predictive CSAT and CES scoring directly into the case list. This feature gives agents a glimpse into whether a customer is likely to be satisfied – even before they submit a survey. With this insight, agents can make real-time adjustments to prevent dissatisfaction and avoid unnecessary escalations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing Support Policies
When crafting support policies, it’s easy to overlook critical details that can frustrate customers and confuse your team. Let’s dive into some frequent missteps and how to avoid them.
Avoiding Vague or Overly Complex Language
Instructions like "respond quickly" or "be friendly" might sound straightforward, but they lack the precision agents need to act effectively. Without clear, measurable goals – such as "respond to emails within 1 hour" – service becomes inconsistent, leaving customers dissatisfied and prompting repeated follow-ups. On the flip side, policies filled with overly technical terms can alienate customers. If your return or refund policy is hard to understand, expect a flood of support inquiries asking the same questions.
The solution? Use simple, specific language. Instead of saying "respond quickly", set a clear standard like "respond within 4 hours." Avoid jargon and write as if you’re explaining things to a friend.
"We have members of the support team who monitor FRT every hour. This lets us keep a pulse on our workload and pivot if necessary." – Brianna Christiano, Director of Support, Gorgias
Clarity is key, but it’s equally important to set realistic expectations that your team can consistently meet.
Setting Unrealistic Expectations in SLAs
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) should reflect what your team can actually deliver. Creating SLAs without consulting your frontline agents often results in unachievable goals. Overpromising on response times not only strains your team but also erodes customer trust. For example, if your escalation rate exceeds 15%, it’s a sign that agents may lack the tools or training to resolve issues effectively.
Before making SLA commitments public, test them internally to ensure they’re realistic. Collaborate with your team to align targets with current staffing and workload. Interestingly, 72% of customers would rather wait longer for a complete solution than receive a rushed, incomplete answer. It’s better to aim for conservative benchmarks that you can exceed than to fall short of overly ambitious ones.
Neglecting Regular Policy Reviews
Even the clearest, most realistic policies can become outdated over time. Regular reviews are essential to ensure your policies keep pace with changing customer expectations and team capabilities. Without updates, inconsistencies creep in, and agents may resort to workarounds.
Set a schedule for policy reviews – monthly for communication guidelines and quarterly for broader documentation. Assign a manager to analyze performance metrics like CSAT scores and escalation rates. For example, at Gorgias, managers audit three agent tickets each week to maintain high service standards. This ongoing evaluation helps keep policies relevant and actionable, ensuring they meet both customer and team needs.
Conclusion
Effective, AI-driven support policies give your team the tools they need to handle customer issues confidently while minimizing costly escalations. By establishing clear triggers, defined response times, and proactive workflows, your agents can address problems efficiently, maintaining a manageable escalation rate and strengthening customer trust.
The impact of these policies is backed by data. Standardized help desk practices have been shown to reduce support costs by 25% and increase customer satisfaction by 60%. For instance, Cynet’s use of generative AI achieved impressive results: a 14-point increase in CSAT, 47% ticket deflection, and resolution times cut in half.
To get started, use the provided templates and adapt them to suit your team’s capabilities and your customers’ needs. Define specific triggers – like escalating unresolved tickets after two hours or using sentiment analysis to flag issues for immediate attention.
FAQs
How can AI tools help prevent customer escalations?
AI tools are transforming the way businesses handle customer support by tackling potential issues before they spiral out of control. For instance, AI-powered models can dig into historical data, analyze customer sentiment, and assess ticket details to predict which cases might escalate. Armed with this foresight, support teams can step in early – whether by prioritizing critical tickets, assigning them to the right agents, or crafting tailored solutions to resolve problems efficiently.
Beyond just prevention, AI also optimizes workflows by automating repetitive tasks like ticket classification and routing. This smart automation ensures tickets land with the most qualified agents, cutting down on delays and speeding up resolutions. On top of that, AI helps fine-tune escalation strategies by pinpointing inefficiencies and preserving context during complex cases, reducing unnecessary escalations and keeping customers happier.
Adding AI to customer support operations isn’t just about efficiency – it’s about being proactive. By addressing concerns faster and streamlining resolutions, businesses can deliver a smoother, more satisfying experience for their customers.
How can I help my support agents resolve issues without escalating them?
Giving agents the tools and confidence to handle issues independently starts with clear guidelines and structured processes. Providing a decision-making framework is key – this should outline when agents can act on their own and when certain issues, like those involving high complexity or urgency, need to be escalated. With these boundaries defined, agents can approach problems with clarity and assurance.
Investing in training programs is another essential step. These programs not only build confidence but also familiarize agents with tools like AI-powered workflows or real-time guidance systems. Such tools can streamline problem-solving, helping agents find solutions more quickly and reducing the need for escalation. A well-organized knowledge base is equally important, giving agents quick access to accurate information when they need it most.
Finally, fostering a supportive work environment is crucial. When agents feel trusted to make decisions within clear parameters, they’re more likely to resolve issues efficiently. This approach not only speeds up resolution times but also boosts customer satisfaction and cuts down on unnecessary escalations.
How often should we update our customer support policies?
Customer support policies should be revisited regularly to ensure they stay effective and adapt to evolving customer expectations, business objectives, and industry standards. As a general practice, aim to review these policies at least once a year or whenever significant changes occur – like the launch of new products, services, or updated compliance requirements.
For companies that operate in fast-paced environments, especially those leveraging AI-powered tools, it’s wise to conduct reviews more frequently – every 6 to 12 months. This approach helps keep policies relevant, integrates new technologies, and ensures a seamless, cost-effective customer experience. Adjust your review schedule based on factors like your company’s size, the complexity of your support systems, and any operational shifts to consistently deliver high-quality service.










