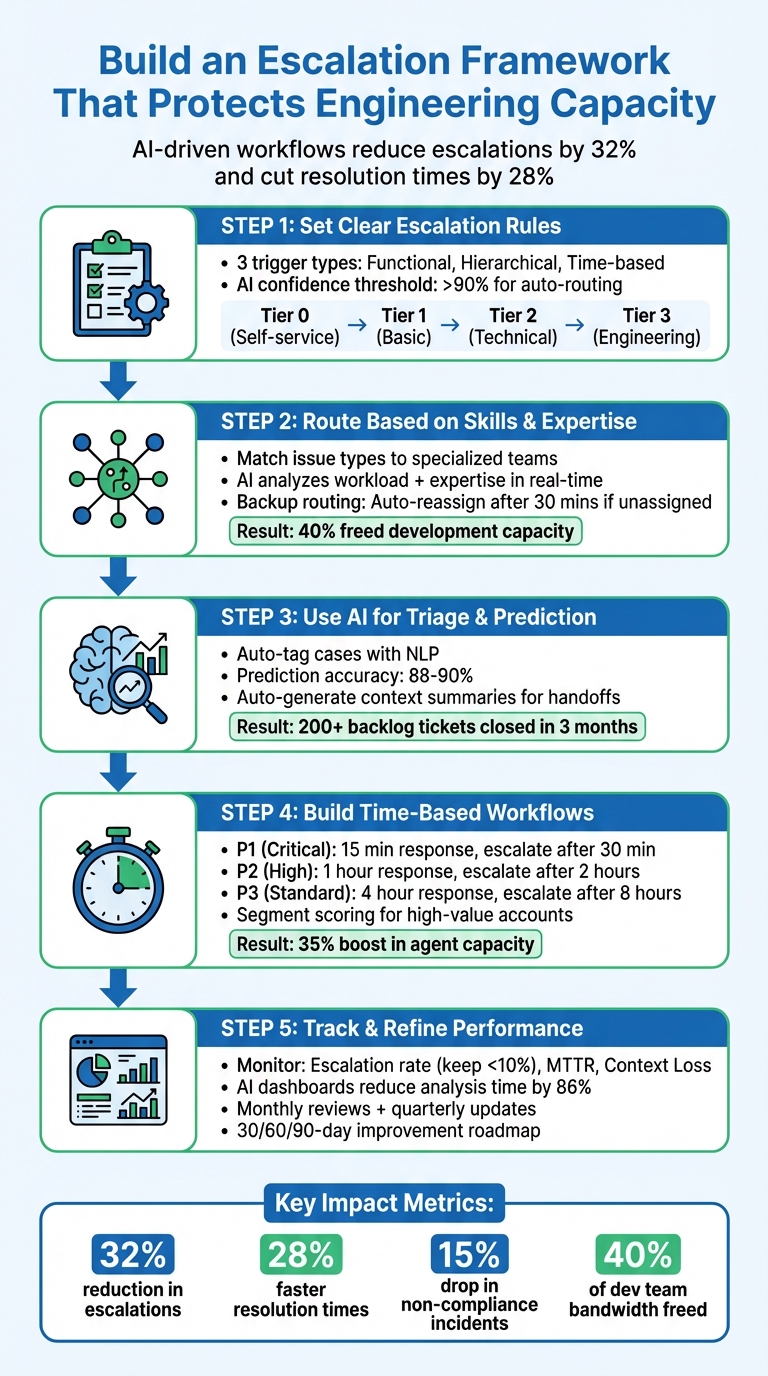
To reduce the burden on Engineering teams, you need clear escalation rules, AI-driven triage, and workflows that prioritize critical issues. Many teams waste time on poor triage, incomplete tickets, or unnecessary escalations. A well-designed framework ensures only high-impact cases reach Engineering, with all the necessary context provided upfront.
Key steps include:
- Define escalation triggers: Use functional, hierarchical, and time-based rules to decide when cases need escalation.
- Leverage AI triage: Automate ticket filtering, priority scoring, and context gathering to minimize manual effort.
- Route based on expertise: Assign cases to the most qualified teams and ensure backup routes prevent delays.
- Automate workflows: Set time-based rules and use AI predictions to prevent SLA breaches.
- Monitor and refine: Track metrics like escalation rates, MTTR, and context loss to improve processes.
With AI and structured workflows, teams can reduce escalations by 32% and cut resolution times by 28%. Focus on sending only well-documented, critical cases to Engineering, freeing them to solve the most pressing problems.
5-Step Escalation Framework to Reduce Engineering Overload
Step 1: Set Clear Escalation Rules and Triggers
Identify When Cases Should Escalate
Start by defining the exact conditions that warrant escalating cases to Engineering. Typically, escalation frameworks rely on three main triggers: functional, hierarchical, and time-based.
- Functional triggers come into play for technical issues or when product customization is needed.
- Hierarchical triggers are activated when decisions beyond standard policies are necessary, such as for high-value accounts or exceptions.
- Time-based triggers ensure unresolved tickets within SLA (Service Level Agreement) windows are escalated promptly.
It’s also critical to assess the complexity and scope of the issue. For example, widespread system glitches impacting multiple users or core business functions should escalate immediately. Additionally, sentiment and urgency are key factors. High-priority cases, such as those involving payment failures, negative customer sentiment, or specific intents like "Software error", should be routed quickly. However, Engineering should be reserved for problems that directly influence revenue or customer satisfaction – not every issue that feels urgent.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI to refine and filter these triggers.
Use AI to Filter Out Unnecessary Escalations
AI tools can help by scoring tickets based on escalation risk, analyzing factors like sentiment changes and product context. This enables intelligent triage, enriching tickets with insights about customer intent and language, which helps teams distinguish between complex cases and routine requests. For example, AI can detect "intent drift" – when a conversation shifts toward requiring technical expertise – and flag such cases for early escalation.
To ensure accuracy, set a confidence threshold of over 90% for automatically routing tickets to Engineering. For cases with lower confidence levels, route them to human supervisors for review. Additionally, establish automation thresholds for AI-driven email support. For instance, limit the number of conversational turns an AI agent can attempt before escalating to a human. This avoids unnecessary loops on complex issues and reduces the risk of false positives being sent to developers.
Create Layered Escalation Thresholds
Once you’ve defined clear triggers and implemented AI filtering, build a tiered support structure to manage case flow more effectively:
- Tier 0: Self-service options like chatbots and help centers.
- Tier 1: General inquiries and basic account setup.
- Tier 2: Technical issues such as advanced configurations.
- Tier 3: Reserved for Engineering, handling only the most complex cases, such as those requiring code fixes or in-depth product expertise.
- Tier 4 (optional): Escalations involving third-party integrations.
To maintain this structure, enforce evidence-based thresholds. For example, before escalating a case to Engineering, require fields like the number of affected accounts, segment weight (e.g., ARR), and links to evidence to be filled out. Additionally, set time-based limits for each tier – for instance, 30 minutes at Tier 1, 1 hour at Tier 2, and 3 hours before reaching Engineering.
Organizations that use AI for escalation predictions have reported a 32% reduction in overall escalation rates and 28% faster Mean Time to Resolution by adopting these layered controls.
This structured groundwork ensures smoother, AI-driven triage processes in the next steps.
Step 2: Route Cases Based on Skills and Expertise
Match Teams to Issue Types
Once escalation triggers are clearly defined, the next step is assigning cases to the right teams based on the type of issue. Start by analyzing past tickets and incident reports to identify recurring patterns and understand which teams have successfully resolved specific problems in the past. This step uncovers common issues and ensures they’re routed to the most capable teams.
For instance:
- Network connectivity issues should go to Network Operations.
- Billing disputes are best handled by Finance.
- UI bugs should be directed to Support Specialists with in-depth product knowledge.
- Critical system failures affecting multiple customers should escalate immediately to on-call Engineers.
Each department has its own focus. During outages, IT prioritizes system restoration, while Customer Success manages high-value accounts, and Sales steps in to address technical blockers that could impact revenue. Documenting these responsibilities simplifies case routing, ensuring that every issue lands in the right hands.
Use AI to Match Cases with Available Experts
AI can take routing a step further by using real-time data to match cases with available experts. This goes beyond simple category matching, as AI systems can assess workload, operating hours, and expertise before assigning cases. It also analyzes past resolution patterns to predict the best match for each issue. You can set confidence thresholds to let AI automatically route cases, while those with lower confidence levels are flagged for supervisor review.
Here’s an example: A U.S. healthcare organization used AI-driven escalation to close over 200 backlogged tickets in just three months, freeing up 40% of their development team’s capacity. AI also compiles key information – like order numbers, error logs, and screenshots – before assigning cases, so experts can dive right into problem-solving. This approach has been shown to reduce Mean Time to Resolution by 28%.
When no experts are immediately available, backup routing ensures no case gets stuck in limbo.
Add Backup Routes to Prevent Bottlenecks
Backup routing mechanisms are critical for keeping cases moving when primary experts are unavailable. If a ticket remains unassigned for too long, failover systems automatically reassign it. For example, if a Support Engineer doesn’t pick up a case within 30 minutes, the system can escalate it to a Senior Support Rep.
Round-robin distribution is a simple way to balance workloads when primary experts are busy. However, adding AI to this process makes it smarter – it can consider skill sets and current workloads to assign the best secondary agent.
| Escalation Level | Primary Contact | Backup Contact | Trigger Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Support Engineer | Senior Support Rep | Unresolved 30–60 mins |
| Level 2 | Senior Engineer | Support Team Manager | Unresolved 2–3 hours |
| Level 3 | Department Head | COO / Head of Ops | Critical/High-value account risk |
| After Hours | Live Messaging | Automated Email Ticket | Outside 9 a.m.–5 p.m. window |
Cross-channel failovers are another safeguard. For example, if messaging agents are offline, cases can automatically switch to email to avoid delays. Support managers who dedicate just 20 minutes twice a day to monitoring these triggers have reported a 30–40% reduction in escalation rates.
Handling customer escalations (as a software engineer)
Step 3: Use AI for Triage and Escalation Prediction
This step takes AI capabilities a step further, using advanced prediction models to ensure escalations happen promptly and with solid reasoning.
Automate Case Tagging and Priority Assignment
AI uses natural language processing (NLP) to automatically sort incoming tickets, creating consistent labeling across your support system. It tracks real-time sentiment and assigns risk scores, bumping up priority when it detects customer frustration or delays.
Machine learning models analyze various factors like sentiment changes, response times, and past severity patterns. For instance, if a customer’s tone shifts from neutral to frustrated over three replies, the system flags the case for immediate attention.
During the triage process, AI enriches tickets with essential details – like requester information, impacted systems, and error logs – so Tier 2 and Tier 3 teams have everything they need upfront. This minimizes the back-and-forth that often slows down resolution. By building on automated tagging, AI also identifies cases that might need early intervention.
Predict Which Cases Will Need Escalation
AI models assess multiple data points – such as sentiment trends, customer tiers, product details, agent workload, and response times – to predict which tickets are likely to escalate. These models typically reach 88% to 90% accuracy in identifying high-risk cases before escalation occurs.
A notable example is the "Triangle System", which achieved 90% prediction accuracy and cut Time to Mitigate by 38%.
"AI predicts which support tickets are likely to escalate by learning from historical patterns, customer profiles, sentiment, and agent workload." – The Pedowitz Group
For predictions with lower confidence, AI can route cases to human agents for review to ensure accuracy. You can also maintain a holdout queue – cases where AI isn’t applied – to measure how well your escalation framework is working. Once high-risk cases are flagged, AI ensures a seamless transfer of context for faster handoffs to engineering teams.
Automate Context Sharing for Handoffs
When escalation is necessary, AI generates concise summaries that include attempted fixes, unresolved issues, stakeholders, and the current system state. This spares engineers the hassle of sifting through lengthy ticket histories or scheduling briefing calls. By reducing redundant tasks, AI keeps engineering teams focused on solving critical problems. It also flags missing details – like error codes or logs – and prompts the support team or customer to provide them before escalation.
AI can go further by searching ticket histories and knowledge bases to link similar past resolutions to the new case. This prevents repetitive troubleshooting. For example, in 2025, Ascendion implemented an AI-driven escalation framework for a major U.S. healthcare client using Java Spring Boot, Kafka, and AWS. The results? Over 200 backlog tickets closed in three months, a 15% drop in non-compliance incidents, and 40% of the development team’s bandwidth freed up.
AI can also review resolved escalations and draft internal runbook entries or knowledge base articles automatically. This approach turns escalations into opportunities for continuous improvement, ultimately lightening the workload for engineering teams over time.
sbb-itb-e60d259
Step 4: Build Time-Based and Adaptive Workflows
Design workflows that respond to time constraints and adapt based on case specifics. These workflows build on earlier AI-driven triage to ensure quick responses without overwhelming the Engineering team. The goal is to meet SLA targets while keeping Engineering focused on critical tasks.
Set Time-Based Escalation Rules
Define escalation triggers based on how long a case remains unresolved. For P1 (critical) issues, aim for a first reply within 15 minutes and escalate automatically if unresolved after 30 minutes. For P2 (high-priority) cases, set a 1-hour first reply goal and escalate after 2 hours. Standard P3 tickets should have a 4-hour first response target, with escalation kicking in after 8 hours.
Use a tiered on-call schedule to streamline incident handling. For example, if the primary engineer doesn’t respond to an alert within 5 minutes, the system automatically notifies the secondary tier. This reduces coordination time, which can account for up to 25% of total Mean Time to Resolution. Automated incident assembly also cuts the time needed to find the right experts and set up communication channels – from 15 minutes to under 2 minutes.
Adjust SLAs for High-Value Accounts
To boost efficiency, use segment scoring to prioritize high-value accounts. Assign points based on factors like ARR tier, plan level, or strategic importance. This scoring system ensures cases from key accounts are prioritized appropriately in the engineering queue.
AI can also track customer sentiment and interaction patterns to predict potential escalations before SLA breaches occur. This allows for proactive intervention, especially for high-value accounts. Companies using this method report a 30–40% drop in escalation rates with just 40 minutes of daily monitoring, compared to the industry standard escalation rate of 10% to 20%.
Combine Rules and AI for Context-Aware Routing
Develop workflows that adjust dynamically based on case details, eliminating the need for manual routing. AI can monitor tickets for changes in sentiment, delayed responses, and customer history, predicting escalation risks in real time. Critical cases can be routed directly to Engineering based on intent detection and agent replies.
Incorporate flexible routing to account for agent availability. For instance, switch to email or ticket creation when engineers are unavailable. Set AI confidence thresholds to ensure only high-certainty tickets are auto-routed, while lower-confidence cases are flagged for human review. Combining rules with AI-driven insights can boost agent capacity by 35%.
Step 5: Track Performance and Refine the Framework
Once you’ve set up AI-driven escalation protocols, the work doesn’t stop there. Keeping an eye on performance and tweaking the framework as needed is crucial to ensure it runs smoothly and delivers results.
Monitor Escalation Rates and Engineering Load
Breaking down Mean Time to Resolve (MTTR) into five phases – Time-to-Detect, Time-to-Acknowledge, Time-to-Assemble, Time-to-Diagnose, and Time-to-Resolve – can help you identify where delays occur. This analysis will tell you if your framework is genuinely easing the load on Engineering or just shifting problems around.
To measure how efficiently your system handles issues, calculate the escalation rate: divide the number of escalated tickets by the total tickets, then multiply by 100. Aim to keep this rate below 10%. If it goes above 15%, it suggests challenges at the frontline level. Other key metrics include Time to Escalate, Handoff Delay, and Escalation Bounceback (the percentage of escalations returned to the frontline). A bounceback rate higher than 20% signals that escalation criteria need fine-tuning.
Another critical metric is Context Loss, which tracks how much essential information is missing during handoffs. Missing details can force engineers to redo investigations, wasting time and resources. Before making changes, establish a baseline for MTTR and escalation rates over a 30-day period to measure the return on investment accurately. Additionally, post-escalation Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) scores offer direct insight into whether the framework is improving customer outcomes.
These metrics should feed into real-time monitoring tools, enabling you to make quick, data-driven changes.
Use Dashboards for Real-Time Visibility
AI-powered dashboards can be a game-changer for tracking and managing escalations. These tools can score tickets based on factors like sentiment changes, response delays, and customer history. Dashboards can also highlight group transfers – patterns where tickets move between frontline support and specialized teams. Such transfers often indicate bottlenecks or training gaps.
Set up automated alerts to flag tickets that meet certain risk thresholds. For example, if a ticket has negative sentiment after five agent replies, an internal note can warn agents that special handling may be needed. This kind of real-time visibility allows you to address issues before they escalate, minimizing interruptions for Engineering teams.
By using AI-enhanced dashboards, you can cut down analysis time from 9–13 hours to just 1–2 hours, reducing manual effort by an impressive 86%.
Once you have these insights, use them to refine and improve your escalation processes continually.
Adjust Rules Based on Performance Data
Regular feedback loops are essential. Hold monthly meetings to review escalation data and identify recurring challenges. These sessions should focus on root-cause analysis rather than just addressing surface-level symptoms. For example, if lower-priority issues are being escalated due to unique circumstances like contractual obligations, refine your scoring criteria to account for these nuances over time.
To keep improving, retrain your AI models monthly using data from resolved cases. This will help reduce false positives and improve prediction accuracy. Maintain holdout queues – control groups that aren’t affected by new interventions – to measure the true impact of your adjustments. Additionally, review and update your service catalog metadata, runbooks, and on-call schedules every quarter to avoid escalations caused by outdated information.
Plan for ongoing improvement with a 30/60/90-day roadmap. Start with a pilot team to establish benchmarks, expand the framework to the entire organization by day 60, and use data insights by day 90 to refine advanced workflows. You might also consider giving frontline agents more authority, such as higher refund limits or advanced troubleshooting tools, to reduce the need for hierarchical escalations.
The key here is flexibility – your framework will need to evolve as your products, team, and customer expectations change. Keeping it adaptable ensures it continues to serve its purpose effectively.
Conclusion: Building an Escalation Framework That Works
Creating an escalation framework that safeguards Engineering capacity hinges on three main components: clear triggers, AI-driven automation, and flexible workflows. These elements reflect the streamlined processes and AI strategies discussed earlier. By combining functional routing (based on expertise) with hierarchical routing (based on authority), you ensure that issues are directed to the right person with the right skill set, avoiding unnecessary management involvement. The goal is simple: connect the problem to the person who can solve it, not just pass it up the chain.
AI plays a pivotal role here, predicting escalations before they become emergencies. This shift has led to a 32% reduction in overall escalations and a 28% improvement in resolution speed. Instead of reacting to problems, teams can now focus on preventing them. Features like automated context gathering, skill-based routing, and sentiment-triggered interventions ensure that Engineering only sees cases that genuinely require their attention – complete with all the information they need to resolve them efficiently. This approach sets the foundation for continuous improvement.
The framework is not static; it evolves over time. Regular monitoring through dashboards, feedback loops, and audits ensures it stays aligned with your team’s changing needs and product updates. Notably, 90% of CX leaders who have adopted AI expect it to resolve 8 out of 10 issues without human intervention in the near future.
For Support and Engineering leaders, the next steps are clear: start with a pilot team to establish benchmarks, then scale gradually across the organization, using performance data to fine-tune your workflows. Equip your frontline teams with better tools and decision-making authority, let AI handle routine problems, and reserve Engineering resources for critical issues. This approach creates a scalable support system that protects your technical team’s time and expertise.
FAQs
How can AI prevent unnecessary ticket escalations in support operations?
AI steps in to help avoid unnecessary escalations by analyzing customer interactions in real-time. It looks at factors like sentiment, tone, urgency, and past interactions to predict which tickets might escalate. This gives support teams the chance to intervene early, offering specific solutions that address issues before they grow. The result? Less pressure on higher-tier engineers and a more efficient workflow.
On top of that, AI keeps an eye on tickets as they progress, adjusting risk assessments based on new updates, changes in customer sentiment, or delayed responses. This way, only the most critical issues get escalated, while lower-risk tickets are resolved at the appropriate level. By simplifying these processes, AI not only balances workloads but also boosts customer satisfaction and helps cut down on operational costs.
What metrics should you track to ensure your escalation framework is effective?
Tracking the right metrics is crucial for maintaining an escalation framework that works efficiently and keeps customers happy. Start with the first contact resolution rate – this shows how often issues are solved without needing to escalate, which speaks volumes about the team’s effectiveness. Another key metric is the customer impact score, which measures how escalations affect the customer experience, focusing on the actual impact rather than just urgency or severity.
It’s also important to keep an eye on escalation volume and frequency to uncover recurring problems or bottlenecks. Pair that with resolution time to see how quickly escalated issues are being handled. Metrics like agent workload during escalations can reveal whether your team is stretched too thin, while customer satisfaction scores (CSAT) and Net Promoter Score (NPS) provide a direct window into how customers feel about the service they’re receiving.
Leveraging AI tools to predict and prioritize escalations can take things a step further, helping reduce delays and improve the overall quality of service.
How can time-based rules enhance escalation management and ensure SLA compliance?
Time-based rules simplify escalation management by automatically taking action when set time limits are surpassed. This ensures that pressing issues are handled without unnecessary delays, minimizing the risk of SLA violations.
By setting clear thresholds for response or resolution times, teams can deliver consistent service, focus on urgent matters, and stay accountable. These rules also help balance workloads, ensuring every issue gets the attention it needs. The result? Improved efficiency and happier customers.










