Switching away from Pylon can disrupt workflows, scatter communications, and complicate customer support. To avoid service issues like missed messages or SLA breaches, you need to rebuild structured workflows for escalations, tiered support, and SLAs. Here’s how:
- Escalations: Map out current processes, create multi-level escalation paths, and use AI-powered ticket routing for urgent issues.
- Tiers: Define clear support levels (e.g., Tier 1 for simple issues, Tier 3 for complex ones) and match expertise to issue complexity.
- SLAs: Set dynamic SLAs tailored to customer segments, issue priority, and business hours, with real-time tracking for compliance.
During migration, document workflows, test systems with historical data, and train your team on the new setup. Tools like AI can streamline tasks, improve triage, and ensure smooth operations post-migration. By focusing on these steps, you can maintain service quality and avoid disruptions.
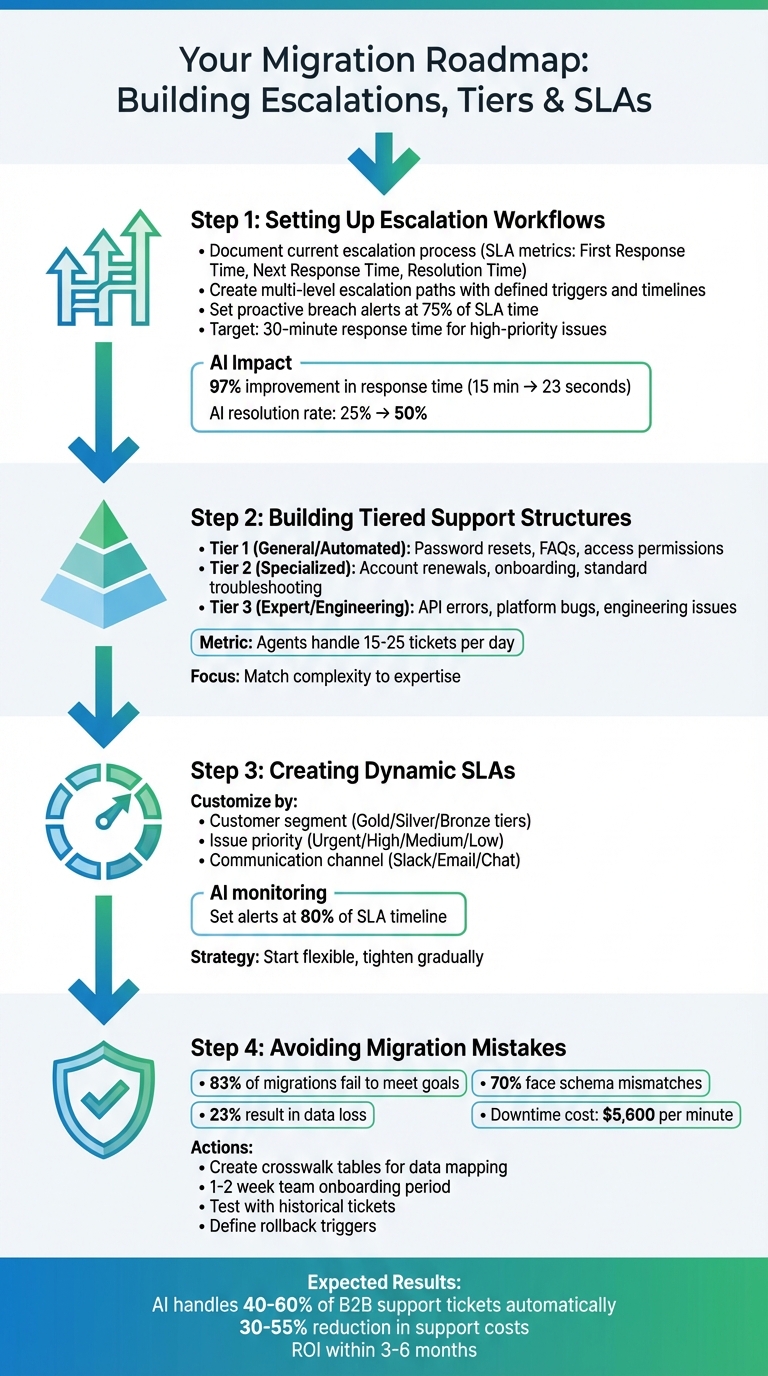
4-Step Migration Process: Escalations, Tiers, and SLAs Setup
Using SLAs and Escalation Rules to Improve Response Times | Helpdesk Software
sbb-itb-e60d259
Step 1: Setting Up Escalation Workflows
Rebuilding your escalation workflows should be your first priority after leaving Pylon. Without well-defined paths for escalation, urgent issues can get stuck in limbo, bouncing between teams while customers wait for solutions.
Document Your Current Escalation Process
Start by thoroughly documenting your existing escalation system. Record key SLA metrics like First Response Time, Next Response Time, and Resolution Time. Map out your channel architecture, including public, private, and escalation-specific channels. List all the trigger conditions that prompt escalations, such as issue priority, customer tier, or the communication channel used.
Make sure to distinguish between Issue SLAs (which cover the entire customer experience from ticket creation to resolution) and Team SLAs (the time a specific team spends on a ticket). Include details like visual indicators and support hours to ensure your new system aligns with your current performance benchmarks. Consistent naming conventions, such as using tags like #ext-company or #customer-company, can help maintain clarity and ensure the seamless mapping of support environments during the migration.
Create Multi-Level Escalation Paths
Once your current processes are documented, you can design clear, multi-level escalation paths. These should include defined triggers, timelines, and ownership responsibilities. Escalation criteria can vary based on factors like customer tier (e.g., enterprise vs. standard accounts), the severity of the issue, or the technical expertise required.
Set up proactive breach alerts to notify your team before SLA deadlines are missed. For instance, you could trigger alerts when a ticket reaches 75% of its allotted response time. High-priority issues should aim for response times of about 30 minutes. Additionally, create private escalation channels on platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams where senior staff can tackle complex problems without disrupting customer-facing communications.
To ensure nothing gets overlooked, configure your system to automatically reassign and flag tickets that meet escalation criteria. This will help maintain service quality during the transition to a new platform.
Use AI to Manage Escalations
AI tools can streamline the escalation process, cutting down on manual tasks and speeding up responses. These tools analyze ticket details, customer history, and agent expertise to route issues more effectively. AI can also detect customer frustration through sentiment analysis and trigger immediate escalations to human supervisors when necessary.
Set confidence thresholds for AI to handle straightforward cases automatically, while flagging ambiguous or complex issues for human review. When AI escalates a ticket, it should provide a smooth handoff with a summary of previous interactions so customers don’t have to repeat themselves.
"The goal of ticket automation isn’t to replace support teams, but to remove repetitive steps that are slowing teams down".
AssemblyAI offers a great example of this in action. In 2025, under the leadership of Lee Vaughn, their Support Engineering team implemented AI-powered routing and runbook automation. This reduced their first response time from 15 minutes to just 23 seconds – a 97% improvement – and increased their AI resolution rate from 25% to 50%.
"Runbooks have helped us handle weird edge cases much more intelligently. Instead of failing the conversation, the agent now guides customers to the right resources automatically".
Step 2: Building Tiered Support Structures
Once your escalation workflows are in place, the next step is creating a tiered support structure. This approach matches the complexity of issues with the right expertise, ensuring smooth operations and avoiding delays caused by unnecessary ticket handoffs.
Define Tier Criteria and Responsibilities
A well-organized tiered structure categorizes issues by priority level (urgent, high, medium, low), customer type (enterprise or standard accounts), issue type (technical bug or billing question), and the communication channel used. Each tier should have clear responsibilities based on the complexity of the problems they handle.
- Tier 1 (General/Automated): Handles high-volume, straightforward requests like password resets, access permissions, and FAQ-based questions.
- Tier 2 (Specialized): Focuses on specific needs like account renewals, onboarding, and standard technical troubleshooting.
- Tier 3 (Expert/Engineering): Deals with advanced technical issues, such as diagnosing API errors or resolving platform-level bugs that require engineering expertise.
To keep things fair and efficient, implement Team SLAs (Service Level Agreements) for each tier. These SLAs only begin counting once a ticket is assigned to the appropriate team, ensuring delays in earlier stages don’t impact downstream performance. Additionally, tailor support hours for each tier – for instance, 24/7 coverage for Tier 1 and standard business hours (9:00 AM to 5:00 PM) for Tier 3 – to ensure SLA tracking reflects actual availability.
Start by automating or tiering high-volume, low-risk issues (like integration FAQs), then gradually address more complex scenarios.
Improve Triage with AI
Once tiers are defined, enhance your triage process with AI tools. AI-powered triage can improve ticket routing by analyzing a customer’s intent (what the issue is about), language, and sentiment (positive or negative). These systems can also consider agent expertise, workload, urgency, and customer priority to assign tickets to the right tier.
To avoid errors, set confidence thresholds for AI actions. If the system isn’t certain, it can escalate the ticket to a human agent for review. This minimizes misrouting and ensures urgent issues are addressed quickly.
AI can also streamline the resolution process by requesting missing information upfront – such as purchase orders, log files, or account IDs – before the ticket reaches an agent. This reduces back-and-forth communication and ensures higher-level tiers have all the necessary details to start working on the issue.
"Intelligent triage is an AI-powered feature that automatically detects what a ticket is about (its intent), what language it’s written in, and whether the customer’s message is positive or negative (its sentiment)." – Jake Bantz, Zendesk Product Manager
When rolling out AI, begin with high-volume, low-risk tasks and gradually expand its role to handle more complex issues as confidence in the system grows. Ensure your AI models are trained using updated documentation, runbooks, and records of past resolutions for better accuracy.
Track Tier Performance After Migration
To confirm your tiered structure is working, monitor performance metrics regularly. Key metrics include:
- Team SLA duration: Tracks how long each tier spends resolving an issue, helping identify bottlenecks in more specialized tiers.
- Escalation frequency: Measures how often tickets are moved to a higher tier, which can reveal gaps in Tier 1 training or triage accuracy.
- Ticket transfers: Analyze patterns in tickets passed from frontline to specialist teams. Frequent transfers for specific issues might signal the need for updated tier definitions or additional training.
Use real-time dashboards to keep an eye on SLA adherence, response times, and customer satisfaction (CSAT) scores, broken down by tier. On average, support agents handle 15 to 25 tickets per day. AI tools can also analyze customer sentiment within each tier – negative feedback in a particular tier might indicate a mismatch between issue complexity and agent expertise.
Regular audits of ticket tags and statuses ensure your data remains accurate and reflects the actual workload.
"Team SLAs should be used when you want to measure individual team performance separately from the overall customer experience." – Pylon Documentation
With these performance metrics in place, your workflow will be ready to incorporate dynamic SLAs in the next phase.
Step 3: Creating Dynamic SLAs
With your tiered support structure ready, the next step is to design dynamic SLAs that align with your customers’ actual needs. Instead of applying a generic approach, these SLAs adjust based on factors like customer segment, issue type, and overall business impact. This ensures your team prioritizes what’s most important during and after the transition.
Customize SLAs by Customer Segment
Building on your tiered structure, tailor SLAs to meet the unique requirements of each customer group. Different segments and issues demand different response times. For example, you could establish support levels such as Gold, Silver, and Bronze tiers, assigning customers based on criteria like contract value, renewal likelihood, or business impact. Within each tier, create detailed SLA rules that account for:
- Issue priority: Urgent, high, medium, or low.
- Issue category: For instance, technical bugs versus billing inquiries.
- Communication channel: Whether it’s Slack, email, or live chat.
Start with more flexible SLA targets and tighten them gradually as the system stabilizes.
Track SLA Compliance with AI
AI tools can play a critical role in ensuring SLA compliance, especially during transitions. These tools monitor adherence in real time and can even predict potential breaches. For instance, you can set automated alerts when 80% of the SLA timeline has elapsed, giving your team a chance to step in and prevent violations.
AI can also analyze customer sentiment. If frustration or urgency is detected in a message, the system can escalate the ticket immediately. Using predictive analytics, AI forecasts customer satisfaction (CSAT) scores and identifies potential SLA breaches by analyzing both historical trends and live data. When an issue requires human intervention, AI ensures that the full conversation history and context are passed along to the agent.
Additionally, AI tools can handle repetitive tasks – like password resets or status updates – so your team can focus on more complex challenges. Sentiment-based escalation can trigger internal alerts if a customer’s tone becomes particularly negative. AI-driven reports also help identify patterns in SLA breaches, enabling root cause analysis and long-term improvements.
Set Temporary SLAs During Migration
During migrations, it’s essential to adopt a different SLA strategy. Start with broader targets and tighten them as the new system stabilizes. To avoid confusion during handoffs, monitor transfer times separately and introduce a specific ticket status for items being escalated. This helps managers distinguish between "escalated time" and "claimed time", making it easier to spot migration bottlenecks.
"You can have excellent treatment times and a terrible patient experience if the handoff to the next care unit takes hours." – Unito
Use AI-driven alerts alongside manual adjustments to manage temporary SLA targets effectively. Align these SLAs with the new system’s support hours to avoid inflated breach counts during evenings or weekends. Once the transition is complete, leverage AI-generated historical data to recalibrate SLA targets regularly, keeping pace with your business growth and evolving customer expectations.
Step 4: Avoiding Migration Mistakes
After setting up dynamic SLA management, the next challenge is ensuring a smooth migration. This step is crucial because migrations often hit roadblocks – 83% fail to meet goals, and 23% result in data loss. These risks make it essential to handle escalations, tiers, and SLAs with precision when transitioning off Pylon. Even a small misstep, like a misconfigured workflow, can erode customer trust.
Plan for Data Migration Complexity
Migrating data isn’t as simple as copying files from one system to another. It involves translating business logic – like Pylon’s 30-minute delay triggers – into a new system that might only allow hourly batch updates. This complexity is why schema mismatches impact up to 70% of migration projects, with issues arising from differences in field names, data types, or relationships between platforms.
"Data migration isn’t just about copying files – it’s about translating, cleaning, and safeguarding information from start to finish." – Danika Rockett, Sr. Manager, Technical Marketing Content, RudderStack
To manage this, create detailed crosswalk tables that map every field and its associated business rules from Pylon to the new system. Use checksums and record counts at multiple stages to ensure data integrity during the transfer. Start with less critical data to refine the process before tackling mission-critical workflows, like escalations or SLA triggers. With downtime potentially costing $5,600 per minute, it’s vital to have a rollback plan. Define clear triggers and document steps to revert changes if something goes wrong.
Technical readiness is just one part of the equation – your team must also be prepared for the transition.
Communicate Changes to Your Team
A smooth migration depends on your team’s understanding of the new system. Schedule a 1–2 week onboarding period to train them on updated workflows, new platform features, and revised escalation criteria. Use walkthroughs to demonstrate tasks like claiming unassigned tickets, updating statuses, and leveraging internal threads for collaboration.
Clarify the distinction between "Issue SLAs" (impacting the customer experience) and "Team SLAs" (measuring internal performance) to ensure agents aren’t unfairly held accountable for delays outside their control. Add visual cues – like emojis or tags for "Urgent", "In Progress", or "Resolved" – to help agents prioritize tasks quickly. Share weekly updates to highlight where automation is working well and where tweaks might be needed.
Once the team feels confident, move on to post-migration testing to ensure everything works as expected.
Test Everything After Migration
Testing is essential to confirm that the new system meets the same standards as the old one. Start by running historical tickets through the new platform to ensure automation and AI responses align with previous manual resolutions. Centralized audit logs can simplify debugging by providing a clear view of how triggers and time-delay systems operate.
"The most successful rollouts balance automation with oversight. AI handles the repetitive requests, while support teams use judgment and empathy to handle complex issues." – Pylon Team
Begin with straightforward, high-volume tasks like password resets or FAQs before testing complex escalation paths for enterprise-level issues. Verify that proactive alerts – such as notifications when 75% of SLA time has elapsed – are routed to the correct channels or supervisors. For teams using tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams, ensure messages sync seamlessly between the communication platform and the support system to maintain context during handoffs. Recreate past issues to evaluate how well new runbooks and AI agents perform before going live.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways for a Successful Transition
Leaving Pylon behind offers a chance to rethink and rebuild workflows around AI-driven principles. For instance, AssemblyAI managed to cut first response times by an impressive 97% by anchoring their AI in solid documentation and establishing clear escalation thresholds. Achieving such outcomes demands careful planning, phased rollouts, and rigorous testing of workflows before they go live.
Drawing from the workflows discussed earlier, here are some critical recommendations to ensure a seamless transition.
Final Recommendations
Start by auditing your current escalation paths, tier definitions, and SLA targets. Configure multi-level escalation rules and dynamic SLAs tailored to customer segments, issue urgency, and business hours. Train your AI system using your knowledge base, past tickets, and runbooks. This enables it to handle routine requests independently while escalating more complex or high-risk issues to human agents. Use confidence score thresholds to determine when the AI should escalate an issue to a person.
Begin automation with high-volume, low-risk tasks – like password resets or frequently asked integration questions – before tackling more complex processes. Current AI systems, when updated with accurate content, can handle 40% to 60% of B2B support tickets automatically. Assign a dedicated owner to maintain your knowledge base and ensure it aligns with your brand’s tone and standards.
Once this groundwork is laid, support teams can shift their focus to operational execution.
Next Steps for Support Teams
Analyze ticket data from the past 3 to 6 months to pinpoint the top 20 request types that account for most of your volume. These are your primary candidates for automation. Engage stakeholders from support, engineering, and customer success early in the process, ensuring everyone understands how escalations, tiers, and SLAs will be restructured. Opt for a platform that integrates Slack, email, and chat into one interface to avoid losing context during handoffs. Prioritize systems that offer Team SLAs – timers that only start when an issue is assigned to a specific team – to prevent your support team from being penalized for delays beyond their control.
As highlighted in Step 4, test the system using historical tickets. Companies that adopt AI-powered support often see returns within 3 to 6 months, alongside a 30% to 55% reduction in overall support costs. Success hinges on establishing robust escalation paths, clear tier structures, and well-defined SLAs from the very beginning.
FAQs
How can AI streamline escalations during a platform migration?
AI can make the escalation process during platform migration much smoother by using predictive analytics to spot potential problems before they grow into bigger issues. By examining data like customer sentiment, response times, and past interactions, AI helps teams tackle problems early, cutting down the chances of delays or unhappy customers.
On top of that, AI takes over critical workflows, such as automatically routing urgent cases to senior agents or notifying managers when their input is required. This keeps service levels steady while reducing the need for manual work. AI-powered dynamic SLAs (service-level agreements) also adjust in real time based on how urgent a case is, allowing teams to resolve issues more quickly and keep customers satisfied throughout the migration process.
How can I set up a tiered support structure effectively?
To build an effective tiered support system, start by defining distinct levels of support based on the complexity of issues and the expertise needed to resolve them. For example, Tier 1 might handle straightforward customer inquiries, while more advanced tiers focus on resolving technical or complex problems. Clearly outline the criteria for assigning issues to each tier to ensure consistency and avoid confusion.
Next, design workflows and routing rules to automatically direct customer requests to the right tier. This way, simple issues get resolved quickly, while more complicated cases are escalated to staff with the appropriate expertise. Including service level agreements (SLAs) for each tier can set clear expectations for response and resolution times, helping maintain a high standard of service.
Lastly, make it a priority to monitor and improve the system over time. Review data on escalations, resolution times, and customer feedback to identify areas for improvement. Adjust workflows, provide additional training, and allocate resources as needed. Using AI tools for ticket routing and prioritization can also boost efficiency and accuracy, ensuring your support system grows with your business and stays focused on customer satisfaction.
What are the benefits of using dynamic SLAs in customer support?
Dynamic SLAs bring a fresh approach to customer support by adjusting response and resolution times in real-time. These adjustments are based on factors like customer priority, the complexity of the issue, and even customer sentiment. The result? Urgent or high-value cases get the attention they need faster, minimizing the chance of SLA breaches and elevating the quality of service.
By aligning support timelines with specific case requirements, dynamic SLAs make resource management smarter, improve team productivity, and increase customer satisfaction. This approach also allows support teams to handle workflows with more agility while staying on track to meet measurable goals.
Related Blog Posts
- What’s the best helpdesk for multi-tier support?
- What’s the best way to set up tier 1 / tier 2 / tier 3 support workflows in a help desk?
- How do you build an escalation framework that doesn’t overload Engineering?
- How do you migrate away from Pylon without losing shared inbox history and customer context?