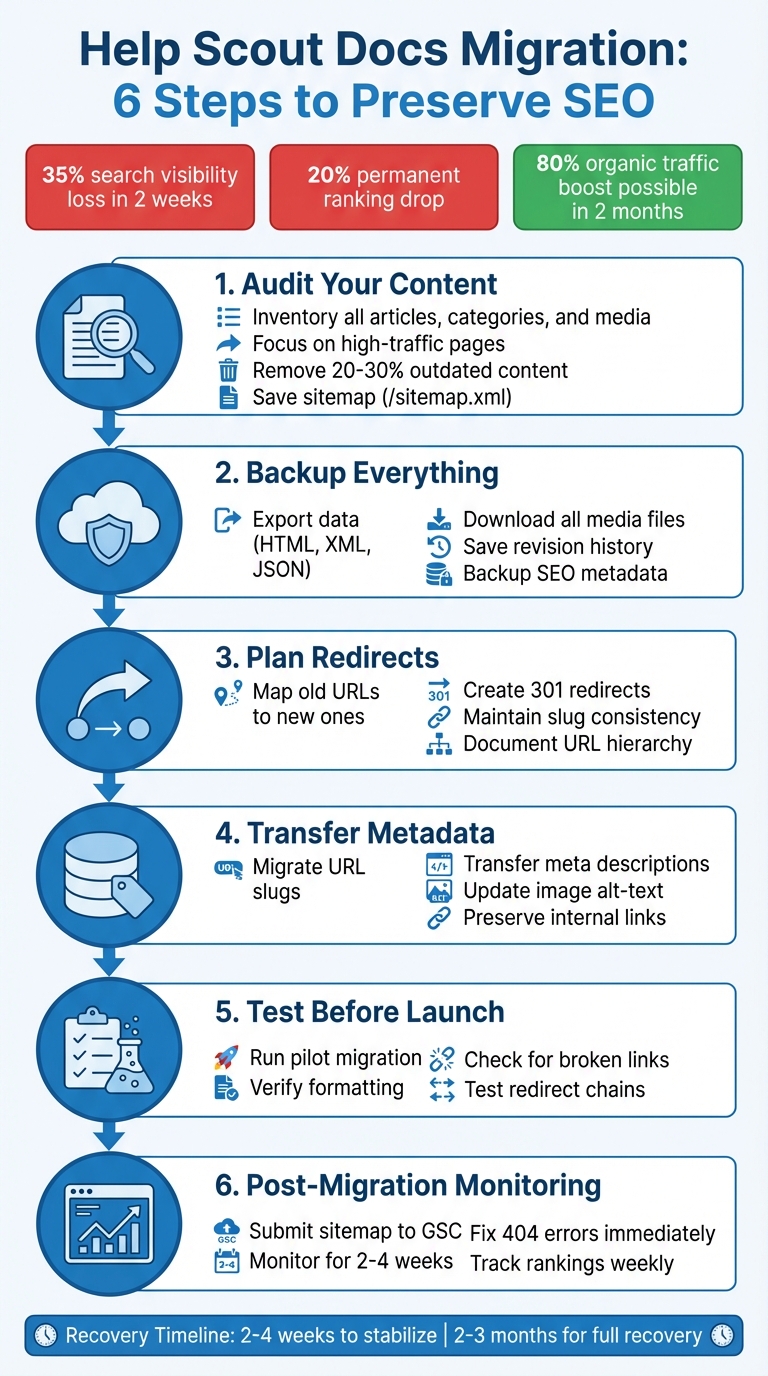
Migrating your Help Scout Docs to a new platform can be tricky, especially if you want to maintain your SEO rankings. Without proper planning, you risk losing up to 35% of search visibility in just two weeks. Worse, some businesses experience a 20% permanent drop in rankings. Here’s how to avoid these pitfalls and ensure a smooth migration:
- Audit Your Content: Take inventory of all articles, categories, and media. Focus on high-traffic pages and remove outdated or redundant content.
- Backup Everything: Export data (HTML, XML, or JSON) and save your sitemap (
/sitemap.xml) to ensure nothing is lost. - Plan Redirects: Map old URLs to new ones with 301 redirects to avoid broken links and preserve link equity.
- Transfer Metadata: Migrate SEO-critical elements like URL slugs, meta descriptions, and image alt-text.
- Test Before Launch: Run a pilot migration to identify issues like broken links or formatting errors.
- Post-Migration Monitoring: Use Google Search Console to verify redirects, fix errors, and track rankings.
Done right, a migration can even improve your SEO. Some companies see an 80% boost in organic traffic within two months. The key is thorough preparation, careful execution, and ongoing monitoring.
6-Step Help Scout Docs Migration Process to Preserve SEO Rankings
Migrating documentation: Best practices and challenges, with David Ingram from Medallia
sbb-itb-e60d259
Pre-Migration Preparation and Audit
The success of any migration hinges on the groundwork you lay beforehand. Rushing into a migration without a proper audit can lead to lost rankings, broken links, and a poor user experience. This phase is where you determine what content is worth keeping, what needs updating, and what can be left behind.
Audit Your Help Scout Docs Content
Start by taking a full inventory of your knowledge base. Catalog every article, category, collection, and media asset. Note where each item is located, who created it, and how often it’s accessed. This helps you identify high-priority pages – the ones that drive the most traffic and conversions. These pages deserve extra care during the migration to avoid formatting errors that could negatively impact user experience or rankings.
Don’t stop at just text. Document the entire data structure, including media, revision history, and SEO-critical elements. Pay close attention to things like URL slugs (the editable portion of the URL), meta descriptions, SEO titles, image alt text, and internal search keywords.
Audits often reveal that a significant portion of your content – 20% to 30%, in many cases – is either redundant or outdated. Instead of migrating everything, focus on the most valuable content. For example, moving 500 high-impact articles is far more efficient than dragging along 800 pages that include 300 irrelevant ones. Use a link status tool to classify existing links as working, redirected, or broken, so you don’t carry over unnecessary clutter.
To get a full list of indexed pages, access your Help Scout sitemap by appending /sitemap.xml to your Docs URL. Before moving forward, back up your entire knowledge base using Help Scout’s export options (HTML, XML, or JSON) or their API. This ensures your data is safeguarded in case anything goes wrong.
Finally, outline your URL structures, metadata, and backlinks to ensure a smooth redirect process.
Document URL Structures, Metadata, and Backlinks
After identifying what content to migrate, plan where it will go. Overlooking your old URL structure can result in broken links and 404 errors. As Brightspot warns:
"If you don’t pay careful attention to your redirects in your migration requirements, you run the risk of creating hundreds of 404 errors, which could lead to your site being penalized in SEO rankings".
Create a master spreadsheet to map old URLs to their new counterparts, along with categories and article IDs. In Help Scout, the slug is the only editable part of an article’s URL. For example, in /article/7-shipping-options, "shipping-options" is the slug. Documenting this hierarchy (Category > Section > Article) ensures you preserve internal link equity.
Update internal links between articles to prevent 404 errors and maintain link value. Don’t forget about external backlinks – these high-traffic entry points should be covered by 301 redirects to avoid losing valuable traffic.
For your top-performing pages, manually capture metadata if your export tool doesn’t handle it. This includes meta descriptions, SEO titles, and image alt text. The table below outlines the key elements to track:
| SEO Element | Documentation Method | Migration Action |
|---|---|---|
| URL Slug | Export via /sitemap.xml | Maintain slug or map to a new one via redirect |
| Meta Description | Manual or API export | Re-insert into the new knowledge base’s SEO fields |
| Internal Links | Crawl the site for <a> tags | Update hrefs to point to new article IDs/URLs |
| Image Alt-Text | Inspect article HTML | Ensure alt attributes are populated in the new editor |
| Keywords | Check Help Scout editor | Transfer to the new platform’s tag/keyword system |
Set Goals and Create a Migration Plan
With a complete audit and URL mapping in hand, define your migration goals. Are you aiming to improve content organization, enhance search indexing, or lower support costs by making self-service easier? Clear objectives will guide your decisions throughout the process.
Decide on your migration strategy: a “big bang” approach (moving everything at once) or a phased migration (moving content in stages). While phased migrations reduce risk, they require more coordination. Whichever method you choose, schedule the cutover during low-traffic periods to limit the impact of temporary ranking dips as search engines re-crawl your site.
Use analytics to prioritize high-traffic pages. These pages may benefit from being manually published in the new system to ensure accuracy. Before the final cutover, enact a content freeze to prevent data discrepancies between systems. Run a pilot migration in a sandbox environment to catch formatting errors, broken links, or redirect issues before scaling up. As knowledge-base.software notes:
"Skipping [planning] is a primary reason migrations fail, leading to broken links, missing content, and frustrated teams".
Your migration plan should include a timeline, resource allocation, and a rollback strategy in case of unexpected issues. The effort you invest now will save you from headaches later, ensuring a smoother transition.
Once your plan is ready, you’ll be set to move forward with confidence.
Step-by-Step Migration Process
With your audit done and your migration plan set, it’s time to dive into the actual move. Following a clear sequence will help ensure that your content, metadata, and SEO efforts transition smoothly to the new platform.
Back Up Your Help Scout Docs Data
Before starting the migration, back up your entire knowledge base. Help Scout allows you to export data in formats like HTML, XML, JSON, or PDF. For a more structured approach, use the Help Scout API to extract content programmatically – you’ll need an API key and collection ID from your profile authentication settings. Save the backup in JSON or CSV format to make future imports easier.
Don’t forget to download all media and attachments, as these files are typically hosted on Help Scout’s CDN and might not be included in the standard export. Ensure that all SEO metadata is backed up, including article slugs, SEO titles, meta descriptions, and keywords. Additionally, save your sitemap by appending /sitemap.xml to your Docs URL for complete URL mapping. If you need audit trails, manually save the revision history of key articles, as many import tools only capture the most recent version.
As knowledge-base.software highlights:
"Having a backup ensures you can recover any data if something goes wrong during migration."
With your backup secured, you’re ready to map your old URLs to the new structure.
Map and Retain URL Structures
Create a detailed mapping document – usually a spreadsheet – that pairs each old Help Scout URL with its new destination. This document will guide your redirect strategy and help prevent content loss during the migration.
Keep slug consistency wherever possible. Help Scout allows you to edit slugs (the part of the URL after the article number), and keeping them identical on your new platform can reduce SEO disruptions. URLs that align closely with search queries can even see up to a 45% boost in click-through rates.
If you need to change URLs, set up permanent (301) redirects to transfer link equity and avoid 404 errors. For large directories, patterned redirects can simplify the process of moving entire sections. When creating your new URL structure, aim for clean, user-friendly URLs:
- Use hyphens as word separators.
- Stick to lowercase letters.
- Keep URLs under 60 characters.
- Focus on slugs with 3–5 relevant keywords, avoiding dates or unnecessary stop words.
| URL Optimization Element | Best Practice | SEO Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Word Separator | Hyphens (-) | Easier to read and crawl |
| Character Case | Lowercase only | Avoids split ranking signals |
| Slug Length | 3–5 keywords | Improves ranking potential |
| Protocol | HTTPS | Builds trust and supports better rankings |
| File Extensions | Omit (.html, .php) | Keeps URLs shorter and tech-neutral |
Transfer Content and Metadata
With your URL map ready, start migrating your articles, images, and metadata to the new platform. Make sure SEO elements – like titles, meta descriptions, and image alt-text – move along with the content to maintain your search rankings. Update internal links within articles so they point directly to the new URLs, avoiding redirect chains that could slow down page speeds.
If you’re using a third-party migration service, keep in mind that costs often depend on the volume of data. For example, some services offer free migrations for up to 500,000 records, with additional records billed at $500 per 500,000.
Once your content and metadata are in place, shift your focus to testing the redirects.
Implement and Test Redirects
Set up permanent 301 redirects for every URL that has changed. Use the mapping document you created earlier to guide this process. If you’re keeping the same domain (e.g., help.yourdomain.com), ensure you have an active CNAME record to manage old links.
Before going live, test the migration with a small batch of content – such as a single category or 10 articles. This lets you confirm that redirects and formatting work as intended. Use a link status tool to check for functioning, redirected, or broken links, and ensure all media files (like images and videos) load correctly.
As Brightspot emphasizes:
"If you don’t pay careful attention to your redirects in your migration requirements, you run the risk of creating hundreds of 404 errors, which could lead to your site being penalized in SEO rankings."
Test and Verify Migration Success
After completing the migration, thoroughly test your new site before making it public. Crawl the site to catch any broken links, missing images, or formatting issues. Review high-priority pages to confirm that all metadata has transferred correctly.
Submit your new sitemap to search engines to speed up re-indexing, and monitor for crawl errors using tools like Google Search Console. Finally, test the user experience: ensure that search functionality works, categories are logically organized, and pages load quickly. Once everything checks out, you can lift the content freeze and resume regular updates.
Using AI for Content Optimization During Migration
Once you’ve worked through the manual migration steps, AI can help you take your content to the next level. Migration is more than moving data – it’s a chance to improve your content. With AI tools, you can streamline tasks like auditing, rewriting, and generating metadata, cutting what used to take weeks into just a few hours.
Audit and Rewrite Content with AI
After completing your initial content audit, AI-powered tools can help you identify redundant or outdated articles much faster. By using natural language processing models like all-MiniLM-L6-v2 paired with FAISS (Facebook AI Similarity Search), you can evaluate content similarity across your Help Scout pages with impressive accuracy. Tests show that 95% of URLs achieve a similarity score above 0.98, making this method highly reliable.
Mark Williams-Cook, Co-owner at Candour, highlights the efficiency of AI in this process:
"The primary advantage of using AI for redirect mapping is the sheer speed at which it can be done. An initial map of 10,000 URLs could be produced within a few minutes and human-reviewed within a few hours."
Focus your efforts on the lowest similarity scores, as these indicate content that has either diverged or has no clear match on the new platform. It’s common to find that 20–30% of knowledge base content is either duplicate or no longer relevant during this stage. This step helps significantly reduce unnecessary content. Tools like BrightEdge Copilot can also rewrite outdated articles to align with modern search trends, such as Google’s AI Overviews. However, always conduct a thorough human review of AI-rewritten content to ensure quality.
Generate Metadata and Keywords with AI
With your content streamlined, AI can assist in creating optimized metadata – titles, descriptions, and keywords – to boost search visibility. Adjust the AI temperature to 0.4–0.6 for a balanced output that maintains tone and accuracy. High-reasoning models like GPT-4o or Claude 3 Sonnet are ideal for minimizing factual errors during this process.
To prevent duplicate title errors in Google Search Console, include unique variables in your AI prompts, such as the primary keyword or a fragment of the article’s H1. Keep meta titles under 60 characters and use action-oriented language in descriptions, staying within the recommended pixel limits. Additionally, AI can generate keyword-rich alt-text for images, improving both accessibility and image search rankings .
Before rolling out AI-generated metadata across your site, test it on low-traffic pages to ensure proper rendering and schema validation. Publishing thousands of machine-written URLs without proper oversight can result in a 30–50% drop in organic clicks within a month. By maintaining strict quality control and using a structured AI migration framework, you can limit post-migration traffic dips to under 5%, far better than the industry average of 40% for poorly managed migrations.
Post-Migration SEO Monitoring and Maintenance
When it comes to website migration, the real test begins after the launch. The next few weeks are crucial, as it typically takes 2–4 weeks for things to stabilize and up to 2–3 months for full recovery. Without careful monitoring, you could miss critical errors that might seriously hurt your rankings.
Verify Migration in Google Search Console
Start by submitting your updated XML sitemap to Google Search Console (GSC). This helps Google quickly discover your new URLs. If you’ve changed domains, use the Change of Address tool to let Google know about the switch. This tool ensures search signals from your old domain are forwarded to the new one for 180 days. Keep your old GSC property active to monitor how redirects are being processed during this time.
Next, use the URL Inspection tool to manually request indexing for your top 5–10 most important pages – especially those driving significant revenue. This step speeds up the re-crawling of your high-impact content. During the first week, check the Pages report daily to catch any unexpected 404 errors caused by missed redirects. Don’t forget to test your robots.txt file to ensure that no accidental "noindex" or "disallow" directives from your staging environment made it live.
Here’s a quick overview of GSC tools and their post-migration uses:
| GSC Tool/Report | Post-Migration Use Case | Key Metric to Watch |
|---|---|---|
| Change of Address | Notifying Google of domain changes | Status of signal forwarding |
| Performance Report | Comparing pre- and post-migration traffic | Clicks, Impressions, Avg. Position |
| Pages (Index Coverage) | Identifying crawl and indexing issues | 404 errors, 5xx server errors |
| Sitemaps | Speeding up discovery of new URLs | "Success" status and URL count |
| URL Inspection | Testing live URLs and requesting indexing | "URL is on Google" status |
| Crawl Stats | Monitoring Googlebot activity | Total crawl requests and response codes |
Once search signals are confirmed as properly transferred, shift your focus to tracking performance metrics and resolving any issues.
Track Rankings and Fix Errors
Compare the performance metrics – clicks, impressions, CTR, and average position – from your post-migration Performance report to the benchmarks you collected before the migration. Any sudden drop in indexed pages or an increase in 404 errors could indicate migration-related issues.
To audit your redirects, use Screaming Frog in "List Mode" with "Always Follow Redirects" enabled. This ensures all redirects are single-hop (Old URL → New URL) rather than multi-step chains, which can dilute link equity.
Fix any 404 errors immediately by mapping broken URLs to relevant new pages. Update internal links to point directly to the new URLs instead of relying on redirects – this improves crawl efficiency and preserves link authority. For better context in future reviews, create an annotation in Google Analytics 4 on the migration date.
"A website’s position in search engines can precipitously drop, taking clicks and impressions with it. Entire sites can end up deindexing, and reclaiming your hard work will not be quick or easy if you’re not prepared." – Zoe Ashbridge, SEO Specialist
Once rankings are under control and errors are resolved, focus on ongoing improvements to ensure long-term SEO success.
Conduct Ongoing Optimizations
Keep your 301 redirects active for at least 180 days, though a full year is recommended to ensure search signals are fully transferred. Monitor desktop and mobile rankings separately to identify any device-specific issues. Also, check if your content appears in AI-generated summaries or "AI Overviews", as this is increasingly relevant in today’s search environment.
Use GSC’s validation flow to confirm fixes. When you click "Validate Fix", Google performs an initial check, but even one unresolved error can cause validation to fail. Validation can take up to two weeks or longer, so for faster results, submit a temporary sitemap with only the fixed URLs and filter the report to focus on that sitemap before requesting validation.
A successful migration, paired with a better site structure, can drive up to 80% growth in organic traffic within two months. On the flip side, poorly managed migrations can lead to immediate visibility losses of over 35%, with recovery taking more than six months in some cases. The key difference? Consistent monitoring and a proactive approach to fixing issues as they arise.
Common Migration Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even with careful planning, website migrations can go off track and wreak havoc on SEO. Research shows that up to 33% of migrations result in major SEO performance issues, and in the worst cases, a poorly executed migration can slash organic traffic by 50% or more overnight. The key to avoiding such disasters lies in steering clear of a few critical missteps.
One of the most damaging errors is not setting up proper 301 redirects. Without them, old URLs lose their connection to new pages, causing severe traffic and ranking drops. Another common mistake is forgetting to remove noindex tags left over from staging environments. This can make your entire site invisible to search engines after launch.
Another pitfall? Making too many changes at once. Revamping the platform, design, and content simultaneously can make it nearly impossible to pinpoint the cause of ranking declines. SEO consultant Modestos Siotos sums it up perfectly:
"The motto ‘let’s launch ASAP and fix later’ is a classic mistake. What most stakeholders are unaware of is that it can take just a few days for organic search visibility to tank, but recovery can take several months".
Automated migrations can also lead to problems like lost metadata and broken internal links. Titles, meta descriptions, and alt-text often don’t carry over, which can hurt keyword relevance and click-through rates. Broken internal links, on the other hand, create redirect chains that waste your crawl budget and frustrate users.
Addressing these pitfalls is essential to protect your SEO during a migration. Below is a quick-reference table summarizing common mistakes, their impact on SEO, and how to prevent them.
Table: Migration Mistakes, Impacts, and Prevention Strategies
| Mistake | Impact on SEO | Prevention Strategy | AI-Native Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| Missing 301 Redirects | 404 errors; loss of link equity and rankings. | Create a 1:1 URL map of all indexed pages before the migration. | Use AI to match old URLs to new ones based on semantic context. |
| Active Noindex Tags | Site becomes invisible; content de-indexed. | Add "Remove Noindex" to your launch-day checklist. | AI crawlers to flag "noindex" tags on production URLs post-launch. |
| Lost Metadata | Reduced CTR and keyword relevance. | Export and verify all meta fields (titles, descriptions) in a CSV. | AI tools to regenerate missing meta tags from original content. |
| Broken Internal Links | Wasted crawl budget; diluted authority; poor user experience. | Use migration tools to update internal links or run find-and-replace scripts. | AI link-mapping tools to auto-correct cross-references in real time. |
| Content Duplication | Diluted ranking signals; page cannibalization. | Block search engines from staging environments during testing. | AI duplicate detection to merge overlapping content during audits. |
| Broken Media/Images | Loss of image search traffic; poor accessibility. | Re-upload all attachments and verify alt-text migration. | AI vision tools to auto-generate descriptive alt-text for images. |
Conclusion
Maintaining SEO during a Help Scout Docs migration demands careful planning, accuracy, and consistent follow-up. Treating the migration as a strategic project is key. As Modestos Siotos, Technical SEO Specialist, explains:
"It is entirely possible to migrate without losing any traffic or revenue; you can even enjoy significant growth right after launching a revamped website. However, this can only be achieved if every single step has been well-planned and executed".
Start by conducting a content audit to eliminate 20–30% of outdated or unnecessary articles. Document all URLs, maintain your slug structures, and prepare a detailed redirect map before moving any pages. It’s essential to ensure that all critical SEO elements are transferred correctly.
AI tools can be invaluable during this process, helping to match old URLs, recreate missing metadata, and identify broken links in real time. For instance, in March 2023, a global luxury fashion brand successfully migrated 150,000 URLs with meticulous planning, resulting in a 63.8% increase in organic sessions and a 20% boost in keyword rankings within a month. With automation handling many of the technical details, your attention can shift to monitoring after the migration.
After launch, monitor Google Search Console daily for the first two weeks, review rankings weekly, and keep 301 redirects in place indefinitely. Keep in mind that complete SEO recovery often takes 2–3 months, even under ideal conditions. Ultimately, the difference between a seamless migration and a traffic drop lies in disciplined preparation and smart use of automation.
FAQs
How long does SEO recovery usually take after a Docs migration?
When migrating documents, the process of SEO recovery generally spans 3 to 6 months. This timeframe can vary based on factors such as the complexity of the migration and how effectively key SEO measures are implemented. Critical steps include maintaining consistent URL structures, correctly transferring metadata, and setting up proper redirects. Careful planning and steering clear of common errors are essential to preserving rankings throughout this transitional phase.
What’s the fastest way to build a complete 301 redirect map?
The fastest way to build a 301 redirect map is by leveraging automated tools that can analyze both your existing and new site structures. To ensure you cover all bases, gather data from multiple sources like domain crawls, XML sitemaps, backlinks, and Google Search Console. For larger websites, AI-driven tools can make the process easier by matching URLs automatically, cutting down on manual effort and streamlining redirect management during a site migration.
How can I verify nothing is accidentally “noindex” after launch?
When launching a site, it’s crucial to ensure that no pages are unintentionally set to “noindex.” To avoid this, conduct a thorough SEO audit that focuses on meta tags and search engine directives. Use tools like Google Search Console to identify any issues, manually inspect your HTML for noindex tags, and run a site crawl using SEO tools to catch anything you might have missed.
Additionally, double-check your sitemap and robots.txt file to ensure they’re properly configured. If you spot any incorrect settings, update them immediately to ensure your pages are indexable by search engines.
Related Blog Posts
- How do you map Kayako statuses, priorities, and custom fields to a new helpdesk?
- How do you migrate Kayako knowledge base articles to a KCS-friendly KB?
- How do you migrate away from Help Scout without losing conversations or history?
- How do you map Help Scout mailboxes, workflows, and statuses to a full helpdesk?