When choosing between a US-based and non-US-based helpdesk, evaluating "foreign access risk" is critical to safeguarding data and ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR. Foreign access risk arises when customer data is accessible by entities in other countries, potentially exposing your organization to legal, financial, and operational challenges.
Key Takeaways:
- Foreign Access Risk Defined: It involves the exposure of data to foreign entities, either remotely or onsite, creating potential compliance and security vulnerabilities.
- Non-US Helpdesks: Higher risk due to varied legal protections, foreign intelligence concerns, and stricter compliance requirements (e.g., Transfer Risk Assessments under GDPR).
- US-Based Helpdesks: Lower compliance complexity, especially if participating in frameworks like the EU–US Data Privacy Framework, and stronger protections under US commercial privacy laws.
Key Evaluation Criteria:
- Data Center Locations: Ensure data is stored and processed in low-risk jurisdictions.
- Compliance Certifications: Look for SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, and FedRAMP certifications.
- Access Controls: Verify multi-factor authentication, role-based access, and encryption standards (AES-256 for data at rest, TLS 1.2+ for data in transit).
- Subprocessor Transparency: Request a detailed list of subprocessors and their locations.
- AI Data Handling: Confirm data minimization, anonymization, and opt-out options for training AI models.
Risks of Non-US Helpdesks:
- Data may fall outside domestic legal protections.
- Foreign intelligence risks under laws like Schrems II.
- Stricter compliance requirements, such as Transfer Risk Assessments.
Benefits of US-Based Helpdesks:
- Simplified compliance under the EU–US Data Privacy Framework.
- Stronger legal remedies and operational transparency.
- Advanced security features like default-deny access policies and encryption.
Quick Comparison:
| Criteria | US-Based Helpdesk | Non-US Helpdesk |
|---|---|---|
| Compliance Complexity | Low (EU–US Privacy Framework) | High (Transfer Risk Assessments required) |
| Legal Protections | Strong under US frameworks | Limited or inconsistent |
| Data Access Risk | Governed by US laws | Potential exposure to foreign intelligence |
| Security Standards | Robust (e.g., FedRAMP, MFA, encryption) | Varies; may lack consistent safeguards |
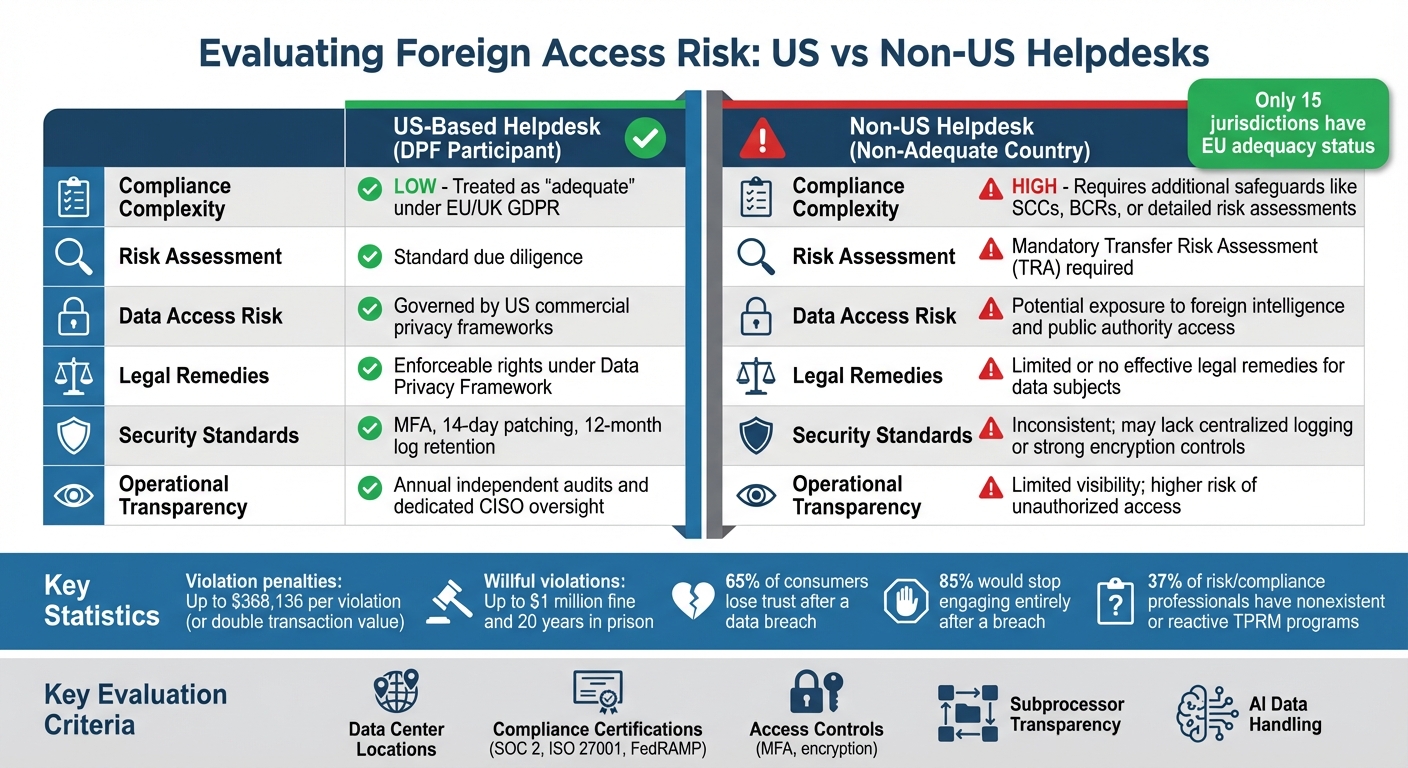
US vs Non-US Helpdesk Foreign Access Risk Comparison
Comparing Foreign Access Risks: US vs Non-US Helpdesks
Risks with Non-US Helpdesks
Using non-US helpdesks can lead to a loss of legal protection. When customer data is accessed by entities abroad, it may no longer fall under domestic data protection laws.
A case from January 2026 highlights this issue. The UK Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) found that a UK business allowing a customer service provider in India to access personal data constituted a restricted transfer. This required additional safeguards under UK data laws.
"People risk losing the protection of UK data protection law if their personal information is sent (or made accessible) outside the UK." – Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO)
Beyond compliance, non-US helpdesks can also pose foreign intelligence risks. Following the Schrems II ruling, organizations must assess whether the destination country’s laws – particularly those related to public authority access – undermine safeguards like Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs). For instance, US standards such as NIST SP 800-53 specifically identify "foreign intelligence entities" as a security threat requiring robust controls.
Additionally, Executive Order 14117 enforces strict rules on data transactions involving certain countries, including China, Russia, and Iran. Violations can bring hefty penalties: up to $368,136 per violation (or double the transaction value) and, in cases of willful violations, fines reaching $1 million and up to 20 years in prison.
These risks make US-based helpdesks a more attractive option for many organizations.
Benefits of US-Based Helpdesks
US-based helpdesks simplify compliance. Providers participating in the EU–US Data Privacy Framework ensure data transfers are treated as "adequate" under EU and UK GDPR. This eliminates the need for extra measures like SCCs or Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs). For B2B teams handling enterprise data, this can streamline contract negotiations and vendor approvals.
Another advantage is operational transparency. US-based providers comply with CCPA requirements, including "Do Not Sell My Personal Information" links and defined 45-day response timelines. They also align with Executive Order 14117 by offering enforceable rights under domestic frameworks.
"Data exporters are responsible for verifying, on a case-by-case basis, whether the law or practice of the non-EEA country impinges… on the effectiveness of the appropriate safeguards." – European Data Protection Board (EDPB)
US-based platforms further reduce risks with measures like default-deny access policies for high-risk countries, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and encryption key isolation.
US vs Non-US Helpdesk Comparison
| Feature | US-Based Helpdesk (DPF Participant) | Non-US Helpdesk (Non-Adequate Country) |
|---|---|---|
| Compliance Complexity | Low; treated as "adequate" under EU/UK GDPR | High; requires additional safeguards like SCCs, BCRs, or detailed risk assessments |
| Risk Assessment | Standard due diligence | Mandatory Transfer Risk Assessment (TRA) |
| Data Access Risk | Governed by US commercial privacy frameworks | Potential exposure to foreign intelligence and public authority access |
| Legal Remedies | Enforceable rights under the Data Privacy Framework | Limited or no effective legal remedies for data subjects |
| Security Standards | MFA, 14-day patching, and 12-month log retention | Inconsistent; may lack centralized logging or strong encryption controls |
| Operational Transparency | Annual independent audits and dedicated CISO oversight | Limited visibility; higher risk of unauthorized access |
Currently, only 15 jurisdictions – including US organizations in the Data Privacy Framework – have been granted adequacy status by the European Commission. Helpdesks outside this category require Transfer Impact Assessments (TIAs) to ensure their surveillance laws don’t compromise data protection.
Regulatory Requirements for Data Security | Exclusive Lesson
Foreign Access Risk Evaluation Checklist
Before signing a helpdesk contract, it’s essential to understand where your data is stored and who has access to it.
Data Center and Subprocessor Locations
Start by identifying where and how your data will be processed.
Request the exact street addresses of all primary and backup data centers. Avoid vague descriptions like “North America” or “multiple regions.” Specific addresses allow you to verify that the vendor isn’t operating in areas with heightened geopolitical or regulatory risks.
Ask for a detailed list of all subprocessors involved in the service, including foreign resellers, cloud infrastructure providers, and any other entities that may access your customer data. For vendors utilizing AI infrastructure, inquire whether foreign individuals might be using these systems to train AI models with potentially harmful applications. Additionally, request the IP addresses used by vendor staff for account administration to monitor for any unauthorized foreign access.
| Information Category | Specific Data to Request | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Beneficial owners with >25% control | Helps identify foreign influence or control |
| Infrastructure | Physical data center addresses | Avoids risks tied to high-risk jurisdictions |
| Access Logs | IP addresses for admin actions | Detects unauthorized access attempts |
| Subprocessors | CIP documentation for foreign resellers | Ensures compliance with security standards |
| AI Usage | Details on AI model training runs | Prevents misuse of dual-purpose technology |
Contract Terms and Data Transfer Restrictions
Carefully examine contract terms related to data transfers and usage.
Ensure contracts include clauses restricting data transfers to jurisdictions outside protected regions. Transfers should comply with adequacy regulations, safeguards like the International Data Transfer Agreement or Binding Corporate Rules, or specific exceptions.
For US-based vendors, verify their participation in the Data Privacy Framework (DPF) by checking the official program website. DPF participants are required to respond to individual complaints within 45 days, while the US Department of Commerce commits to addressing data protection authority complaints within 90 days. Contracts should also specify that third-party controllers process data only for purposes aligned with individual consent. Vendors acting as agents must notify you if they can no longer meet privacy obligations. If no adequacy regulation applies, conduct a Transfer Risk Assessment (TRA) to ensure the destination country’s data protection measures are comparable to those in the US.
Cybersecurity and Access Controls
Strong cybersecurity measures are key to safeguarding data accessibility.
Request SOC 2 Type II reports and ISO 27001 certifications to confirm the vendor undergoes regular independent security audits. Make sure these audits cover the specific systems and services that will support your helpdesk, not just general infrastructure.
Verify that the vendor enforces multi-factor authentication, unique credentials, and role-based access controls to ensure the principle of least privilege. This means limiting helpdesk technicians to only the permissions they need to perform tasks, without giving them the ability to alter security policies or access live customer data. For vendors handling sensitive data, look for FedRAMP authorization, which indicates compliance with stringent US government security standards.
Ensure data is protected with HTTPS/TLS for data in transit and AES-256 encryption for data at rest. Additional layers of security like firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and DDoS protection are critical to blocking unauthorized traffic. Statistics show that 65% of consumers lose trust in a company after a data breach, and 85% would stop engaging entirely following such an incident.
AI Data Handling and Minimization
Evaluate how AI systems manage customer data and reduce exposure risks.
Check how the vendor’s AI systems handle data minimization and anonymization. Look for tools or features that can automatically redact personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), and financial data in real-time before it’s stored or accessed by support agents. Many AI platforms now include features for real-time threat detection, automated data masking, and identifying sensitive content.
"Encryption is essential for protecting data from unauthorized access, both when it’s stored and when it’s transferred over a network." – Aatish Mandelecha, Founder of Strac
Confirm the vendor provides data residency controls, allowing you to select specific storage locations (e.g., US-only), reducing risks tied to foreign legal jurisdictions. Ask for clear documentation on how the vendor collects, stores, and protects AI training data. They should also outline whether customer data is used to train AI models and offer an opt-out option.
Violation Reporting and Monitoring
Put systems in place to detect and address violations quickly.
Ensure the vendor provides clear mechanisms for reporting suspected violations and demonstrates transparency in addressing risks. Request annual certifications of their Customer Identification Program (CIP) updates to track how they adapt to emerging foreign access threats. The CIP should include details on how they verify the identity of foreign users and beneficial owners.
Regularly review detailed logs of data access to identify unusual patterns that could indicate breaches or unauthorized foreign access. Implement continuous monitoring systems to detect and respond to suspicious activity in real-time.
Maintain thorough documentation of all contracts and data flows to map out every point where data could be accessed by foreign entities. This approach allows you to apply a three-step test: determine if GDPR applies to the processing, confirm whether a transfer to an organization outside your jurisdiction is occurring, and verify that the recipient is a separate legal entity.
sbb-itb-e60d259
Using AI to Monitor and Reduce Foreign Access Risks
Modern AI-native platforms are transforming how organizations monitor and manage helpdesk data access. These systems actively track who is accessing data, their login locations, and whether their behavior aligns with typical patterns. Operating 24/7, they eliminate the delays associated with quarterly audits, enabling threats to be identified and addressed before they escalate. This constant vigilance is at the core of AI-powered risk detection.
AI-Powered Access Monitoring and Risk Detection
AI tools are designed to analyze access logs in real time, assigning risk scores to activities like foreign IP logins or large-scale data exports. They also filter both input prompts and outputs to block malicious content. For instance, these platforms can identify "confirmed foreign IP activity" that might indicate operations in high-risk countries, triggering immediate alerts for your security team to act upon.
Failing to comply with U.S. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) or AI-related regulations can come with hefty penalties. Civil violations can lead to fines of up to $250,000 per violation or double the transaction value, while willful violations may result in criminal penalties of up to $1,000,000 or 20 years in prison. Additionally, under the Protecting Americans’ Data from Foreign Adversaries Act (PADFA), data broker violations can incur civil penalties of up to $50,120 per instance.
Automated Data Protection and Access Controls
AI-driven automation simplifies the process of protecting sensitive data, reducing the need for constant manual intervention. Automated agents can classify and prioritize support tickets based on factors like sentiment, language, and urgency. This ensures that sensitive information is routed only to authorized personnel, while real-time masking prevents unnecessary exposure.
"Forethought protects PII and sensitive data with encryption, role-based access, and enterprise-grade safeguards, ensuring security and compliance at every step." – Forethought
Advanced systems also employ tools like "Prompt Shields" to isolate and label untrusted data within prompts. These tools monitor for suspicious activity and enforce strict blocking of any attempts to extract data. Even if unauthorized users gain access, these safeguards prevent them from retrieving sensitive customer information. Such measures highlight how US-based AI-native platforms can significantly lower overall risk.
Why US-Based AI-Native Platforms Reduce Risk
US-based AI-native platforms integrate security controls into every aspect of their operations. This built-in approach reduces risk through continuous AI monitoring and quick compliance evidence collection. These platforms comply with regulations like PADFA, which prohibits the transfer of sensitive data to entities in countries like North Korea, China, Russia, and Iran. Unlike older systems that require costly add-ons to incorporate AI features, AI-native platforms embed these security measures directly into workflows like case management and knowledge creation.
Vendor Assessment Framework
Evaluating vendors effectively requires a structured approach, like using a risk scoring matrix. This ensures vendors meet both operational needs and regulatory requirements while minimizing risks tied to foreign access.
Risk Scoring Matrix
Start by prioritizing data residency. Can the vendor guarantee storage solely in the U.S., or could your data – like support tickets – end up in high-risk jurisdictions? Next, check for compliance certifications. While SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, ISO 27018, and ISO 27701 are baseline standards, FedRAMP authorization is non-negotiable if you handle highly sensitive data or work with government agencies.
Security measures like AES-256 encryption for data at rest and TLS 1.2 or higher for data in transit should also be part of the evaluation. These factors help quantify vendor risks.
| Risk Factor | High-Risk Profile | Low-Risk Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Data Location | Undisclosed or foreign jurisdictions | US or EU residency with customer choice |
| Compliance | Self-certified or no audits | SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, FedRAMP |
| AI Training | Uses customer data for global models | Ensures data is isolated or sanitized |
| Encryption | Proprietary or weak standards | AES-256 at rest; TLS 1.2+ in transit |
| Transparency | Static privacy policies | Regular updates every 12 months (CCPA) |
Once risks are scored, dive deeper with comprehensive vendor questionnaires.
Due Diligence and Vendor Questionnaires
Standardized questionnaires like the Cloud Security Alliance‘s Consensus Assessment Initiative Questionnaire (CAIQ) or the Standardized Information Gathering (SIG) questionnaire cover over 17 security domains, making vendor comparisons easier.
Adopt a tiered assessment strategy based on the sensitivity of data involved. Vendors handling high-risk data, such as customer PII or financial details, should undergo rigorous checks, including third-party audits and penetration test results. Lower-risk vendors might only require automated monitoring. Contracts should include specific security obligations, such as a 24-hour breach notification requirement and a clear "right-to-audit" clause.
"Telling your vendors they must implement ‘a reasonable amount of security measures’ is meaningless. Specific and actionable language will protect you from legal scrutiny and liability." – Melissa Stevens, Director of Digital Marketing & Demand, BitSight
Ensure vendors enforce multi-factor authentication for administrative access and maintain robust incident response plans with automated alerts. Request a detailed list of subprocessors and the exact reasons data is shared, such as for debugging, auditing, or security monitoring. If a vendor cannot provide this level of detail, they likely lack the readiness to safeguard your data.
After confirming compliance and security measures, it’s time to weigh the financial aspect.
Choosing Cost-Effective, Low-Risk Solutions
Combine cost analysis with the risk scoring framework to find solutions that align security with affordability. Legacy helpdesk vendors often charge extra for AI capabilities, compliance tools, and advanced security features. In contrast, modern AI-native platforms include these functionalities, cutting down on overall costs.
Take Supportbench, for example. Operating entirely on US-based infrastructure with SOC 2 Type II compliance, it eliminates foreign access risks without requiring costly add-ons. Features like AI-powered case management, predictive CSAT and CES scoring, automated triage, and dynamic SLAs are included in the base price, starting at $32 per agent per month. This setup reduces total ownership costs while maintaining top-tier security.
When assessing vendors, calculate the true cost, factoring in add-ons for AI, compliance, and advanced workflows. Transparent pricing helps avoid unexpected expenses as your organization scales.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
Managing foreign access risk is an ongoing process that includes identification, due diligence, contracting, monitoring, and secure termination. Helpdesk platforms are particularly vulnerable due to their elevated access to sensitive data, which makes evaluating jurisdictional risks a top priority. Always ensure that vendors and their operations are based in low-risk jurisdictions.
While certain operations can be outsourced, regulatory compliance and cybersecurity oversight remain the ultimate responsibility of senior leadership. This means your team must actively engage with vendors, ask the tough questions, and exercise independent judgment to protect your organization.
Leverage the risk scoring matrix to evaluate key factors like data residency, compliance certifications (e.g., SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, FedRAMP), encryption protocols (AES-256 for data at rest, TLS 1.2 or higher for data in transit), and AI training practices. Contracts should include tailored provisions for data residency, mandatory breach notifications, and the ability to reject specific subcontractors. When vendor relationships end, take immediate steps to revoke SSO, OAuth tokens, API integrations, and confirm data destruction.
These strategies equip your organization to implement practical safeguards and structured evaluations when selecting vendors.
Next Steps
Start by embedding Privacy by Design into your vendor selection process. Use the risk scoring matrix and standardized vendor questionnaires, such as those from the Cloud Security Alliance, to ensure a thorough and streamlined assessment.
Apply the frameworks and checklists outlined in this guide to prioritize "Must Have" over "Non-Critical" features. Regularly test secure backups, conduct frequent security audits (including penetration testing), and deploy AI-based monitoring tools to flag compliance issues in real time. Alarmingly, 37% of risk and compliance professionals report their Third-Party Risk Management programs are either nonexistent or reactive – don’t let your organization fall into this category.
Focus on selecting US-based, SOC 2 Type II compliant platforms that are AI-enabled and offer transparent pricing. With the right tools and processes, you can minimize foreign access risks while maintaining cost efficiency and operational effectiveness in your B2B support operations.
FAQs
What legal protections do US-based helpdesks provide compared to non-US helpdesks?
US-based helpdesks operate under federal privacy laws and frameworks designed to prioritize data security and accountability. They comply with regulations like the proposed American Data Privacy and Protection Act, which establishes strict rules for how data is handled and stored. Many also align with the NIST Privacy Framework, a trusted guideline for protecting sensitive information.
These measures not only ensure compliance with U.S. laws but also offer businesses a clear legal framework for managing issues like data breaches or misuse. This approach provides businesses with greater confidence and transparency when it comes to handling customer data.
How can companies protect their data from foreign access risks when choosing a helpdesk?
When selecting a helpdesk, safeguarding your company’s data from foreign access risks should be a top priority. Start by examining the legal and jurisdictional risks tied to the vendor. Laws like Section 702 of the FISA in the U.S. or similar regulations in other countries could allow foreign governments access to your data. Understanding these legal frameworks is crucial to assessing the potential for unauthorized access.
Next, perform thorough vendor risk assessments. This means digging into their security measures, data handling practices, and compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR or CCPA. These evaluations help you determine whether a vendor aligns with your company’s data protection standards.
To strengthen your defense, use contractual safeguards to set clear expectations for data protection. Additionally, consider deploying AI-driven monitoring tools. These tools can provide real-time insights, helping you identify and address risks before they escalate.
By combining legal analysis, vendor audits, and proactive monitoring, your company can reduce foreign access risks and maintain control over sensitive data.
What compliance certifications should I look for when choosing a helpdesk provider?
When choosing a helpdesk provider, it’s important to focus on certifications that highlight their commitment to data security and compliance. Two key certifications to look for are SOC 2 and ISO 27001.
- SOC 2 confirms that the provider has implemented controls to address security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. This ensures they have robust systems in place to safeguard your data.
- ISO 27001 outlines the requirements for creating and maintaining an effective information security management system, providing a structured approach to managing sensitive information.
These certifications indicate that the provider adheres to best practices for data protection and meets compliance requirements, such as GDPR or CCPA. This minimizes risks related to unauthorized access and potential regulatory violations.
Related Blog Posts
- Which helpdesk tools are built outside the United States (UK/EU/Canada/Australia)?
- What should Canadian teams check before switching to a non-US SaaS helpdesk?
- How do Canadian data residency requirements affect helpdesk selection?
- Is PIPEDA compliance enough if your helpdesk data is processed outside Canada?