If your helpdesk processes Canadian customer data overseas, PIPEDA compliance alone may not fully protect that information. While PIPEDA holds organizations accountable for safeguarding personal data, it doesn’t shield against foreign laws that could override contractual safeguards. For example, data processed in the U.S. may be subject to the USA PATRIOT Act, granting access to local authorities. This creates risks for privacy, transparency, and regulatory compliance.
Key takeaways:
- PIPEDA allows cross-border data transfers but requires organizations to ensure third-party processors provide equivalent protections.
- Foreign jurisdictions can bypass contracts, exposing data to subpoenas or surveillance.
- Helpdesk operations are particularly vulnerable due to sensitive data consolidation and subcontracting risks.
To secure offshore helpdesk data:
- Conduct risk assessments and map data flows.
- Use strong contracts with clear security protocols and audit rights.
- Implement encryption, access controls, and AI tools for real-time monitoring and compliance.
PIPEDA is a starting point, but additional safeguards and advanced tools are critical to protect data processed abroad and maintain customer trust.
Cross border & international data privacy issues
How PIPEDA Applies to Cross-Border Data Transfers
PIPEDA doesn’t prohibit cross-border data transfers. Instead, it places the responsibility squarely on your organization to safeguard customer information. Unlike the EU approach, which limits transfers to countries deemed "adequate", Canada emphasizes holding organizations accountable for their outsourcing arrangements.
PIPEDA’s Accountability Principle
According to Principle 1 in PIPEDA’s Schedule 1, your organization is responsible for personal information under its control – even when that data is sent to third parties for processing. PIPEDA considers such transfers a "use" of the data, not a disclosure.
This means you’re required to ensure that third parties provide comparable protection – essentially the same level of safeguards the data would have if it stayed in Canada. Achieving this typically involves binding agreements that specify security protocols, staff training, breach reporting procedures, and audit rights to verify compliance. For example, a case involving a major bank highlighted the importance of risk management guidelines in ensuring compliance. The next section will explore how these accountability standards apply to third-party processors.
Cross-Border Data Transfers: Permitted but With Conditions
PIPEDA allows data to be processed abroad but mandates transparency. Organizations must notify customers – preferably during data collection – that their information might be processed in another country and could be subject to access by local law enforcement or national security authorities.
However, there’s an important caveat: no contract can override the laws of a foreign country. The Office of the Privacy Commissioner clarified this point:
What the organization cannot do through contract – or indeed by any other means – is to override the laws of a foreign jurisdiction.
The 2006 SWIFT case underscored this limitation. While Canadian organizations are accountable for protecting data, they cannot use contracts to block lawful subpoenas or security demands from foreign governments. This highlights the need for additional measures, which will be covered in the next section.
Risks of Relying Only on PIPEDA for Offshore Helpdesk Operations
The Office of the Privacy Commissioner has made it clear: no contract can override the laws of another country. While PIPEDA outlines accountability standards, it doesn’t offer your company immunity from the legal realities of foreign jurisdictions.
Legal and Privacy Risks in Foreign Jurisdictions
Foreign laws can bypass contractual protections. For example, if customer data is processed in the United States, it becomes subject to laws like the USA PATRIOT Act, which grants law enforcement and national security agencies broad access to data. This means that even with robust contractual safeguards in place, foreign authorities may still gain access to sensitive information.
To make matters worse, customers often have little to no recourse when it comes to foreign data requests. PIPEDA’s framework places the burden of protecting data squarely on your organization. However, the Office of the Privacy Commissioner has limited authority to enforce compliance against foreign entities. As the Commissioner has put it, "The result may well be that some transfers are unwise because of the uncertain nature of the foreign regime". Non-compliance isn’t just risky – it can lead to fines of up to CAD $100,000 per violation.
These legal hurdles are only part of the problem. Helpdesk operations, in particular, face unique risks that complicate data security even further.
Helpdesk-Specific Vulnerabilities
Beyond the broader legal concerns, helpdesk operations come with their own set of challenges. These systems often consolidate sensitive customer data – ticket histories, AI-analyzed cases, financial disputes, customer complaints, and personal identifiers – all in one place. When this data is transferred across borders, it becomes more vulnerable to breaches during both transit and storage, heightening the risk of cyberattacks.
The situation becomes even more precarious when subcontracting enters the picture. Offshore helpdesk providers often rely on subcontractors in other countries, which can result in data being passed through jurisdictions with even weaker privacy protections. These multi-layered data flows make it harder for your organization to maintain oversight, especially in global, 24/7 support operations. This lack of control can expose your company to additional risks that are difficult to mitigate effectively.
Legal and Operational Safeguards Beyond PIPEDA
To address the risks associated with cross-border helpdesk data, organizations need to go beyond the baseline protections offered by PIPEDA. While PIPEDA provides a framework, additional legal and operational measures are necessary to ensure data security and compliance.
Provincial Laws and International Comparisons
In Canada, provincial laws add another layer of privacy requirements. For instance, Alberta, British Columbia (via PIPA), and Quebec (via Law 25) have privacy regulations that complement PIPEDA. However, when it comes to cross-border data transfers, PIPEDA remains the governing legislation. A notable example is British Columbia’s recent amendments to FOIPPA, which now mandate public bodies to perform additional assessments when sensitive personal data is stored outside of Canada.
When comparing PIPEDA to international standards, its limitations become evident. PIPEDA’s "organization-to-organization" accountability model contrasts sharply with the GDPR’s "state-to-state" approach. Under the GDPR, data transfers to other countries are generally prohibited unless those countries are deemed to have "adequate" privacy protections. The Schrems II ruling further tightened the GDPR’s standards by requiring that data transfers be suspended if foreign national security laws, such as those in the U.S., undermine the effectiveness of Standard Contractual Clauses. While PIPEDA lacks such stringent safeguards, it also doesn’t offer the same level of regulatory oversight. This is where regional legislation and robust contractual measures play a critical role in securing offshore helpdesk data.
Contractual Risk Mitigation
Contracts serve as a cornerstone of operational safeguards, translating legal requirements into enforceable standards. Although contracts cannot override foreign laws, they remain a vital tool for protecting personal information:
The primary means by which an organization may protect personal information that is sent to a third party for processing is through a contract.
These agreements should include provisions that address confidentiality, specific security protocols, and the right to audit and inspect the third party’s data handling practices.
Key contractual elements include:
- Mandatory staff training: Ensure that personnel handling data are well-trained in privacy and security protocols.
- Breach notifications: Require immediate reporting of any data breaches.
- Data-use limitations: Specify that data can only be used for its original, intended purpose.
- Access logs: Maintain detailed records of who accesses the data and when.
Additionally, third-party processors should have documented security policies in place and adhere to strict compliance measures. While these contracts cannot prevent foreign courts from issuing orders, they establish clear accountability and provide tools for monitoring compliance.
The Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI) sets a high bar for managing risks tied to foreign service providers in the financial sector. The Office of the Privacy Commissioner (OPC) encourages other industries to adopt similar diligence, especially when assessing risks linked to foreign political and economic conditions.
sbb-itb-e60d259
Practical Steps for Securing Helpdesk Data Offshore
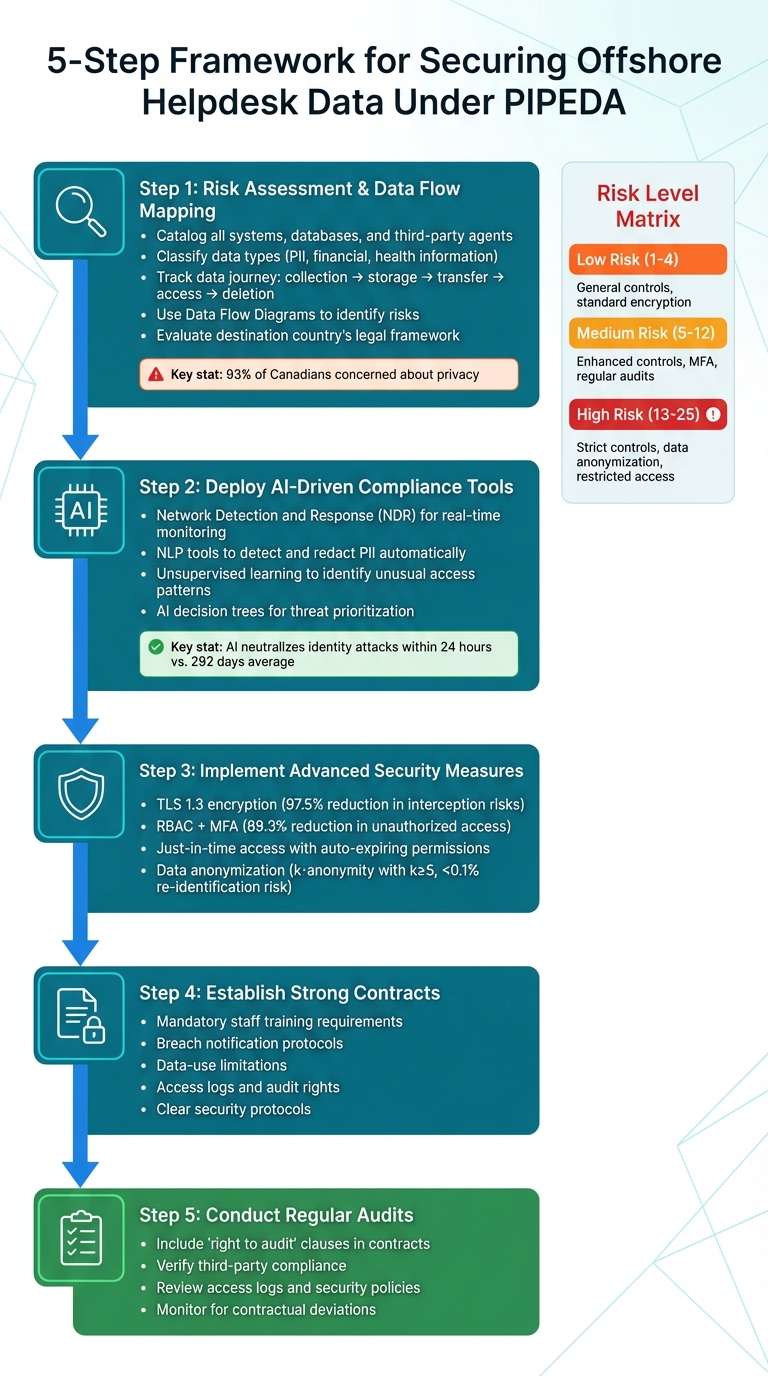
5-Step Framework for Securing Offshore Helpdesk Data Under PIPEDA
Building on legal and contractual measures, these steps ensure compliance is woven into everyday operations. Customer support leaders must take actionable measures to safeguard offshore helpdesk data.
Conduct Risk Assessments and Map Data Flows
Before transferring helpdesk data across borders, it’s crucial to understand its entire journey and the people or systems handling it. Start by cataloging all systems, databases, and third-party agents involved in managing customer data. Then, classify the data (e.g., PII, financial, or health information) to determine the appropriate protection level.
Mapping out the data flow is essential. Track every step, from data collection to storage, cross-border transfers, access points, and eventual deletion. A visual representation, like a Data Flow Diagram, can help identify potential risks or unauthorized transfers. Use a risk matrix to evaluate vulnerabilities at each transfer point by balancing the likelihood of a breach against its potential impact. Additionally, assess whether the destination country’s legal systems could force data disclosure without prior notification.
For instance, in 2024, Ping An Insurance implemented a "Compliance Efficiency Balancing Model" (CEBM) that utilized machine learning to streamline compliance processes during its global expansion. Within a year, the company reduced compliance-related delays by 40% and improved its compliance ratings by two levels. The Office of the Privacy Commissioner of Canada emphasizes the importance of Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs), stating:
PIAs are an early warning system, allowing institutions to identify and mitigate risks as early and as completely as possible.
This is particularly relevant since 93% of Canadians report concerns about their privacy.
Once you’ve mapped the data flows, the next step is to integrate technology to streamline compliance.
Deploy AI-Driven Compliance Tools
Handling large volumes of helpdesk data effectively requires AI-powered tools that offer real-time monitoring and automate risk detection. Platforms like Network Detection and Response (NDR) use AI to analyze network behavior, flag potential threats, and stop attacks across diverse systems. This reduces security blind spots and alleviates the workload for security teams.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools can automatically detect and redact PII from helpdesk tickets before they are transferred offshore. Meanwhile, unsupervised learning algorithms identify unusual patterns that could indicate unauthorized access. AI decision trees assign confidence scores to potential threats, helping prioritize responses. One of the most impressive capabilities of AI is its ability to neutralize identity attacks – one of the most dangerous threats – within 24 hours. This is a dramatic improvement compared to the average 292 days it typically takes to contain such breaches involving stolen credentials.
Kevin Kennedy, Senior Vice President of Cybersecurity at Blackstone, shared:
Through one simple integration, completed in just a single day, we were able to add over 50 new threat detections.
Modern platforms like Supportbench integrate these AI-driven compliance tools directly into helpdesk workflows. With features like automated case prioritization, issue type assignment, and case tagging, these systems ensure sensitive data is handled securely from the moment it’s captured.
Implement Advanced Security Measures
AI tools are powerful, but they should be paired with robust technical safeguards. For data in transit, use TLS 1.3 to reduce interception risks by 97.5%. For stored data, ensure offshore processors use encryption standards that meet or exceed regulatory requirements.
Access control is another critical layer of security. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) combined with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) can reduce unauthorized access by 89.3%. Just-in-time access, where permissions expire automatically after a set period, further minimizes risks.
Regular audits are essential to verify that these measures are effective. Including "right to audit" clauses in contracts allows organizations to inspect how third-party processors handle sensitive data. In non-production environments, data anonymization techniques, such as k-anonymity with a value of k≥5, can lower the risk of re-identifying individuals to less than 0.1%.
| Risk Level | Risk Value Range | Recommended Control Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Low | 1–4 | General controls and standard encryption |
| Medium | 5–12 | Enhanced controls, including MFA and regular audits |
| High | 13–25 | Strict controls, data anonymization, and restricted access |
How AI-Native Solutions Support Cost-Effective PIPEDA Compliance
AI-native platforms offer a practical way to balance cost efficiency with PIPEDA compliance. By automating labor-intensive tasks, these solutions reduce the need for expensive legal reviews and streamline compliance efforts, making it easier to manage offshore helpdesk operations without overspending.
AI for Compliance Monitoring and Risk Mitigation
AI tools simplify the complex process of tracking cross-border data flows and ensuring third-party accountability. Under PIPEDA’s Accountability Principle, organizations must guarantee a "comparable level of protection" for personal information handled by offshore processors. AI platforms step in by monitoring third-party activities, flagging any deviations from contractual safeguards, and generating audit-ready reports – no IT intervention required.
Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs), which traditionally take weeks, are expedited with AI. These tools automatically pinpoint high-risk factors like sensitive data, large-scale impacts, or the use of automated decision-making. By mapping data flows in real-time and assigning risk scores based on jurisdiction, sensitivity, and access patterns, AI makes risk evaluations faster and more precise.
AI also reinforces purpose limitation by monitoring helpdesk interactions, ensuring personal information is used only for its intended purpose. This prevents unauthorized secondary uses, a critical feature when 93% of Canadians express concerns about privacy. Automated policy enforcement not only protects customer trust but also slashes compliance costs.
| PIPEDA Principle | AI Automation Capability | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Accountability | Tracks third-party compliance automatically | Ensures offshore data protection |
| Limiting Use | Monitors for unauthorized data use | Prevents misuse in helpdesk operations |
| Safeguards | Detects unauthorized disclosures in real-time | Mitigates risks tied to foreign jurisdictions |
| Openness | Automates clear privacy notices | Meets transparency standards at data collection points |
AI-Powered Efficiency Features
Beyond compliance, AI-powered features significantly cut costs and reduce data exposure risks. For instance, AI case summarization limits sensitive data exposure by providing offshore agents with only the essential details needed to resolve tickets. This aligns with PIPEDA’s principle of limiting use and disclosure.
Platforms like Supportbench incorporate predictive CSAT and CES scoring into case management, helping teams detect potential privacy-related dissatisfaction before it escalates to formal complaints. This proactive approach not only enhances customer satisfaction but also reduces the likelihood of regulatory scrutiny.
Another cost-saving feature is AI-driven knowledge base creation, which turns resolved tickets into self-service content without manual input. This deflects future inquiries while ensuring knowledge articles adhere to PIPEDA’s data minimization principles. Additionally, automated case prioritization, tagging, and issue type assignment eliminate administrative burdens. These tools also reduce costs associated with privacy training, manual audits, and external consultants.
AI-native platforms offer real-time guidance to helpdesk agents, ensuring they communicate data collection purposes "accurately, clearly, and consistently". This eliminates the need for extensive legal drafting during customer interactions, further streamlining operations.
Conclusion: Going Beyond PIPEDA for Cross-Border Data Security
PIPEDA provides a starting point, but it doesn’t fully address the complexities of cross-border data security. The law’s Accountability Principle ensures Canadian organizations remain responsible for personal information sent overseas, but it doesn’t shield that data from foreign legal systems. Even with strong contracts in place, foreign laws can override them, leaving offshore helpdesk data exposed to subpoenas, surveillance, or government access. This gap highlights the need for more robust safeguards.
To truly protect offshore helpdesk data, organizations need to go beyond contracts. This means implementing a mix of strategies, including risk assessments, technical controls like encryption, and real-time monitoring. Privacy Impact Assessments are a critical tool to pinpoint vulnerabilities before they escalate, while data minimization ensures that only essential information crosses borders. These aren’t just regulatory requirements – they’re key to maintaining customer trust.
AI-powered tools can also play a crucial role in strengthening these defenses. Platforms built with AI can automate risk detection, enforce strict data usage policies, and reduce the need for external support. Tools such as AI-based case summarization limit sensitive data exposure, while predictive CSAT scoring identifies potential privacy concerns early, helping to prevent customer dissatisfaction from turning into formal complaints.
In short, complying with PIPEDA is just the first step. A layered approach that blends legal diligence with advanced AI tools ensures stronger, continuous protection. Since foreign laws can override contractual safeguards, it’s wise to assume that contracts alone won’t suffice. Building comprehensive defenses is the best way to protect customer data, reduce compliance costs, and minimize regulatory risks.
FAQs
Is PIPEDA compliance enough when helpdesk data is processed outside of Canada?
Relying solely on PIPEDA compliance might not cut it when handling helpdesk data outside of Canada. Different countries come with their own data protection laws and risks, which means organizations need to go the extra mile to ensure security and legal compliance.
Start by conducting a legal and risk assessment of the privacy regulations in the destination country. This helps uncover potential vulnerabilities and ensures you’re aware of the local requirements. Follow this up with strong contractual protections, such as data processing agreements. These agreements clearly outline security responsibilities and establish protocols in case of a data breach. Privacy impact assessments (PIAs) are another useful tool to pinpoint and address risks tied to transferring data across borders.
On top of that, prioritize technical safeguards. Encryption, access controls, and continuous monitoring are key to securing data during both transfer and storage. Combining these strategies with PIPEDA compliance creates a layered defense, ensuring sensitive customer information remains protected during international operations.
Is PIPEDA compliance enough if your helpdesk data is stored or processed outside of Canada?
Following PIPEDA guidelines might not fully protect your helpdesk data if it’s processed outside of Canada. That’s because other countries have their own laws governing data protection, access, and disclosure, which may not align with Canadian regulations.
For instance, in some regions, government agencies can access personal data without the safeguards required by Canadian law. This creates a potential vulnerability – even if your organization adheres to PIPEDA, your data could still be at risk under foreign legal frameworks. To address this, you should consider implementing extra layers of protection like encryption, robust contractual agreements, and transparent communication with users about where and how their data is being handled.
The key takeaway? Conduct a detailed risk assessment for cross-border data transfers. This helps ensure you’re not only meeting compliance standards but also protecting sensitive information from potential exposure.
Is PIPEDA compliance enough if your helpdesk data is handled outside Canada?
PIPEDA compliance is a crucial step in safeguarding customer data. However, if your helpdesk data is processed outside of Canada, you could face additional challenges. Different countries operate under distinct privacy laws, which can create extra risks and legal responsibilities when handling data across borders.
To boost security and stay compliant, consider implementing extra precautions like data encryption, strict access controls, and continuous monitoring. AI-powered tools can also play a key role by automating compliance checks, identifying potential threats, and ensuring data is anonymized or pseudonymized before international transfers. These steps not only fortify your data security but also help you adhere to privacy laws in multiple regions.