Separating internal engineering tickets from customer support tickets during a platform migration is essential to avoid delays, confusion, and operational inefficiencies. Misrouting can lead to issues like engineers handling routine tasks or critical customer problems being overlooked. Here’s how to do it effectively:
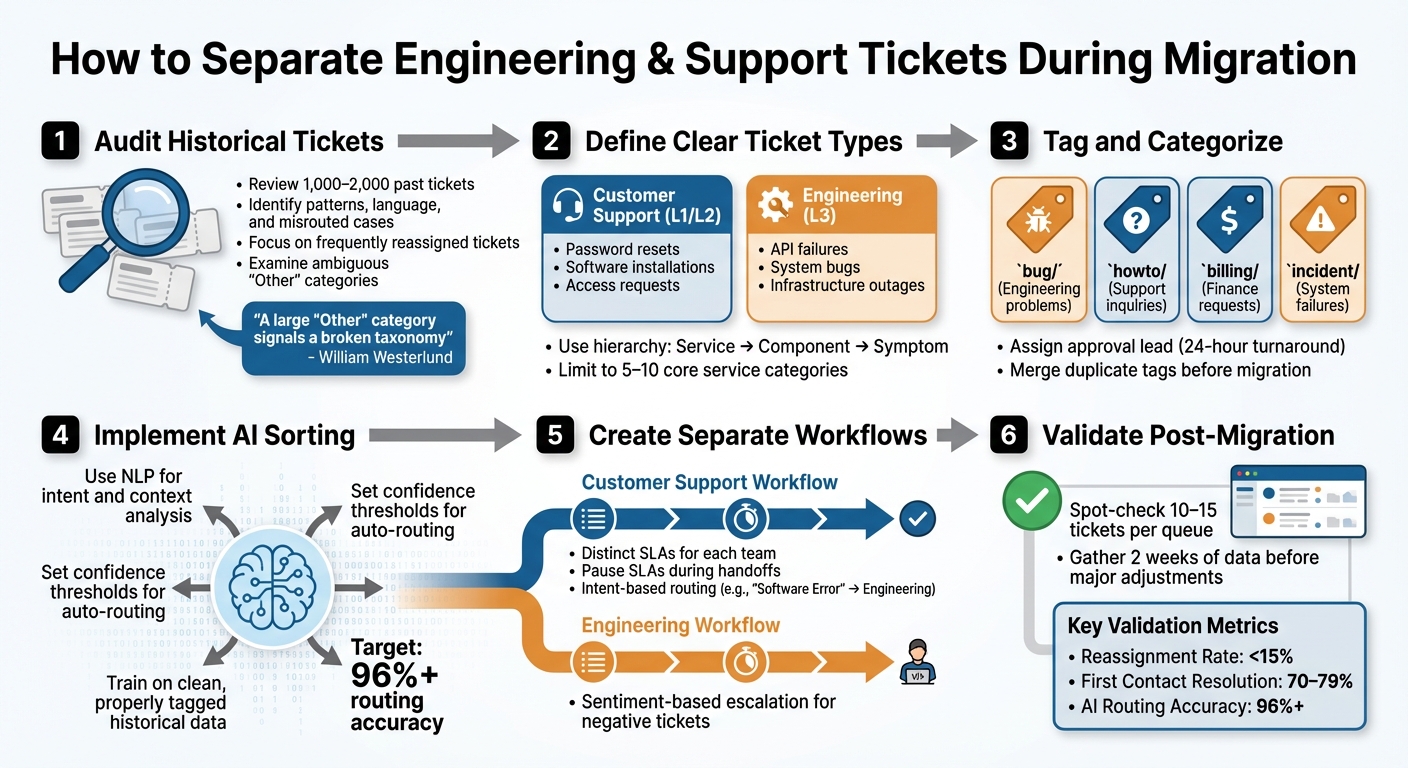
- Audit Historical Tickets: Review 1,000–2,000 past tickets to identify patterns, language, and misrouted cases. Focus on frequently reassigned tickets and ambiguous categories like "Other."
- Define Clear Ticket Types: Distinguish between customer support (routine tasks like password resets) and engineering tickets (complex issues like API failures or bugs). Use a simple hierarchy: Service, Component, and Symptom.
- Tag and Categorize: Apply prefix tags (e.g.,
bug/,incident/) to organize tickets. Avoid redundant or overly broad tags. - Use AI for Sorting: Implement AI tools with Natural Language Processing (NLP) to auto-tag tickets based on intent and context, reducing reliance on rigid keyword rules.
- Set Up Separate Workflows: Create distinct workflows for engineering and support teams, pausing SLAs during handoffs and ensuring smooth transitions.
- Validate Post-Migration: Spot-check ticket categorization, monitor metrics like reassignment rates (<15%), and refine workflows based on real-time data.
Key Metrics to Monitor:
- Reassignment Rate: <15%
- First Contact Resolution (FCR) for Tier 1 tickets: 70–79%
- AI Routing Accuracy: 96%+
6-Step Process for Separating Engineering and Support Tickets During Migration
Pre-Migration Planning: Audit and Categorize Your Tickets
Before diving into migration, it’s essential to audit your tickets. This step helps uncover flow patterns and identify gaps in your ticket taxonomy. Skipping this process often leads to misrouted tickets in the new system. Many organizations find that a significant number of their tickets sit in ambiguous "Other" categories – a clear sign of a flawed taxonomy that can wreak havoc on routing in the new environment.
An audit not only highlights ticket flow patterns but also reveals categorization issues. From there, you can define ticket types more precisely, ensuring accurate categorization and smoother workflows.
Define Internal Engineering vs. Customer Support Tickets
Understanding the distinction between customer support and internal engineering tickets is key to building a solid taxonomy.
- Customer Support Tickets (L1/L2): These handle routine service requests like password resets, software installations, hardware troubleshooting, and access requests. They’re typically resolved using standard operating procedures or knowledge base articles.
- Internal Engineering Tickets (L3): These involve complex technical issues requiring code-level access or deep system expertise. Examples include system-wide bugs, API failures, infrastructure outages, and feature enhancements. What sets these apart isn’t just their complexity – it’s the need for debugging, code changes, or architectural adjustments.
To keep things manageable, use a simple hierarchy: Service, Component, and Symptom. Limit your core service categories to 5–10, and avoid going beyond three levels of depth. Overly complex taxonomies can confuse agents, making ticket classification more difficult. Also, clearly distinguish between "incidents" (something is broken) and "service requests" (something is needed). Typically, engineering handles complex incidents, while support takes care of service requests and simpler incidents.
Once these definitions are established, go back and tag historical tickets to standardize classifications.
Audit Existing Tickets and Apply Tags
Start by reviewing 1,000–2,000 historical tickets to identify patterns in language, intent, and escalation paths. Pay close attention to tickets that were bounced between teams. Frequent "Group Transfers" often indicate engineering issues that were miscategorized initially.
Introduce prefix tags to organize tickets effectively and assign a lead to approve taxonomy updates within 24 hours. For example, use tags like bug/ for engineering problems, howto/ for support inquiries, billing/ for finance-related requests, and incident/ for system failures. This approach keeps your tags organized and prevents "tag sprawl", where redundant labels like issue, problem, and trouble clutter the system.
"A large Other category signals a broken taxonomy." – William Westerlund, Suptask
Export tag usage reports and merge similar or duplicate tags before migration. If you plan to use AI for ticket routing, remember: clean data is critical. AI models depend on historical data to learn, and properly tagged tickets are essential for achieving high routing accuracy – top organizations report up to 96% accuracy.
sbb-itb-e60d259
Step-by-Step Process for Separating Tickets
Once you’ve completed your audit and established a clear taxonomy, it’s time to dive into ticket separation. This process involves careful planning across data export, automated categorization, and workflow setup to ensure tickets are routed to the correct queues from the start.
Export Tickets and Apply Filters
Begin by exporting your historical ticket data and applying high-level filters to eliminate irrelevant entries like spam, system notifications, or closed test tickets. This step helps keep your new system clean and prevents skewed AI training data.
Next, map support fields to engineering fields. For instance, align "Priority" with "Severity" or "Description" with "Incident Details". Make sure the data types match (e.g., text fields align with text fields, numbers with numbers) to avoid any data mismatches or loss.
To pinpoint high-priority tickets, focus on sentiment and urgency indicators. Look for keywords such as "outage", "system down", or "critical failure". Additionally, identify misrouted escalations by filtering for tickets with repeated group transfers. During migration, ensure that when tickets move between teams, the original ticket is archived, and a new one is created for the destination team. Both tickets should be linked as "related tickets" to maintain a full audit trail.
Once your tickets are exported and filtered, you’re ready to move on to automated tagging for better categorization.
Use Automated Tagging and Sorting Tools
Manually categorizing tickets isn’t scalable, making AI-driven tagging a must. Unlike rigid rule-based systems that rely on keyword matching, AI-powered tools use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to grasp the intent and context of tickets, even when customers use vague language or make spelling errors.
| Feature | Keyword Rules | NLP Context |
|---|---|---|
| Logic | Rigid IF-THEN keywords | NLP and Machine Learning context |
| Urgency | Based on static fields/tiers | Sentiment and interaction patterns |
| Maintenance | High; manual updates needed | Low; models adapt to new issues |
| Accuracy | Fails on misspellings | High; understands meaning |
Before activating automated routing, gather at least two weeks of data to identify common escalation paths and ticket intents. This period allows the AI model to learn which tickets should be routed to engineering versus support. Use intent-based filtering to distinguish issue types like "Software error" versus "Refund request" and route them accordingly.
"AI ensures that tickets are classified based on their actual content, leading to much cleaner and more reliable data for reporting, trend analysis, and identifying areas for product or process improvement." – Nooshin Alibhai, Founder and CEO, Supportbench
To ensure accuracy, set triggers to activate only when "Intent Confidence" surpasses a low threshold. Tag tickets (e.g., triage_trigger_fired) to avoid creating automation loops.
With accurate tagging in place, you can now design workflows tailored to the needs of your engineering and support teams.
Create Separate Workflows for Each Team
Engineering and support teams often have different priorities, so they require distinct workflows and SLA management. When a ticket transitions from support to engineering, the SLA for the support team should pause, and a new SLA should begin for the engineering team. This separation ensures that delays in one team don’t impact the other’s performance metrics.
Leverage automated, intent-based routing to direct tickets to the appropriate team. For instance, if the AI detects a "Software Error" intent, the ticket should go straight to engineering. On the other hand, a "Billing Question" intent would route to support. You can also implement sentiment-based escalation – tickets flagged with "Negative" or "Very Negative" sentiment can be routed to a specialized escalation group or a senior engineering lead to address customer concerns promptly.
Once a ticket reaches its destination, the receiving team should take charge of external communication, applying their branding and signatures while retaining the historical context from the previous team. If engineering uses a separate tool like Jira, set up webhooks to automatically transfer relevant ticket details (e.g., name, subject, original message) when specific intents are detected.
Using AI for Ticket Triage and Routing
AI-powered systems use Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning to interpret the meaning behind tickets, even when the language used is informal or nonstandard. This ensures that engineering-related tickets reach the correct team, regardless of how the issue is described. By integrating AI into your workflow, you can streamline ticket separation, reducing delays and minimizing the chances of misrouted issues.
Implement AI Auto-Tagging and Prioritization
Modern AI tools can now grasp both the intent and sentiment within ticket content. For example, if a customer writes, "The API keeps timing out and our production environment is affected", the system can recognize this as a critical engineering issue – even if terms like "bug" or "urgent" aren’t explicitly mentioned. AI evaluates the full context, including technical terms, urgency, and tone, to apply relevant tags automatically.
Supportbench’s AI features simplify this process by categorizing tickets based on their content without requiring a complicated IT setup. Using NLP, the system can differentiate between issues like a "Product Bug" and a "Billing Question", ensuring tickets are routed to the right team. You can even set confidence thresholds, so tickets with high-confidence matches are routed automatically, while ambiguous cases are flagged for manual review (e.g., when "Intent Confidence" is below a certain level).
"AI is revolutionizing the operational backbone of support by bringing intelligence and context‐awareness to ticket routing and prioritization." – Nooshin Alibhai, Founder and CEO of Supportbench
The system also allows for team-specific configurations, locking priorities, statuses, and workflows to particular groups. For instance, engineering tickets can have distinct workflows with dynamic SLA rules, while support tickets follow a different logic. This adaptability ensures that your system evolves alongside your product and processes, with AI automating much of the heavy lifting.
Use AI Case Summaries for Faster Triage
When tickets come with extensive histories, triage can become a time-consuming process – especially during migrations when agents might be unfamiliar with older cases. AI-generated case summaries solve this by condensing the key details, helping teams quickly decide whether a ticket should go to engineering or support. Instead of sifting through lengthy back-and-forth messages, agents receive a concise overview highlighting technical details, customer sentiment, and the ticket’s current status.
Supportbench keeps these summaries updated in real-time as new interactions occur. This feature is particularly helpful during migrations, where triage teams need to assess historical tickets without diving into every detail. AI can identify patterns like repeated escalations, unresolved issues, or signs of customer frustration, allowing for faster and more accurate routing decisions.
These summaries also enable skill-based ticket assignment. For example, if an AI-generated summary identifies an API-related problem, the system can route the ticket directly to a specialist in that area. This eliminates unnecessary handoffs, ensuring tickets land with the right expert from the start. By doing so, AI not only accelerates triage but also ensures that complex engineering issues are handled by the most qualified team member.
Post-Migration Validation and Cleanup
Once the migration is complete, it’s time to validate your ticket categorization and refine workflows based on how they perform with real data. Even with the most meticulous planning, some tickets will inevitably be miscategorized, and workflows may need adjustments. This phase focuses on ensuring your automated processes and AI-driven workflows function effectively in real-time. The goal is straightforward: spot and fix errors quickly without interrupting daily operations, while using these insights to continually improve.
Review Ticket Categorization Accuracy
Start by spot-checking 10–15 tickets from each queue to compare automated categorization with expert judgment. This process helps identify consistent errors in your AI model or migration logic.
Pay attention to your reassignment rate – the percentage of tickets rerouted between teams after their initial assignment. If more than 15% of tickets are being transferred between, say, support and engineering, it signals a categorization issue. A detailed report tracking group field changes (e.g., "Previous" to "New") can pinpoint where tickets are being misrouted.
Another warning sign is a high volume of tickets landing in a general "Other" category. This suggests your separation rules are too broad, or your AI model needs additional training data. Additionally, watch for the "Watermelon Effect" – when SLAs appear to be met, but customer satisfaction remains low.
To catch miscategorized tickets that require urgent attention, use sentiment analysis. For example, a customer expressing frustration or urgency may be mistakenly categorized as a routine engineering task due to technical keywords. These cases often require immediate customer support intervention.
Adjust Workflows Based on Migration Data
Once categorization is validated, use post-migration data to fine-tune workflows. Allow about two weeks to gather enough data before making significant changes. This timeframe helps you distinguish real patterns from one-off issues.
Track your recategorization rate – how often agents manually adjust a ticket’s category after it’s assigned. If this rate is high or increasing, your triage logic likely needs tweaking. Look for trends, such as recurring issues with API-related tickets, and adjust your keywords or retrain your AI model with corrected examples.
Evaluate your separation effectiveness by monitoring key metrics. Top-performing support teams aim for 96% AI routing accuracy and keep their reassignment rate below 15%. Additionally, First Contact Resolution (FCR) for Tier 1 tickets should fall between 70% and 79%. If your numbers deviate, dig into the data to uncover where workflows might be breaking down.
| Metric | Purpose | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Reassignment Rate | Tracks how often tickets are rerouted between teams | < 15% |
| Recategorization Rate | Measures how often agents manually fix ticket categories | Low/Declining |
| First Contact Resolution | Percentage of tickets resolved without escalation | 70-79% |
| Auto Triage Rate | Percentage of tickets categorized by AI vs. humans | 50%+ |
It’s worth noting that 83% of data migration projects fail or go over budget, often because teams skip the critical post-migration quality assurance step. Avoid becoming part of that statistic by prioritizing this phase.
"AI isn’t ‘set it and forget it.’ Monitor the accuracy of AI-driven categorization, prioritization, and routing. Provide feedback to the system and refine configurations based on performance." – Nooshin Alibhai, Founder and CEO, Supportbench
Common Mistakes and Best Practices
Even well-thought-out migrations can hit a few snags. The upside? With a proactive mindset and some planning, most of these issues can be avoided.
Keep Categorization Rules Simple
Trying to manage overly complicated categorization logic can lead to unnecessary headaches. Rigid, rule-based systems – like those relying on exact keyword matches (e.g., "IF subject contains ‘Billing’") – often fall short. They struggle with misspellings, vague language, or situations where customers describe problems in unexpected ways. Plus, as your product evolves, these systems demand constant manual updates, which can bog down your team.
A smarter starting point? Use a straightforward, prefix-based tagging system, such as bug/login or billing/refund. This keeps things organized, improves searchability, and makes it easier to group related tickets. Assign a team lead to oversee the taxonomy and schedule quarterly reviews to clean up duplicates, retire outdated tags, and tweak automated rules as needed.
To go a step further, consider AI-powered triage. Unlike rigid systems, AI can analyze the actual content and tone of tickets, bypassing the need for exact phrases or customer-selected categories.
"AI cuts through the noise to identify truly urgent issues requiring immediate attention, regardless of how poorly the initial request might have been phrased." – Nooshin Alibhai, Founder and CEO, Supportbench
This kind of approach reduces misrouting caused by unclear or incomplete customer input. Once you’ve streamlined your tagging system, the next challenge is ensuring smooth collaboration between your engineering and support teams.
Maintain Team Alignment and Communication
Efficient ticket categorization is just the foundation – clear communication between teams is what keeps everything running smoothly. Miscommunication between support and engineering can lead to delays, frustrated customers, and a phenomenon often called the "ping pong effect" – where tickets bounce back and forth between teams, wasting time and eroding trust. In fact, companies relying on manual classification for technical issues may see up to 3x more ticket reassignments.
To address this, shift toward intelligent swarming instead of the traditional tiered escalation process. Rather than passing tickets off to engineering, bring engineers into the support ticket to collaborate directly. This keeps everyone on the same page and eliminates the delays caused by handoffs. For cases that still require escalation, use AI-generated internal summaries to provide engineers with concise, relevant details – saving them from wading through lengthy chat logs.
Another game-changer? Create a shared priority matrix that evaluates tickets based on business impact and urgency rather than subjective judgments. This ensures both teams are aligned on what needs attention first, reducing friction and improving response times. Also, plan migrations during off-peak hours to minimize customer disruption if downtime occurs.
Wrapping It All Up
Streamline the separation of internal engineering issues from customer support tickets by setting clear categorization rules, using AI automation, and validating results immediately after migration. A structured audit, combined with smart routing and real-time monitoring, can help you avoid migration headaches. This approach works hand-in-hand with AI tools to improve ticket triage.
AI-powered triage now analyzes both the content and sentiment of tickets, moving beyond fragile keyword-based systems. The result? Fewer misrouted tickets, quicker resolutions, and happier customers.
But don’t overlook the critical post-migration phase. Many teams stumble here. Running parallel systems briefly, tracking key metrics from day one, and collecting feedback from frontline staff can help you identify and fix routing errors early.
"Post-migration isn’t just about catching bugs. It’s about restoring usability, validating trust, and proving the value of your new system." – Eric Klimuk, Founder and CTO, Supportbench
In today’s AI-driven B2B support world, platforms like Supportbench provide scalable solutions. They offer AI-powered categorization, customizable workflows tailored to divisions, and real-time dashboards that track SLA compliance the moment your new system goes live. Whether you’re handling 50 tickets or 50,000, the platform adjusts effortlessly, keeping costs in check and API usage predictable.
FAQs
What’s the simplest way to define “engineering” vs “support” tickets?
Engineering tickets deal with tasks like technical development, system configuration, or infrastructure-related work. On the other hand, support tickets address customer-facing issues or inquiries that need assistance. Clearly separating these categories helps organize workflows and ensures tickets are routed correctly during migration.
How much clean historical data do we need to train AI routing?
When training AI routing models, the amount of historical data you need depends on your ticket volume and the variety of ticket types. Generally, you don’t need massive datasets – anything over 50,000 tickets is often excessive. Instead, aim for a timeframe that offers diverse and relevant examples. This approach ensures the model learns effectively without overloading it with unnecessary data, which can make the process more complex.
How do we avoid SLA and ownership confusion during handoffs?
To avoid confusion with SLAs and ownership during handoffs, it’s essential to have well-defined processes for managing tickets and transferring knowledge. Start with detailed documentation to capture all relevant information. Ensure tickets are properly categorized and use automated workflows to direct them to the right team, complete with the necessary context.
Incorporate tools like AI-driven triage to prioritize and assign tickets accurately. Establish clear ownership rules so everyone knows who is responsible at every stage. Consistent communication is also key – keep all stakeholders informed to minimize misunderstandings. These steps help reduce ambiguity, smooth out transitions, and ensure SLA commitments are met while responsibilities remain clear.