When deciding what tasks belong to Support versus Customer Success, the key is understanding their distinct roles:
- Customer Support: Handles immediate, technical problems like login issues or bugs. Focus is short-term, reactive, and transactional.
- Customer Success: Focuses on long-term customer goals, retention, and growth. Deals with strategic, consultative tasks like adoption planning or upsell opportunities.
To assign tasks effectively:
- Urgency: Support resolves urgent blockers; Customer Success addresses future-focused goals.
- Customer Lifecycle: Support manages technical setup; Customer Success ensures adoption and long-term value.
- Revenue Impact: Support prevents churn through quick fixes; Customer Success drives renewals and upsells.
Avoid common pitfalls:
- Support shouldn’t handle adoption questions.
- Customer Success shouldn’t troubleshoot technical issues.
- Both teams must share data for better alignment.
AI tools can automate task routing, predict escalations, and improve efficiency, ensuring the right team handles the right task at the right time.
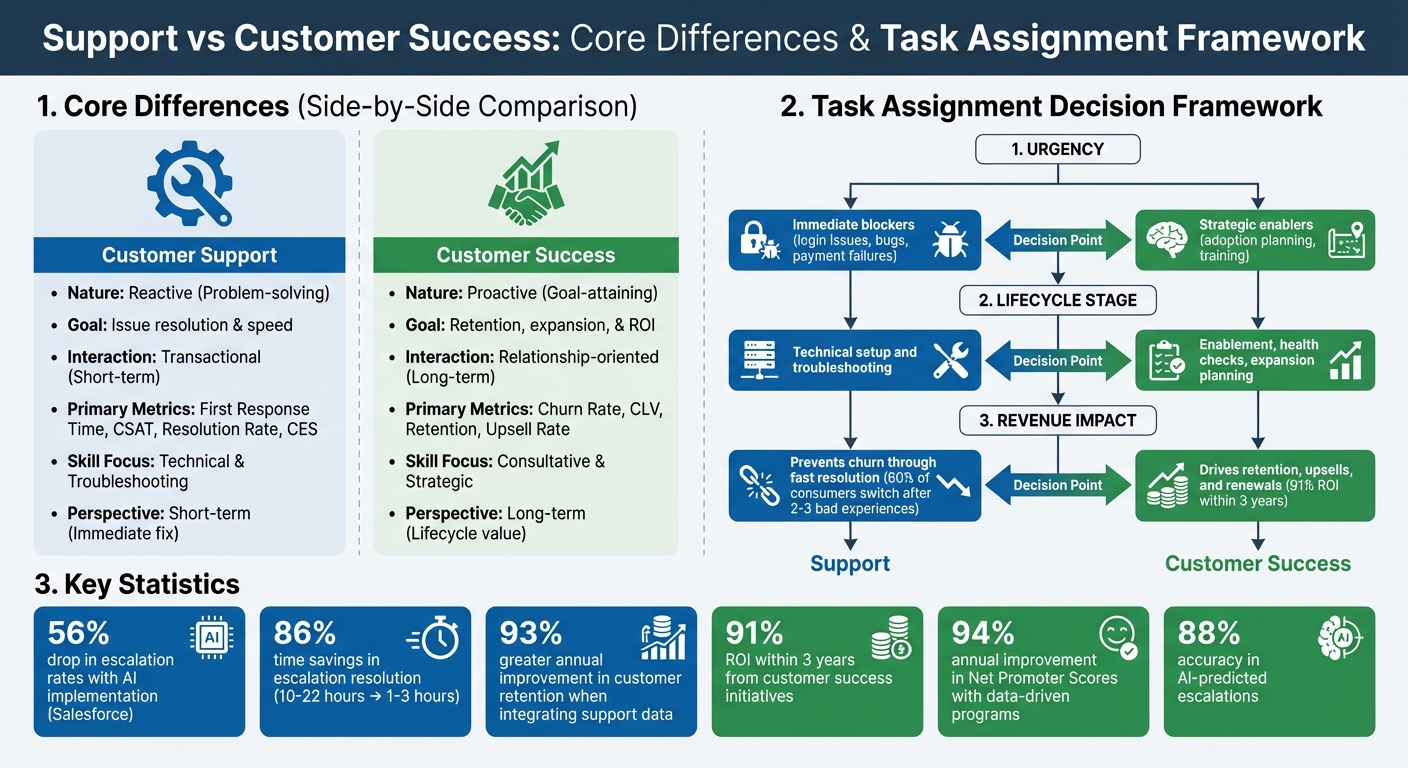
Customer Support vs Customer Success: Key Differences and Task Assignment Framework
The Ultimate Guide: Customer Success vs Customer Support
Support vs Customer Success: Core Differences
Understanding the key distinctions between Support and Customer Success helps clarify their unique roles. Customer Support focuses on solving immediate technical problems, while Customer Success emphasizes proactive efforts to ensure customers achieve long-term value from a product or service. Although both aim to assist customers, their approaches, goals, and required skills differ significantly.
The difference isn’t just about the job titles. Support has been around for decades, building on established practices, whereas Customer Success is a relatively newer field that continues to evolve. Support is often seen as an operational cost necessary for maintaining the business, while Customer Success is increasingly viewed as a revenue-generating function, focused on customer retention and growth. Let’s break down these distinctions further.
Reactive vs Proactive Work
The way these teams operate highlights their contrasting approaches. Support is reactive, stepping in when customers encounter problems. For example, if someone experiences a login issue or a software bug, they contact Support, which works to resolve the issue promptly.
On the other hand, Customer Success takes a proactive stance. Customer Success Managers (CSMs) monitor product usage to identify potential issues before they escalate. For instance, if a key feature hasn’t been used in 30 days, a CSM might schedule a call or provide training to re-engage the customer.
Technical vs Consultative Skills
The skills required for these roles also differ. Support teams need strong technical knowledge and troubleshooting abilities, along with the capacity to de-escalate tense situations. They focus on diagnosing errors, guiding customers through fixes, and resolving technical hiccups efficiently.
In contrast, Customer Success relies on consultative and strategic skills. CSMs work closely with customers to align the product’s capabilities with their business goals. Instead of just explaining how a feature works, they might help customers decide which metrics to track during quarterly business reviews.
"Customer Success is kind of like a tax preparation service… CSMs know the software in and out and they know how customers use it, so they can give you all the best practices." – Ricky Perez, Director of Customer Support, Appcues
Short-Term vs Long-Term Relationships
Support interactions are typically short-term and transactional. The focus is on resolving an issue quickly, with metrics like first response time and resolution rate being key indicators of success.
Customer Success, however, is all about building long-term relationships. CSMs often work with the same accounts for months or even years, gaining a deep understanding of each customer’s business goals and challenges. This long-term engagement allows them to identify upsell opportunities and address potential churn risks early.
| Feature | Customer Support | Customer Success |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Reactive (Problem-solving) | Proactive (Goal-attaining) |
| Goal | Issue resolution & speed | Retention, expansion, & ROI |
| Interaction | Transactional (Short-term) | Relationship-oriented (Long-term) |
| Primary Metrics | First Response Time, CSAT, Resolution Rate, CES | Churn Rate, CLV, Retention, Upsell Rate |
| Skill Focus | Technical & Troubleshooting | Consultative & Strategic |
| Perspective | Short-term (Immediate fix) | Long-term (Lifecycle value) |
How to Decide Which Team Owns Each Task
Once you’ve identified the core differences between Support and Customer Success, the next step is determining which team should handle specific tasks. Clear task assignment prevents confusion, ensures efficiency, and allows each team to focus on what they do best. Here’s a framework to guide those decisions, based on the strengths of each team.
Check Task Urgency
Start by asking: Is this task urgent for the customer right now? If the issue is blocking the customer – like login problems, failed payments, or broken features – that’s a job for Support. These are high-priority situations that require immediate resolution, and Support teams excel at quickly restoring functionality.
On the other hand, Customer Success takes on tasks that aren’t time-sensitive but have a big impact over the long term. Think of activities like adoption planning, quarterly reviews, or training on new features. These tasks might not need instant attention, but they play a critical role in ensuring retention and driving growth. In simple terms: if the issue prevents usage today, it’s for Support; if it improves future usage, it’s for Customer Success.
Match Tasks to Customer Lifecycle Stages
The customer’s lifecycle stage can also help define task ownership. During onboarding, for example, both teams often play a role. Support typically handles technical setup and troubleshooting, ensuring the software works as expected. Meanwhile, Customer Success focuses on getting the customer up and running with quick wins and early value.
Here’s a practical example: If a customer says, "I can’t import my data," that’s a technical problem for Support to resolve. But if they ask, "What features should we roll out first to maximize value?" that’s a consultative discussion for Customer Success. As customers move into the adoption and renewal stages, Customer Success takes the lead on health checks and planning for growth, while Support stays ready to handle any technical hiccups along the way.
Assess Impact on Retention and Growth
Tasks tied directly to revenue – like renewals, upsells, and advocacy – are best handled by Customer Success. These activities require a deep understanding of the customer’s goals and a strategic approach to building long-term relationships.
Support, meanwhile, plays a crucial role in preventing churn caused by frustration. Research shows that 60% of consumers will switch to a competitor after just two or three bad support experiences. Resolving tickets quickly not only keeps customers happy but also provides the foundation for Customer Success to build lasting value.
| Decision Factor | Route to Support | Route to Customer Success |
|---|---|---|
| Urgency | Immediate blockers (login issues, bugs, payment failures) | Strategic enablers (adoption planning, training) |
| Lifecycle Stage | Technical setup and troubleshooting | Enablement, health checks, expansion planning |
| Revenue Impact | Prevents churn through fast resolution | Drives retention, upsells, and renewals |
| Time Horizon | Short-term (resolve now) | Long-term (value over months/years) |
| Interaction | Transactional (clear start and end) | Continuous (ongoing relationship) |
sbb-itb-e60d259
Common Mistakes When Dividing Support and Customer Success
Even with well-defined plans, teams can struggle to clearly separate Support and Customer Success roles. This often leads to confusion, operational inefficiencies, and unhappy customers who feel shuffled between departments. Below are some common missteps that can disrupt the balance between these two functions.
Mistake: Support Handling Adoption Questions
When Support teams take on questions like, "Which features should we prioritize?" or "How can we increase team engagement?", they’re stepping outside their primary role of troubleshooting technical issues. These are adoption-related concerns that require a forward-thinking, consultative approach – something that falls squarely within the realm of Customer Success.
This role confusion not only drains Support’s resources but also fails to address the ongoing nature of adoption challenges. Adoption isn’t a quick fix; it’s about building a lasting relationship, which is the core responsibility of Customer Success.
How to Fix It:
- Develop self-service resources to handle common adoption questions before they even reach Support. This can include knowledge base articles, video tutorials, and detailed guides.
- During onboarding, clarify who handles what: Support for technical issues, Customer Success for strategic advice and growth.
- If a customer contacts the wrong team, use a transparent handoff process. Acknowledge the mix-up and ensure a smooth transition to the appropriate department.
This misalignment doesn’t just affect Support – it can also disrupt Customer Success operations.
Mistake: Customer Success Handling Technical Tickets
The reverse problem is equally damaging: when Customer Success Managers (CSMs) find themselves troubleshooting technical issues instead of focusing on strategic goals. This pulls them away from high-priority tasks, such as engaging with at-risk accounts, and reduces their ability to prove the value they bring to the business.
"Customer support is understood as a necessary cost of doing business, while customer success often has to prove its ROI among business leaders."
- Michael Redbord, Former VP of Services at HubSpot
When CSMs are bogged down with support tasks, their ability to demonstrate ROI diminishes.
How to Fix It:
- Establish clear escalation workflows that outline which issues should be handled by Support versus Customer Success. For example, technical bugs or broken integrations should go straight to Support, while questions like, "Why aren’t we seeing results?" should trigger a strategic review led by Customer Success.
- Use out-of-office messages or redirects to guide customers with urgent technical issues to the proper Support channels.
- Be upfront with customers when a question needs to be escalated. As Bri Adams, Manager of Customer Success at ChurnZero, advises:
"Be really forward about ‘Hey, you just asked me a question that I need to check with our support team on. I will follow up with you later,’ instead of saying, ‘I don’t know the answer.’"
- Bri Adams, Manager of Customer Success at ChurnZero
This approach not only educates customers but also reinforces the distinct roles of each team.
Mistake: Teams Not Sharing Data
Even when roles are clearly defined, a lack of data sharing can create silos that harm both team alignment and customer outcomes. For instance, a customer submitting multiple tickets about the same feature might signal frustration – a red flag visible to Support but invisible to Customer Success. Meanwhile, the CSM could be preparing for a renewal conversation, unaware of the customer’s dissatisfaction.
These gaps can increase churn risk. Support interactions often serve as early warning signs of customer frustration, offering insights that Customer Success can use to intervene before the situation escalates. In fact, organizations that integrate support data into customer health metrics – such as sentiment analysis and ticket trends – see a 93% greater annual improvement in customer retention.
How to Fix It:
- Implement shared dashboards and automated alerts to keep both teams informed. For example, set up alerts for CSMs when a key account shows a spike in tickets or a drop in sentiment scores.
- Use shared inboxes with internal notes and mentions to streamline collaboration between teams without losing context.
- Schedule regular cross-team meetings to review trends, identify recurring issues, and discuss areas where customer satisfaction is slipping.
Using AI to Route Tasks and Align Teams
AI technology has become a game-changer for streamlining task routing and escalation management, addressing long-standing challenges in role clarity. Manual task routing often leads to bottlenecks, team burnout, and delayed customer resolutions. Now, AI-driven workflows analyze ticket content, sentiment, and account details in real time, assigning tasks efficiently and preventing issues from spiraling. These tools integrate directly into existing workflows, benefiting both Support and Customer Success teams.
AI-Driven Escalation Prediction
AI models are designed to pick up on urgency signals like “this is blocking our launch” or detect shifts in emotional tone that suggest frustration. By analyzing factors like sentiment trends, SLA (Service Level Agreement) status, and account value, these systems can predict potential escalations before they occur. For example, if an enterprise account worth over $100,000 ARR registers a sentiment score of -35, the system triggers an immediate alert.
Salesforce, for instance, reported a 56% drop in escalation rates after implementing AI to act on signals of urgency and dissatisfaction. The platform also slashed escalation resolution times from 10–22 hours to just 1–3 hours, achieving 86% time savings.
"First and foremost, we saw north of fifty percent reduction in our escalations – game changer" – Katherine Sullivan, SVP of Customer Success at Salesforce
Supportbench takes this a step further by embedding AI Predictive CSAT (Customer Satisfaction) and CES (Customer Effort Score) into their case management tools. These features analyze ticket data to forecast satisfaction levels even before customers complete surveys. If a low score is predicted, teams can intervene immediately, reducing churn risks. This proactive approach reinforces clear team roles and responsibilities.
Predictive CSAT and CES Routing
AI doesn’t just handle ticket routing – it also predicts how customers will feel about their experience. By analyzing factors like case complexity, response times, and how much effort a customer puts into resolving an issue, AI forecasts satisfaction and effort scores in real time. If a high CES score is predicted (indicating the customer is struggling), the case can be automatically escalated to a senior agent or customer success manager.
This proactive approach shifts teams from reactive problem-solving to preemptive service recovery. For example, agents receive real-time alerts about dissatisfaction trends, allowing them to adjust their approach mid-conversation. Companies using predictive CSAT models report that AI achieves around 88% accuracy in identifying potential escalations when trained on historical data.
Supportbench also displays forecasted CSAT and CES scores directly within the case list, giving teams immediate insight into which interactions need attention – no need to wait for post-resolution surveys.
Automated Workflow Assignment
AI-powered triage systems use natural language processing (NLP) to analyze ticket context, urgency, and intent. Instead of relying on agents to manually categorize and assign cases, AI can automatically route technical bug reports to Support and adoption-related questions to Customer Success.
For more tailored routing, AI can trigger workflows based on the customer’s lifecycle stage. For instance:
- A new account with a spike in tickets might activate an "onboarding acceleration" workflow.
- A long-term account with no activity for 60+ days could prompt a proactive health check from Customer Success.
AI also prioritizes feedback based on account value. For example, negative sentiment from high-ARR customers gets escalated to a customer success manager immediately, while lower-tier accounts follow standard protocols.
Supportbench’s AI Automation features handle prioritization, issue tagging, and routing seamlessly. Teams can refine these systems over time by marking AI-generated alerts as “accurate” or “not relevant,” reducing alert fatigue and improving accuracy.
| Support Signal | AI Detection Logic | Recommended Routing/Action |
|---|---|---|
| Sudden Ticket Spike | 3x increase in 7 days | Route to Customer Success for immediate check-in |
| Negative Sentiment | Score below -40 (High ARR) | Route to Customer Success for root cause analysis |
| Technical Bug | Topic clustering detected across users | Route to Support for permanent fix |
| Competitor Mention | Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Route to Customer Success for retention playbook |
| Zero Interactions | 60+ days of inactivity | Route to Customer Success for health check |
Conclusion
Defining clear roles for Support and Customer Success has a direct impact on retention, efficiency, and revenue growth. While Support focuses on resolving immediate issues, Customer Success is all about driving long-term value for customers.
To assign tasks effectively, consider urgency, lifecycle stage, and revenue impact. For example, technical bugs and product-related questions fall under Support, while challenges like product adoption, strategic planning, and expansion discussions are the domain of Customer Success. When these teams share data and collaborate on recurring issues, they create a unified approach that prevents problems from escalating. This type of alignment strengthens the cross-team data-sharing practices already mentioned earlier.
AI tools can take this alignment even further by ensuring tasks are routed with precision. Features like predictive CSAT/CES routing, automated escalation alerts, and ARR-weighted sentiment analysis help teams prioritize high-impact issues without the guesswork.
Investing in role clarity and AI-driven task alignment delivers measurable outcomes. For instance, customer success initiatives designed with these principles can deliver a 91% ROI within three years. Additionally, data-driven programs have been shown to improve Net Promoter Scores by 94% annually. These numbers reflect customers who not only stay loyal but also spend more and advocate for your brand because they receive tailored and effective support.
FAQs
How does AI help assign tasks between Support and Customer Success teams?
AI takes the guesswork out of task assignment by analyzing customer data like interaction history, product usage patterns, and sentiment. Here’s how it works: routine, straightforward issues are automatically routed to Support teams for quick fixes. Meanwhile, more complex, relationship-driven tasks are directed to Customer Success teams, ensuring the right experts handle the right problems.
Beyond just routing tasks, AI can predict potential escalations and prioritize work based on factors such as customer health scores, churn risks, or upsell opportunities. This targeted approach allows each team to focus on their strengths, streamlining workflows and cutting down on manual effort. The result? More efficient teams and better experiences for customers.
What skills do Support and Customer Success teams need, and how are they different?
The skill sets for Support and Customer Success teams are shaped by their distinct goals and approaches. Support roles are all about reactive problem-solving. These team members need strong technical skills, quick troubleshooting abilities, and clear communication to tackle product-related issues as they arise. Their expertise lies in diagnosing problems and guiding customers to solutions in real time.
In contrast, Customer Success roles take a proactive and relationship-focused approach. Success managers work to ensure customers achieve long-term value, which requires skills like strategic thinking, empathy, consultative communication, and the ability to interpret customer data. Their focus is on anticipating needs, addressing potential issues before they occur, and building customer loyalty. While both roles call for excellent interpersonal skills, Support leans heavily on technical problem-solving, whereas Customer Success centers on relationship management and strategic planning.
How does sharing data between Support and Customer Success teams improve customer retention?
Sharing data between Support and Customer Success teams can make a big difference in keeping customers happy and sticking around. When support data – like sentiment analysis, common issues, or escalation patterns – is shared with customer success, it opens the door to spotting at-risk accounts early. This way, teams can step in with specific actions to fix potential problems before they grow into something bigger. The result? Stronger relationships with customers and better chances of renewals or even upsells.
But it doesn’t stop there. Sharing this information creates a two-way street where insights from support interactions help shape customer success strategies, improve products, and fine-tune engagement efforts. When both teams are on the same page, they can deliver more personalized and timely solutions that not only reduce churn but also build loyalty over the long haul. Breaking down the barriers between these teams isn’t just about internal alignment – it’s about creating better experiences and outcomes for customers.