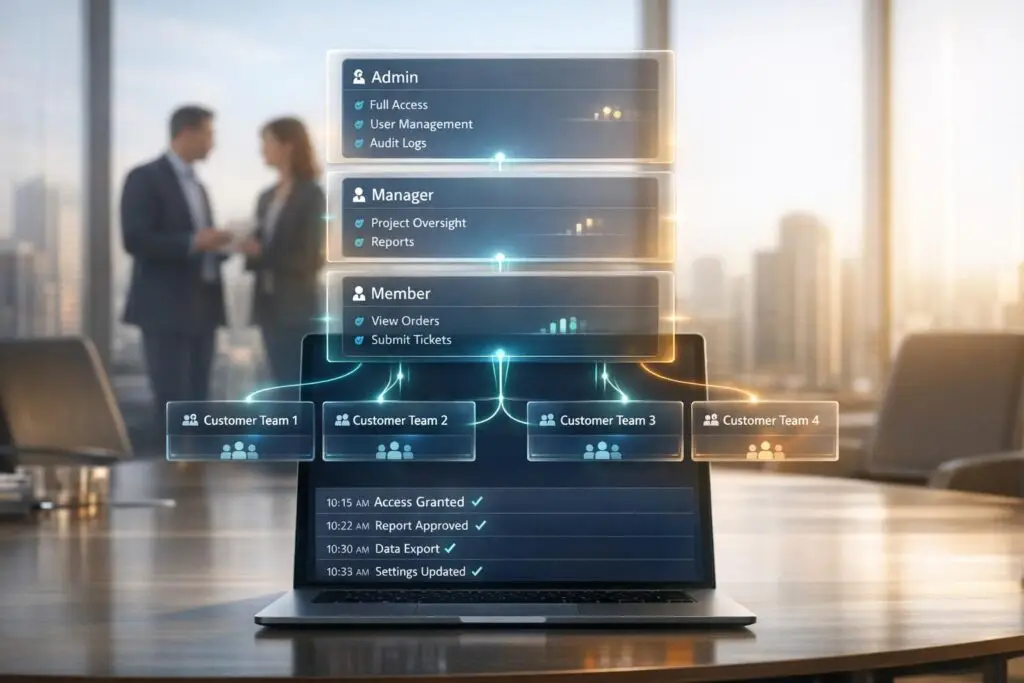
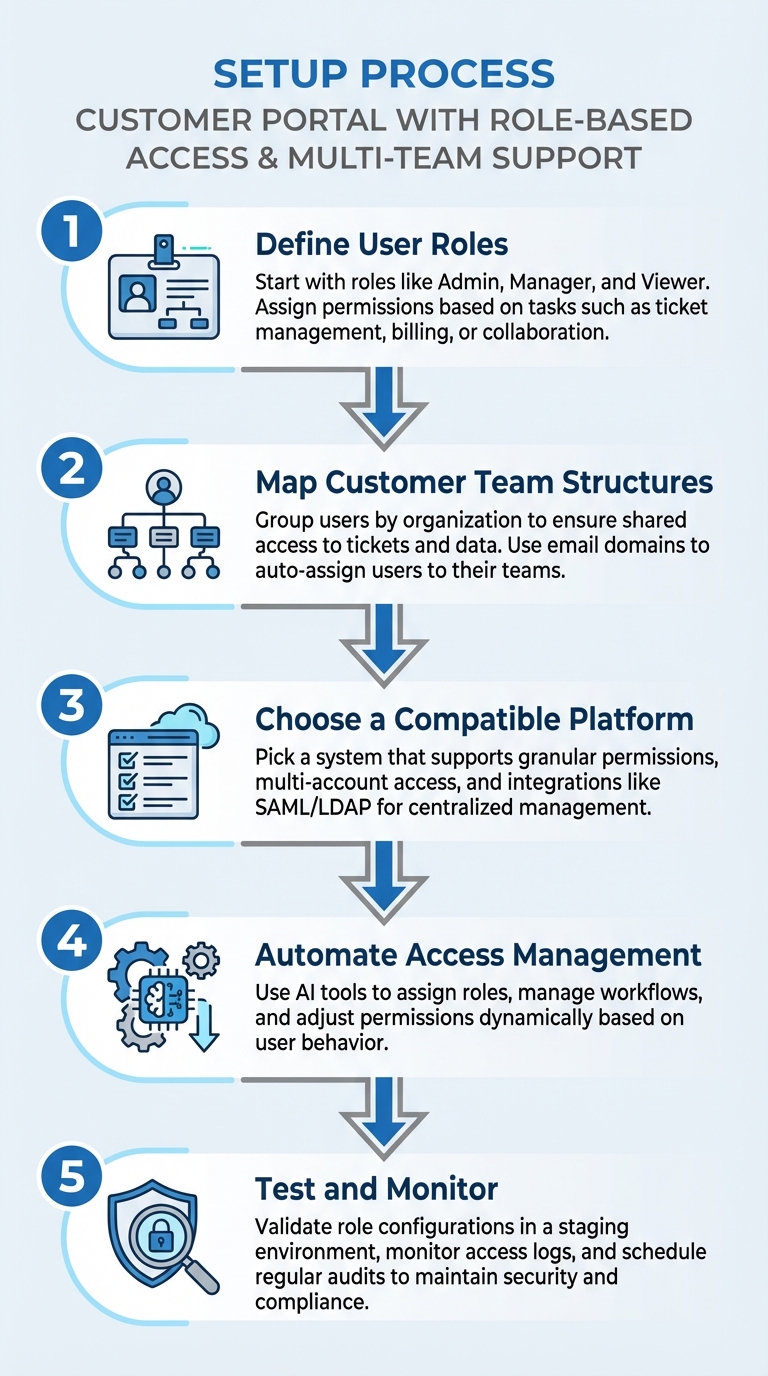
To set up a customer portal with role-based access and support for multiple customer teams, follow these steps:
- Define User Roles: Start with roles like Admin, Manager, and Viewer. Assign permissions based on tasks such as ticket management, billing, or collaboration.
- Map Customer Team Structures: Group users by organization to ensure shared access to tickets and data. Use email domains to auto-assign users to their teams.
- Choose a Compatible Platform: Pick a system that supports granular permissions, multi-account access, and integrations like SAML/LDAP for centralized management.
- Automate Access Management: Use AI tools to assign roles, manage workflows, and adjust permissions dynamically based on user behavior.
- Test and Monitor: Validate role configurations in a staging environment, monitor access logs, and schedule regular audits to maintain security and compliance.
5-Step Process to Set Up Customer Portal with Role-Based Access
Identifying Your Role-Based Access Requirements
Carefully mapping out user access needs is crucial to avoid security vulnerabilities and prevent support issues. This step lays the groundwork for defining clear user roles and permissions.
Start by differentiating between internal users (like your support staff, sales team, or field technicians) and external customer users (clients accessing your portal). In B2B setups, this distinction is especially important, as customer organizations often have intricate team structures that must be mirrored in your portal.
One of the main challenges is ensuring data isolation and privacy. It’s essential to prevent users from one customer organization from accessing another company’s sensitive data.
"A customer portal needs robust authentication. Otherwise, anyone can see any individual customer’s information, which would frustrate customers and raise legal concerns".
Another common issue is the administrative workload. Managing permissions for hundreds of users across various teams can quickly become overwhelming. A practical solution is to delegate this responsibility to "Customer Admins", who can invite colleagues and assign permissions, reducing strain on your internal support team.
Mapping User Roles and Responsibilities
Start with three core roles – Admin, Manager/Moderator, and Viewer/Member – and expand as necessary to meet your customers’ needs. For each role, tie permissions to specific portal features. Break down access by module, such as billing, support tickets, license management, or collaboration areas. For example, you might allow one user to "view all transactions" while another can "create a payment."
Here’s how roles typically align in B2B portals:
| Role Type | Typical Permissions | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Admin | Full access to account features; can manage users | Main contact for a B2B client |
| Customer Regular | Limited access to specific modules (e.g., Billing) | Employees handling specific tasks |
| Moderator | Full control over specific entities or blueprints | Team leads overseeing projects |
| Member | Read-only access with some self-service options | General users needing data visibility |
| Multi-Account Access | Role-based permissions per account | Consultants managing multiple organizations |
Decide early on the data visibility levels. Should users only see assets they personally own (Contact-level visibility) or all assets tied to their organization (Company-level visibility)? This affects everything from ticket access to billing details.
Don’t forget non-human users like "Service Accounts." These are bots or automated systems that require API access with restricted permissions.
Understanding Customer Team Hierarchies and Workflows
Once roles are defined, structure your portal to reflect how customer teams operate. Group individual users into "Organizations" so team members from the same company can share access to tickets and assets. This prevents duplicate efforts and allows managers to oversee team activities.
While roles dictate individual permissions, team hierarchies align these roles with the organization’s structure. Access can be set at three levels:
- Owned by me: Individual visibility for sensitive requests.
- Organization tickets: Shared visibility across the team.
- Criteria-based: Visibility based on specific properties or roles.
For more complex setups, use dynamic filters with AND/OR logic to decide which users see company-wide data. Automate the process by assigning users to the correct organization based on their email domains.
Organize your portal workflows around specific request types, like "Billing", "Technical Support", or "License Management." This helps customer sub-teams quickly find the processes they need. Clearly define workflows with status transitions, enabling users to resolve tickets (e.g., marking them as "Resolved") without requiring agent intervention.
Finally, document Separation of Duties requirements to ensure proper role segregation.
"Using Azure RBAC, you can segregate duties within your team and grant only the amount of access to users that they need to perform their jobs".
For instance, the person requesting a license quote shouldn’t also have access to approve or view billing details.
Additionally, plan for multi-account access where users may have different roles across accounts. For example, a consultant might be an Admin for one client and a Viewer for another. This flexibility ensures seamless operations across varied customer setups.
Selecting a Platform That Supports Role-Based Access
Once you’ve outlined your access requirements, the next step is choosing a platform that seamlessly supports complex roles and multi-team collaboration – without relying on custom development. Look for systems that allow you to define roles once and apply them consistently. This approach cuts down on administrative work and ensures your support team can adjust access controls independently, without involving engineers.
Cost considerations matter. Many legacy platforms charge extra for features like advanced role management, SSO integration, or multi-portal capabilities. Modern platforms, such as Supportbench, bundle these features into their base pricing, starting at $32 per agent per month. This includes role-based access control, team isolation through Divisions, and AI-driven automation.
Equally important is finding a platform that balances security with scalability. While granular permissions might be available now, if the system cannot integrate with your identity management tools or scale as your user base grows, it may become obsolete quickly. Integration with SAML and LDAP is crucial for centralized access management. The following sections break down the essential and advanced features your platform should offer.
Required Features for Role-Based Access Control
A robust platform should enable the creation of customizable roles – like Customer Admin, Manager, Agent, or Viewer – with fine-tuned permissions across modules such as tickets, billing, and license management.
Division and team isolation is critical for preventing data crossover between customer organizations. For example, Supportbench uses Divisions to ensure agents only see cases within their assigned areas, maintaining data privacy for clients.
Identity provider integration is a must for B2B portals. By connecting with SAML and LDAP, you can ensure orphaned accounts are deactivated promptly and manage access centrally.
Platforms should also support multi-account access with role differentiation. For instance, a consultant managing multiple clients can have Admin rights for one account and Viewer access for another – all under a single login.
Features That Enable Multi-Team Collaboration
To streamline collaboration, platforms should allow customer organizations to sync team access automatically based on email domains. Automated organization assignment further reduces manual setup.
Team-specific views and reporting are essential for keeping teams focused on their responsibilities. For example, billing teams can handle payment-related issues while technical teams work on support tickets. Configurable filters – based on request types, statuses, or custom properties – help create these tailored views.
For businesses serving diverse customer bases, multi-portal management becomes indispensable. Some platforms allow up to 500 separate portals per account, each with unique branding, content, and access settings. This flexibility lets you customize experiences for different clients or internal teams without hitting architectural limits.
Audit logging and compliance reporting provide transparency into who accessed what and when. These tools not only enhance security but also help demonstrate compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
AI Features for Managing Access
AI-driven tools take access management to the next level by adapting roles and workflows dynamically. Instead of static role-based access, AI can transform it into a system that evolves with usage patterns. For example, automated ticket triaging uses AI to categorize requests and route them to the right teams without manual input.
Proactive access optimization analyzes ticket trends to identify workflows that could be automated or restricted to specific roles.
AI can also improve your knowledge base with AI-driven knowledge maintenance. By analyzing support tickets, it identifies gaps and suggests updates or new articles when users with similar roles frequently ask the same questions.
Contextual resource suggestions personalize the portal experience based on user roles and behaviors. For instance, users with billing permissions might see payment-related articles, while technical users are shown troubleshooting guides.
Lastly, automated role assignments predict access needs based on factors like job titles, email domains, or behavioral patterns. When a new user joins from an existing customer organization, AI can recommend the appropriate role, reducing onboarding time and ensuring consistency.
How to Set Up Role-Based Access and Team Support
Once you’ve identified your access needs and chosen the right platform, the next step is configuring your portal to enforce precise role-based access and team structures. This setup is crucial – it can either enhance security and compliance or create vulnerabilities. The aim is to establish a system where permissions are clear, teams function independently, and access controls adapt seamlessly as users switch roles or clients. This approach ensures secure, scalable customer interactions while keeping operations cost-effective.
Creating and Configuring User Roles
Start by defining a straightforward role hierarchy with three levels: Admins (full control), Moderators/Editors (asset management), and Members (read-only or self-service access). This structure works well for most B2B scenarios without adding unnecessary complexity.
To speed up deployment and reduce errors, clone an existing role as a starting point. Assign permissions based on specific functional areas, such as:
- Support: Viewing and submitting tickets
- Billing: Managing licenses and handling quote requests
- Collaboration: Uploading and managing documents
Avoid using wildcards (*) when defining actions and permissions. For instance, granting wildcard access to billing might unintentionally allow new, sensitive functionalities – like payment processing – if the platform updates. Instead, use explicit permissions to maintain control.
Incorporate variables like current_user or $team to filter data based on user context. For example, this ensures users only see records tied to their account or organization. If your portal supports self-registration, configure settings to require users to join a specific group before accessing sensitive information.
Once your user roles are set, move on to structuring team-based entities for smoother collaboration.
Organizing Team-Based Structures
To simplify ticket visibility, align customer groups with their corresponding organizations. Set up domain-based auto-grouping so new users are automatically assigned to the correct organization based on their email domain.
Adjust visibility settings to control what team members can view. For example, team members might only see their own requests, or they could access all requests for their organization. For consultants or partners managing multiple clients, enable multi-account access, allowing a user to hold different roles – like Admin for one client and Viewer for another.
Create team entities by defining clear identifiers and titles, such as "Billing Team" or "Technical Support". Assign ownership of assets to specific teams by setting the ownership property to "Direct." Use SSO (Single Sign-On) to automatically populate team memberships from your organization’s directory. Organize request types into logical groups like "Common Requests", "Billing", or "Technical Support" to make it easier for teams to find and submit information.
Testing and Validating Access Controls
Once roles and team structures are configured, thorough testing is essential. Use a staging environment to test roles before rolling them out in production. Simulate real-world scenarios by logging in as different user types to ensure tasks can be completed as expected. Equally important, confirm that unauthorized users are blocked from accessing restricted areas.
Involve business managers and end-users in the testing process to catch any errors or oversights. Use a conflict matrix to verify Segregation of Duties (SoD) – ensuring no single role can perform conflicting sensitive tasks, like both initiating and approving financial transactions. Test workflow transitions (e.g., "Mark as Resolved") for each user role to confirm proper functionality.
Schedule periodic access reviews every 6 to 12 months, where managers certify that their team’s access permissions are still appropriate. Keep detailed audit logs of all access-related events, including successful and failed logins and permission changes. These logs are essential for forensic analysis and compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. Automate deprovisioning by linking access revocation to your HR systems, so permissions are immediately removed when employees leave or change roles.
sbb-itb-e60d259
Automating and Monitoring Access Management
Once you’ve implemented role-based access controls, the real challenge begins: keeping permissions accurate as your organization grows and changes. Managing access manually simply doesn’t scale, especially when dealing with multiple customer teams, shifting responsibilities, and evolving personnel. This is where AI-driven automation and continuous monitoring come into play, cutting down the administrative workload while ensuring compliance.
Using AI for Access Automation
AI tools can take over the heavy lifting when it comes to managing permissions. For instance, they can automatically categorize support tickets and assign them the appropriate role-based permissions, ensuring that sensitive information is only visible to the right users. These tools analyze incoming requests, classify them correctly without human intervention, and prevent any accidental access leaks across teams.
Automated approval workflows are another game-changer. Instead of waiting for manual approvals, these workflows evaluate access requests against pre-set security policies and grant or deny permissions instantly. Virtual service agents can also step in to handle routine customer interactions, pulling information from a knowledge base without requiring constant permission tweaks for every query.
AI platforms can even predict when permissions need to be updated by analyzing historical access patterns. For example, they can flag inactive accounts or revoke unnecessary permissions automatically, helping to shrink your attack surface without the need for time-consuming manual audits. It’s no surprise that 90% of organizations are already leveraging AI to bolster their cybersecurity defenses.
In technical environments, automation can handle tasks like managing network access, data rates, and IP assignments – areas that would otherwise demand manual configuration for each customer team. Tools like GraphiQL allow administrators to programmatically create and update roles, making it easier to deploy complex permission structures in bulk across multiple teams. This builds on earlier role definitions to streamline ongoing updates.
All these automation capabilities naturally feed into continuous monitoring, which is essential for maintaining compliance and security.
Monitoring and Maintaining Compliance
Automation is only part of the equation. Continuous monitoring ensures that your access controls stay effective over time. With continuous monitoring, you can track user permissions, identity activities, and resource usage across your entire system, spotting unusual behavior before it becomes a problem. This approach provides real-time visibility into what actions – like creating, reading, updating, or deleting – each user can perform and why.
Failing to maintain proper access controls can be costly. Anthem Inc., for instance, faced a $16 million fine for HIPAA violations after a data breach exposed the records of 79 million people. Similarly, Target Corporation settled lawsuits for $18.5 million following a PCI-DSS violation that compromised customer financial data. And under GDPR, non-compliance can lead to fines as high as €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue.
Real-time alerts can help you stay ahead of threats by flagging high-risk events, such as the reactivation of dormant accounts or unexpected changes to administrative permissions. Centralized audit logs are another must-have, capturing every access action – successful or failed login attempts, permission changes, and more. These logs ensure you’re prepared for audits like SOC 2, PCI-DSS, or ISO 27001.
"Access control compliance is a constant battle for most organizations. With cyberattacks that increasingly target identity systems to exploit excessive privileges, dormant accounts, and mismanaged permissions… outdated methods or partial solutions no longer constitute effective access control".
To further enhance security, consider creating a Read-Only Auditor role for third-party developers or compliance reviewers. This allows them to review your systems thoroughly without the risk of unauthorized changes. And to keep things consistent, modify role permissions rather than individual user settings whenever updates are needed.
Conclusion
Building a customer portal with role-based access and tools for multi-team collaboration can be straightforward and budget-friendly. The process starts with establishing a clear organizational hierarchy, defining roles like Administrator, Manager, Agent, and Viewer that reflect actual responsibilities, and setting up division-based restrictions to ensure users only access the data relevant to their roles.
You can create as many roles as your business needs. As Frontegg highlights:
"RBAC roles are critical for user productivity, because they can potentially block users from performing their day-to-day activities. This makes it important to test roles before deploying them".
Once roles and teams are configured, thorough testing and automation become essential for maintaining portal reliability. Testing in a staging environment helps catch issues before they affect users, while automation minimizes manual errors that often lead to security vulnerabilities. This proactive approach ensures your portal remains secure and efficient over time.
After launching your portal, ongoing maintenance is key. Regular audits, continuous monitoring, and leveraging AI tools for automation and role adjustments help keep permissions accurate as your organization evolves. Platforms like Supportbench simplify this process by offering multi-tiered portal structures with roles restricted to specific divisions. This setup ensures agents and customers only access the data they need. With built-in roles, detailed permission controls, and AI-powered features, Supportbench eliminates the need for costly add-ons or heavy IT involvement.
This approach provides a cost-effective, scalable solution that adapts as your organization grows – without surprise expenses or feature gaps. By following these steps and using a platform designed for this purpose, you can create a secure, collaborative customer portal while staying within budget.
FAQs
What should I look for in a platform that supports role-based access for a customer portal?
When choosing a platform for role-based access, it’s essential to opt for one with strong Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). This feature lets you assign specific roles – like admin, moderator, or member – ensuring that each user or team gets the right level of access without overstepping boundaries.
You’ll also want a platform with flexible configuration options. Features like API integrations, simple user management tools, and synchronization with identity providers (IdPs) can make onboarding and updating permissions much easier. It’s especially helpful if the platform can handle complex account structures, accommodate team-specific workflows, and offer detailed control over permissions for assets or processes.
Finally, focus on security, scalability, and automation. Look for AI-powered tools that simplify access management while maintaining robust security measures. A platform with these features can deliver efficient, secure, and cost-effective role-based access management for your customer portal.
How can AI improve role-based access management in customer portals?
AI has the potential to streamline role-based access management in customer portals. By examining user behavior and job responsibilities, AI tools can suggest suitable roles and permissions. This minimizes manual errors and saves time, making the process more efficient. On top of that, AI can adjust access dynamically, ensuring users only access what’s necessary, which boosts both security and operational efficiency.
AI also simplifies tasks like onboarding and offboarding by automatically assigning or revoking roles as team structures evolve. It can keep an eye on access patterns to detect unusual activity, helping to guard against potential security threats. For portals that manage multiple teams or deal with intricate hierarchies, AI provides scalable and precise access control, enabling seamless collaboration while maintaining robust security.
How can I ensure data privacy and secure access in a customer portal for multiple teams?
To protect data privacy and ensure secure access in a multi-team customer portal, start by implementing role-based access control (RBAC). This approach limits users to accessing only the information relevant to their specific roles, minimizing the chances of unauthorized access. Clearly defining user roles and assigning permissions is key to maintaining tight control over who sees what.
You should also structure the portal to separate data effectively. This can be achieved by setting distinct access permissions and creating unique content for each team or customer group. Using granular permission settings and organized account hierarchies ensures that data remains segmented and doesn’t unintentionally cross between teams.
Lastly, prioritize security best practices like data encryption, frequent audits, and monitoring access logs. These steps not only safeguard sensitive information but also allow for quick detection and resolution of potential threats. Together, these measures build a secure and trustworthy environment for multi-team collaboration.