When managing a busy help desk, organizing your support team into tiered workflows can save time, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. A tiered model – Tier 1, Tier 2, Tier 3 – assigns issues based on complexity, ensuring the right agents handle the right tasks. Here’s how it works:
- Tier 1: Handles routine, high-volume issues (e.g., password resets, account setups). These agents use scripts and escalate unresolved problems.
- Tier 2: Focuses on more technical issues (e.g., system errors, connectivity problems) requiring specialized tools and knowledge.
- Tier 3: Solves advanced, complex problems (e.g., software bugs, infrastructure failures) with no strict time limits.
Key benefits:
- AI tools help automate ticket routing, saving time and improving accuracy.
- Knowledge bases enable collaboration and reduce escalations.
- Clear escalation paths and dynamic rules ensure smooth workflows.
The result? Faster resolutions, reduced agent burnout, and better resource allocation. For optimal performance, continuously monitor metrics like escalation rates and resolution times, and adjust workflows as needed.
How to Organize A Tier 1, 2, 3 Customer Service Team
What Each Support Tier Does
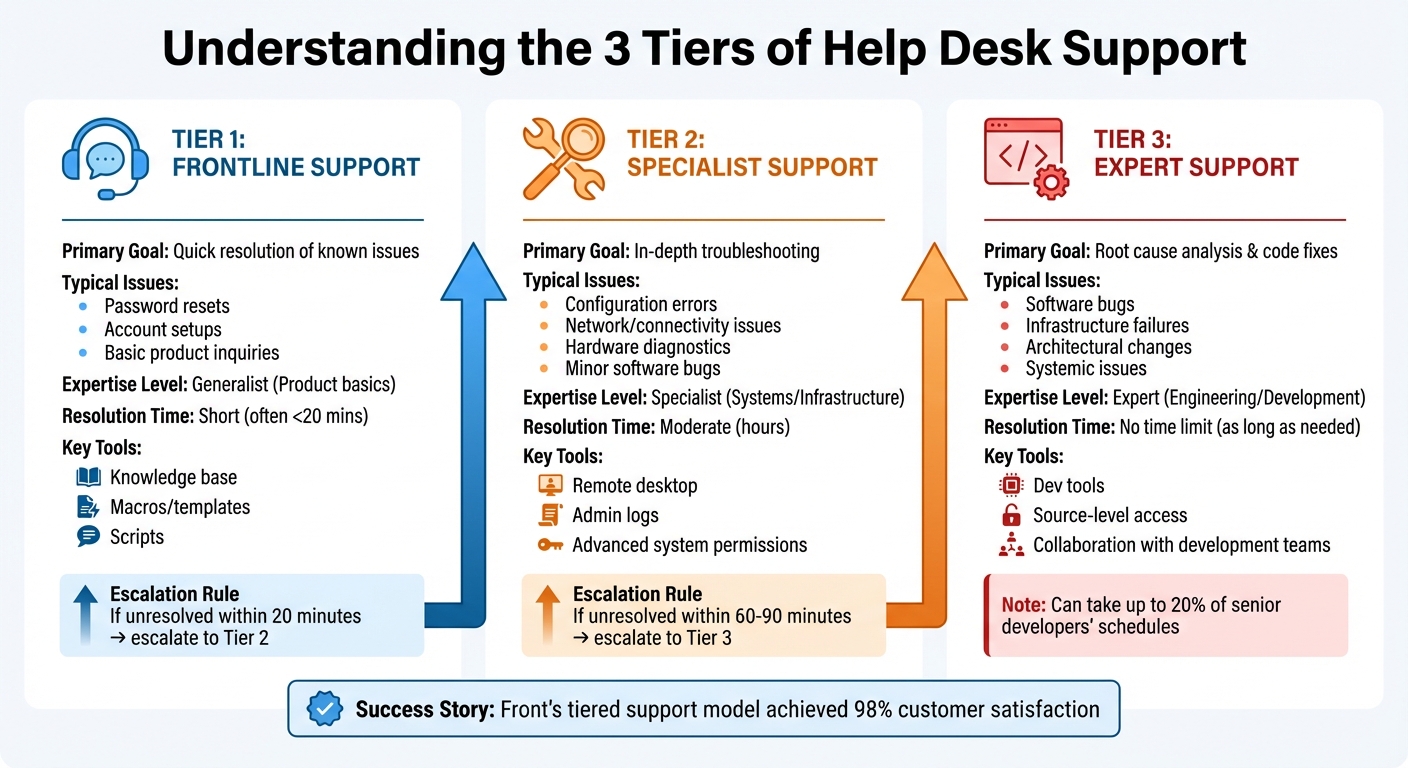
Tier 1 vs Tier 2 vs Tier 3 Support: Roles, Issues, and Resolution Times
Understanding the role of each support tier is crucial. Each tier addresses issues based on their complexity and the expertise required. Here’s a breakdown of what each tier does.
Tier 1: Frontline Support
Tier 1 is the first human touchpoint after self-service options. These agents handle straightforward issues using scripts and a knowledge base. Their tasks typically include resolving common problems like password resets, account setups, and basic product inquiries. They also perform initial triage to determine if an issue needs escalation. If an issue isn’t resolved within 20 minutes, it’s passed to the next tier.
"The reason you should hire me is because I have soft skills, and I’m good with people. (…) I could learn all the IT stuff, but you can’t teach soft skills."
– Kevin Apolinario, Senior Desktop Engineer
Clear communication and basic troubleshooting define Tier 1’s approach. When necessary, unresolved cases are escalated for more advanced support.
Tier 2: Specialist Support
Tier 2 steps in when problems exceed Tier 1’s capabilities. This level deals with more technical issues, such as configuration errors, connectivity problems, hardware diagnostics, and minor software bugs. With access to more advanced tools and system permissions, Tier 2 agents are equipped for detailed troubleshooting.
"What sets tier 2 apart from tier 1 is the level of technical investigation that’s required. While tier 1 focuses on common, well-documented issues… tier 2 handles problems that require deeper system knowledge and custom troubleshooting."
– Ashmita Shrivastava, Content Marketing Manager, Moveworks
Beyond resolving issues, Tier 2 agents contribute to long-term improvements by documenting solutions in a shared knowledge base. This practice helps reduce the recurrence of similar problems.
Tier 3: Advanced and Escalation Support
Tier 3 represents the highest level of technical expertise. This tier is staffed by senior engineers, architects, or subject-matter experts who tackle highly complex problems that lower tiers cannot resolve. Their responsibilities include conducting root cause analyses, reproducing rare bugs, fixing source code, and collaborating with development teams to address systemic issues.
"Tier 3 support includes agents who have the highest level of technical support and can tackle the toughest user problems… these agents are specialists who take on one-off issues that haven’t been encountered before."
– Mozhdeh Rastegar-Panah, Senior Director, Product Marketing, Zendesk
Unlike the lower tiers, Tier 3 agents don’t operate under strict time constraints, as resolving these advanced issues can take significant time – sometimes up to 20% of senior developers’ schedules. Proper escalation through the earlier tiers is critical to ensure Tier 3 focuses only on the most complex cases. For example, Front’s tiered support model has achieved a customer satisfaction score of over 98%.
| Feature | Tier 1: Frontline | Tier 2: Specialist | Tier 3: Expert |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Quick resolution of known issues | In-depth troubleshooting | Root cause analysis & code fixes |
| Typical Issues | Password resets, basic setup | Configuration errors, network issues | Software bugs, architectural changes |
| Expertise Level | Generalist (Product basics) | Specialist (Systems/Infrastructure) | Expert (Engineering/Development) |
| Resolution Time | Short (often <20 mins) | Moderate (hours) | No time limit (as long as needed) |
| Key Tools | Knowledge base, macros/templates | Remote desktop, admin logs | Dev tools, source-level access |
Step 1: Design Your Tiered Support Workflows
Before diving into tools or automation, it’s essential to create a solid plan. Start by analyzing your historical ticket data to identify the types of issues your team frequently encounters. Categorize these tickets by their complexity and nature. This step helps you determine which types of queries belong in each support tier, eliminating guesswork and setting the stage for clear roles and escalation protocols.
Map Customer Issues to Support Tiers
Assigning issues to the right tier ensures agents with the appropriate expertise handle them. Here’s how it typically breaks down:
- Tier 1: Handles high-volume, routine inquiries. This tier sets baseline expectations for capacity and workflow design.
- Tier 2: Tackles more technical problems, like software glitches or connectivity issues, which often require administrative access.
- Tier 3: Focuses on complex, structural problems needing code-level access or in-depth root cause analysis.
To keep things moving, establish clear escalation triggers. For instance, the 20-minute rule – if a Tier 1 agent can’t resolve an issue within 20 minutes, it’s automatically escalated. Alternatively, expertise-based triggers, such as issues requiring code changes, can go straight to Tier 3. Document these boundaries carefully to avoid unnecessary back-and-forth between tiers.
Set Clear Roles and Responsibilities
Each tier should have well-defined responsibilities:
- Tier 1: These agents handle common issues using standardized scripts and procedures. They act as the first point of contact, performing quick triage and providing detailed incident logs.
- Tier 2: Agents in this tier need deeper system knowledge and administrative permissions to troubleshoot escalated tickets.
- Tier 3: Often staffed by engineers or developers, this tier handles the most complex problems without the strict time constraints of lower tiers.
A great example of this in action comes from Broadcom. In June 2025, they implemented an AI assistant across multiple teams, including engineering and HR. By linking the AI to their enterprise knowledge base and clearly defining tier responsibilities, they achieved an 88% autonomous resolution rate, significantly reducing routine ticket volumes. This clarity in roles not only streamlines workflows but also enhances collaboration across tiers.
Use Knowledge Bases for Tier Collaboration
A shared knowledge base is essential for smooth collaboration between tiers. When Tier 2 or Tier 3 resolves a complex issue, they should document the solution immediately. This creates a "shift-left" approach, enabling Tier 1 agents to handle similar issues independently in the future, reducing escalations.
To make escalations seamless, use standardized templates. For example, Tier 1 agents should include critical details like error logs, device specifications, and attempted solutions before passing a ticket to Tier 2. This eliminates redundant work and speeds up resolutions. For service desks managing over 1,000 requests monthly, structured knowledge management is key to maintaining efficiency and scalability.
Step 2: Automate Triage and Routing
Once you’ve established a solid tier structure, the next step is automating triage and routing. Manual triage can be a major bottleneck, especially for smaller teams managing 200 to 250 conversations daily. By automating this process, tickets are routed directly to the right agents, cutting down delays and setting the stage for AI to take over with pinpoint accuracy.
AI-Driven Triage for Faster Assignment
Modern AI tools can analyze ticket details like intent, language, and sentiment, enriching them for more precise routing. This means tickets can be assigned faster and more accurately, improving response times.
The trick is setting the right confidence thresholds. Tickets should only be routed automatically when the AI is highly confident. Otherwise, they’re flagged for human review. For instance, if AI identifies a "password reset" request with high confidence, it can send the ticket directly to Tier 1 or even redirect it to a self-service solution.
Here’s another example: let’s say a ticket mentions a return but doesn’t include an order number. The system can automatically request the missing information, reducing unnecessary back-and-forth. AI can also prioritize tickets based on sentiment – flagging frustrated customers and sending them straight to Tier 2 or Tier 3 experts to prevent potential churn.
| AI Detection Feature | Support Workflow Application | Target Tier |
|---|---|---|
| Intent | Routes specific topics (e.g., "Refunds") to specialized groups. | Tier 1 or 2 |
| Sentiment | Flags frustrated customers for immediate attention. | Tier 2 or 3 |
| Language | Assigns tickets to agents with required language skills. | Tier 1 |
| Missing Info | Sends automated requests for additional details (e.g., order numbers). | Tier 0 (Self-Serve) |
In addition to AI-driven detection, dynamic rules can further streamline escalation and prioritization.
Dynamic Rules for Escalation and Prioritization
Static rules often fall short in complex B2B setups, where factors like customer value and contract terms can vary. Dynamic SLA management steps in to adjust priorities on the fly. For example, high-value customers nearing contract renewals can have their SLAs tightened, with their tickets escalated to senior Tier 2 agents for quicker resolution.
Time-based triggers also play a crucial role. If a Tier 1 ticket remains unresolved for 15 to 30 minutes, it should automatically escalate to Tier 2. Similarly, unresolved Tier 2 tickets should escalate after 60 to 90 minutes. These triggers help align with resolution targets.
To ensure no ticket falls through the cracks, tag-based workflows and availability blocks can reroute tickets automatically – even outside of standard business hours. This ensures consistent support coverage and keeps the workflow running smoothly.
sbb-itb-e60d259
Step 3: Create Clear Escalation Paths
Once automated triage and dynamic rules are in place, the next step is ensuring tickets move smoothly through escalation paths. Automation might handle routing, but clear escalation protocols are essential for resolving more complex issues efficiently. Without these, tickets can stall, forcing customers to repeat themselves and delaying resolutions. To avoid this, it’s crucial to define escalation triggers, document the process, and use tools to track every step.
Define Escalation Triggers
Escalation triggers generally fall into three main categories: expertise gaps, time constraints, and business impact. For example, an agent should escalate a ticket if they lack the technical skills, access, or authority to resolve it. This could include cases like refund requests exceeding an agent’s approval limit or technical problems requiring specialized knowledge. Similarly, tickets that exceed predefined time limits should escalate automatically. High-stakes scenarios, such as outages affecting many users or issues involving high-value customers, may also demand immediate attention from senior experts, bypassing standard queues entirely. AI can assist by flagging escalations, such as detecting negative sentiment in customer interactions or spotting patterns in related issues.
| Escalation Type | Trigger Factor | Typical Action |
|---|---|---|
| Functional | Insufficient expertise | Transfer to a specialist (e.g., technical support) |
| Hierarchical | Insufficient authority | Escalate to a supervisor or manager |
| Automated | SLA breach or time limit reached | System reassigns ticket to a higher tier |
| Priority | High-value client or major outage | Immediate routing to Tier 3 experts |
Document Escalation Protocols
Proper documentation is vital for smooth escalations. By using custom fields to log every step, teams can avoid repetitive work and improve collaboration between tiers. For instance, noting whether an escalation was due to technical limitations, authority issues, or an SLA breach ensures that Tier 2 or Tier 3 agents have all the context they need. This also creates a feedback loop: higher-tier teams can add their solutions to a shared knowledge base, equipping Tier 1 agents to handle similar issues in the future without escalating unnecessarily.
Keeping customers informed during escalations is equally important. Regular updates help manage expectations and minimize frustration, especially when wait times grow longer. Studies suggest that nearly 50% of customers might switch to a competitor after a single poor experience, and this number jumps to 80% after repeated negative interactions. Integrated tools can help by providing real-time updates on escalation progress, ensuring transparency and a smoother customer experience.
Track and Manage Escalations with Tools
Modern help desk tools can eliminate manual bottlenecks in the escalation process. For example, time-based triggers can send automated alerts to team leaders when tickets approach SLA deadlines. Omnichannel routing tools also consolidate tickets from email, chat, and voice into a single system, prioritizing them based on agent availability and expertise. Platforms like Supportbench take this a step further with dynamic SLA management, automatically adjusting priorities in real-time – for instance, routing high-value customer tickets directly to senior agents.
Standardized macros for escalation handoffs ensure that all relevant details, including prior troubleshooting steps, are passed along clearly to the next tier. This prevents customers from having to repeat themselves and speeds up resolution times. Additionally, AI integration streamlines workflows while keeping costs in check. Regular quality assurance audits can further refine the process by identifying cases where agents escalate unnecessarily or hold onto complex tickets for too long, ensuring that each tier operates efficiently.
Step 4: Use AI to Optimize Support Workflows
Once you’ve established structured workflows and clear escalation paths, AI can take your tiered support system from simply reactive to forward-thinking. By analyzing patterns, adding context, and spotting inefficiencies, AI helps resolve more issues at lower levels, ensuring complex cases get to the right experts more quickly.
AI for Predictive Case Prioritization
AI can examine incoming tickets to understand intent, language, and sentiment – even before a human sees them. For example, if a customer submits a ticket about a software error, AI can prioritize it based on urgency, like flagging a frustrated customer for immediate attention or escalating unresolved tickets with multiple agent replies directly to Tier 2.
AI also steps in to gather missing details proactively. Let’s say a ticket arrives without an order number or error log – AI can send an automatic request for that information before a Tier 1 agent even opens the case.
"Intelligent triage is an AI-powered feature that automatically detects what a ticket is about (its intent), what language it’s written in, and whether the customer’s message is positive or negative (its sentiment)."
- Jake Bantz, Zendesk Product Manager
AI-Powered Knowledge Management
AI doesn’t just work on tickets – it also strengthens your knowledge base by identifying gaps and creating new articles. When Tier 2 or Tier 3 agents solve tough issues, AI can turn those solutions into structured articles, complete with summaries and keywords. This allows Tier 1 agents to handle similar cases in the future without escalating them.
For escalations, AI enriches tickets with technical metadata or system logs, so Tier 2 specialists don’t waste time redoing basic discovery work. It can also suggest relevant knowledge base articles or resolution steps based on the ticket’s intent.
Unlike static FAQ pages, conversational AI assistants provide real-time, personalized answers. For instance, platforms like Supportbench embed AI-driven knowledge tools directly into workflows, allowing agents to instantly access both internal and external resources while assisting customers. This can cut mean time to resolution (MTTR) for routine issues from hours to just minutes.
These AI-driven practices not only streamline workflows but also provide valuable insights for continuous improvement.
AI-Driven Insights for Workflow Improvements
AI analytics can uncover inefficiencies by tracking metrics like escalation rates, group transfers, and resolution times. For example, if tickets tagged as "Software error" frequently escalate from Tier 1 to Tier 2, it signals a need for updated documentation or better routing rules. Similarly, if certain tickets bounce between multiple agents, it highlights the need for refined AI routing.
Self-service performance is another area AI can improve. If specific search terms consistently lead to ticket creation rather than resolution, it’s a sign that new or updated knowledge base articles are needed. AI also groups recurring issues, enabling Tier 3 teams to address root causes instead of just symptoms.
| Metric to Monitor | AI Insight Provided | Workflow Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Escalation Rate by Intent | Highlights topics Tier 1 struggles to solve | Update Tier 1 scripts or Knowledge Base |
| Sentiment Analysis | Flags frustrated or high-value customers | Escalate to Tier 3 or a manager immediately |
| Reassignment Rate | Shows tickets bouncing between agents | Improve AI routing for better initial matching |
| Self-Service Success | Reveals where AI bots fail to resolve issues | Create or refine help articles for those intents |
Regularly auditing AI-predicted intents against actual escalation paths helps fine-tune routing rules and reduce unnecessary escalations. Monitoring how long tickets stay in Tier 1 before escalating to Tier 2 can also help identify bottlenecks in triage. Over time, AI transforms support workflows into flexible systems that adapt and improve with every ticket, reducing costs while boosting customer satisfaction.
Step 5: Monitor and Adjust Performance
Tiered workflows only work well if they’re continuously monitored and fine-tuned. Without careful oversight, Tier 1 could escalate too many issues, Tier 2 might get bogged down with simple tasks, or customers could face frustrating delays. Keeping an eye on performance is essential to improving your support strategy.
Track Metrics with Dynamic SLAs
Start by setting clear Service Level Agreements (SLAs) for each tier, outlining response and resolution time goals. For instance, Tier 1 might have a strict 20-minute window to resolve issues before escalating them. Dynamic SLAs take things a step further by adjusting priorities based on customer needs – like prioritizing high-value accounts or urgent contract renewals.
Focus on key metrics to keep everything running smoothly. First Contact Resolution (FCR) measures how many tickets Tier 1 resolves without escalation. A high Escalation Rate, on the other hand, might signal that Tier 1 agents need better training or more authority. Keep tabs on First Reply Time (FRT) to ensure customers get quick responses, and watch for high Ticket Reassignment Rates, which could point to unclear routing or knowledge gaps. Frequent ticket bouncing or reopened tickets are red flags that your workflow needs immediate attention.
Real-world examples highlight the value of tracking these metrics. Khan Academy’s automated triage system achieved a 92% customer satisfaction score. Similarly, Baleària introduced a chatbot for Tier 0 support, handling common questions before escalating to human agents, which led to a 96% satisfaction rating. Both cases show the importance of monitoring deflection rates and resolution quality by tier to identify what’s working and what needs improvement.
Analyze Workflow Data for Continuous Improvement
AI-driven analytics can reveal patterns that manual reviews might miss. For example, if certain tickets regularly escalate from Tier 1 to Tier 2, it could mean your documentation or routing rules need tweaking. Sentiment analysis is another powerful tool – it flags frustrated customers in real time, giving you a chance to step in before satisfaction drops further.
"AI tools can help address this challenge by surfacing patterns from historical ticket data, suggesting priority based on business impact, and providing guidance on resolution paths that have been successful for similar past issues."
- Moveworks
If Tier 2 resolution times are climbing, it might mean simple cases are being misrouted to higher tiers. Use occupancy data to ensure agents are neither overwhelmed nor underutilized, and let AI identify which agents excel at resolving specific types of issues. Peek, a travel company, used workforce management software to cut scheduling time from 4–5 hours to just 5 minutes, freeing up resources for meaningful workflow improvements.
Here’s how different metrics provide actionable insights:
| Audit Metric | Strategic Insight Provided |
|---|---|
| First Contact Resolution (FCR) | Shows whether Tier 1 agents have the tools and knowledge to resolve issues independently |
| Average Resolution Time by Tier | Pinpoints bottlenecks or handoff issues if times are increasing at Tier 2 or 3 |
| Escalation Rate | Highlights whether Tier 1 needs better training or if product issues require deeper fixes |
| Backlog per Tier | Identifies staffing shortages or mismanaged escalations at specific tiers |
Conduct Regular Workflow Audits
Once you’ve gathered data, schedule quarterly reviews to refine your processes. These audits should focus on updating tier definitions, improving routing rules, and identifying top-performing agents for promotion. Analyze escalation data from the first 2–3 months to check if ticket boundaries are clear or if agents are hesitating to escalate when necessary. Break down customer satisfaction scores by tier to pinpoint weak spots – whether Tier 1 needs better documentation or Tier 3 is too technical in its communication.
"Set a recurring review to update tier definitions, optimize workflows, and promote high-performing agents into more advanced tiers."
- Nidhi Lohia, Content Marketer, Hiver
Document all decisions and outcomes to continuously improve AI-driven processes. Keep an eye on deflection rates to ensure self-service tools are effective at resolving issues before they reach human agents. As your product evolves, so will your customers’ needs. Regular audits ensure your tiered system stays aligned with your business goals and delivers efficient, customer-focused support.
Conclusion
Building tiered support workflows isn’t something you set and forget – it’s an evolving process that demands structure, automation, and constant fine-tuning. Start by clearly defining roles and ensuring issues are routed to the right people. Then, layer in automation: automated triage reduces manual effort, intelligent routing ensures tickets land with the right team, and predictive analytics help you identify and address potential roadblocks before they escalate into customer dissatisfaction.
The true strength of tiered workflows lies in treating them as an interconnected system rather than siloed teams. For example, when Tier 1 agents have access to robust knowledge bases and AI-powered tools, they can resolve more issues on the first attempt. Tier 2 specialists, on the other hand, can work more efficiently when tickets arrive with full context – like logs, troubleshooting steps, or device specs – eliminating redundant work. Meanwhile, Tier 3 experts can focus on long-term improvements rather than getting bogged down with routine escalations. This connected approach is the backbone of a smooth and efficient support operation.
"Standardizing multi-tiered troubleshooting transforms chaotic support operations into predictable, efficient workflows that deliver consistent results across your entire team."
To scale effectively, align your workflows with both customer expectations and operational goals. Keep a close eye on metrics like first-contact resolution rates, escalation percentages, and average resolution times to identify areas for improvement. Regularly reviewing and updating your tier definitions ensures your system evolves alongside your product and customer base.
A unified strategy, blending automation with clear performance metrics, is essential for scaling support. Tools like Supportbench simplify this process by integrating AI into case management, knowledge base updates, and workflow automation – without the costly add-ons or disjointed systems found in older platforms. With features like dynamic SLAs, predictive CSAT scoring, and AI-driven triage, you can grow your support team’s capabilities while maintaining high customer satisfaction. The result? A smarter, faster support operation that delivers consistent results across every tier.
FAQs
How does AI improve tiered support workflows in a help desk?
AI is transforming tiered support workflows by taking over repetitive tasks, streamlining ticket routing, and offering helpful insights at every level. Here’s how it works across different tiers:
For Tier 1, AI takes care of routine tasks like password resets or account access issues. This reduces the workload for agents, ensures quicker responses, and ultimately improves customer satisfaction.
For Tier 2, AI adds more context to escalated tickets. It can provide details like previous troubleshooting steps or system data, giving agents the information they need to handle more complex problems. Plus, AI uses analytics to predict potential escalations, helping teams address issues before they grow.
At every level, AI enhances ticket accuracy through intelligent triage. It identifies intent, language, and sentiment, ensuring tickets reach the right team without delay. These improvements lead to faster resolutions, smarter resource use, and a smoother support experience for both customers and agents.
What are the main differences between Tier 1, Tier 2, and Tier 3 support in a help desk?
The differences between Tier 1, Tier 2, and Tier 3 support come down to the complexity of the issues they handle and the level of expertise required.
- Tier 1 support is the front line. These agents handle simple, routine problems like password resets, account access issues, or general questions. Their goal is to resolve issues quickly and efficiently while managing a high volume of basic requests.
- Tier 2 support steps in when problems go beyond what Tier 1 can handle. These agents have more technical expertise and focus on tasks like in-depth troubleshooting, analyzing systems, or making configuration changes.
- Tier 3 support is for the toughest challenges. Staffed by highly skilled experts or engineers, this level tackles complex issues such as deep system bugs, systemic failures, or problems requiring code-level solutions. They often collaborate with product developers when necessary.
This tiered approach ensures that problems are directed to the right level of expertise, helping resolve issues efficiently while keeping resources well-managed and customers satisfied.
When should a support ticket be escalated to a higher tier?
When a support ticket goes beyond the current team’s skill set, remains unresolved within a specific timeframe, or demands specialized knowledge, it’s time to escalate it to a higher tier. Establishing clear criteria – like technical triggers or time-based thresholds – helps determine when to pass the issue to Tier 2 or Tier 3 support.
To make this handoff smoother, ensure agents follow a standardized diagnostic process and thoroughly document all relevant details before escalation. Additionally, AI-powered tools can improve this workflow by spotting patterns, flagging unresolved cases, and automatically routing complex issues to the right team. This minimizes delays and ensures customers get quicker, more effective solutions.










