Running a helpdesk RFP for Canadian organizations involves a structured process to identify the best vendor for your needs. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Define Objectives & Scope: Outline your goals and determine the scope of services (e.g., basic support, after-hours assistance, or advanced features like analytics).
- Involve Stakeholders: Assemble a team including business, legal, financial, and technical experts to ensure a balanced evaluation.
- Set Timelines: Create clear deadlines and submission protocols for vendors to follow.
- Specify Requirements: Include functional needs like AI-native systems, multi-stakeholder workflows, and technical criteria like cloud-based architecture, APIs, and security features (e.g., SSO, MFA).
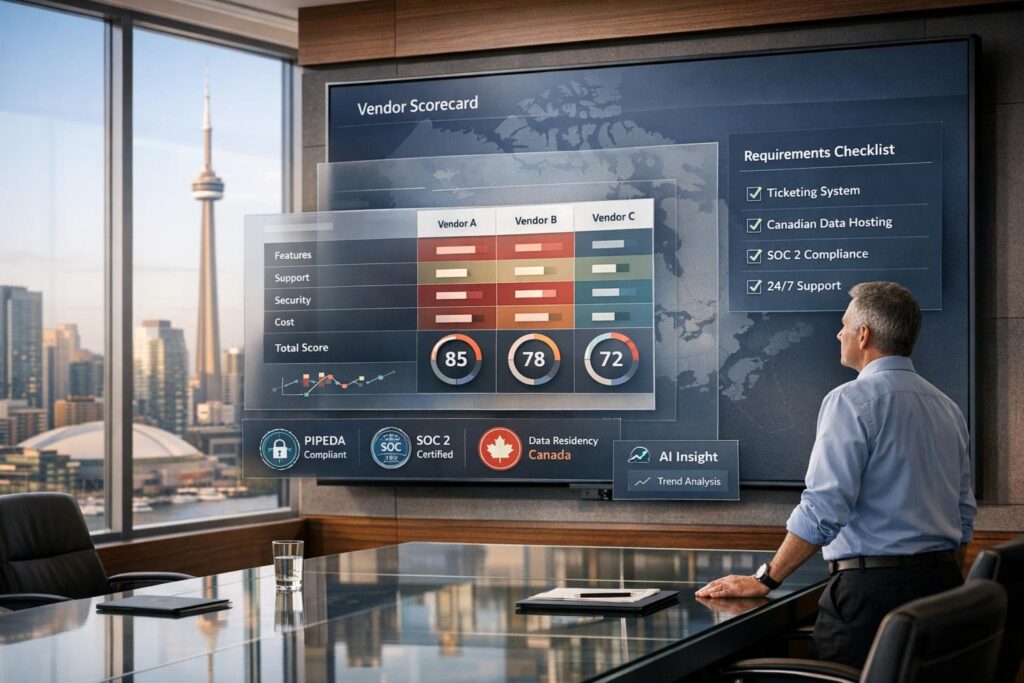
- Compliance Standards: Address data residency, privacy laws, and certifications (e.g., SOC 2, ISO 27001).
- Evaluation Criteria: Use mandatory (pass/fail) and point-rated (scored) criteria, prioritizing technical merit and compliance over cost.
- Scorecard: Design a weighted scorecard (e.g., 40% technical, 30% compliance, 20% price, 10% experience) to assess vendor proposals consistently.
This process ensures fair competition, aligns vendor capabilities with your goals, and supports informed decision-making.
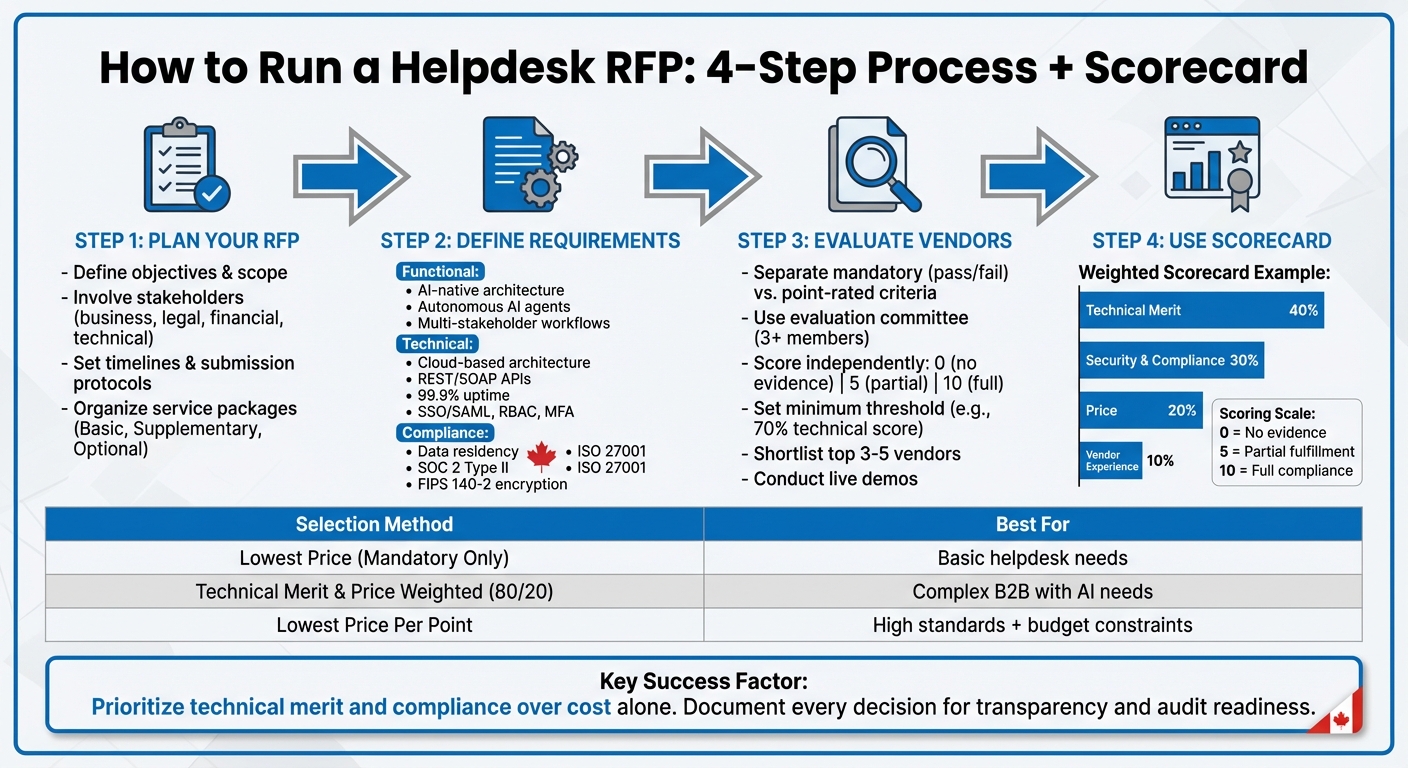
4-Step Helpdesk RFP Process for Canadian Organizations with Scorecard Framework
The RFP Process | A 20-Step Guide for Modern Procurement Teams
Step 1: Plan Your Helpdesk RFP
A well-thought-out RFP is the cornerstone of efficient vendor evaluation and a high-performing helpdesk.
Define Your RFP Objectives and Scope
Begin by outlining your goals. What are you aiming for? Prioritize operational efficiency and getting the best value for your investment. For helpdesk services, determine whether vendors will manage just the initial support tiers or handle escalations as well.
Next, clearly define the scope of work. Specify the functions, processes, and activities you expect the vendor to cover. For instance, will they only provide tier-one support, or will they also offer after-hours assistance? Setting these boundaries upfront minimizes confusion later.
Consider organizing your requirements into service packages. For example:
- Basic Service Package: Covers standard ticket management.
- Supplementary Services: Addresses department-specific needs such as technical support or billing inquiries.
- Optional Service Extensions: Includes advanced features like analytics or custom reporting.
This structured approach helps vendors understand your core needs while leaving room for future enhancements.
Once your objectives and scope are clear, the next step is assembling the right team.
Identify Stakeholders and Procurement Guidelines
With your scope in place, bring together a team of stakeholders. Include roles such as a business owner, contracting authority, financial advisor, legal expert, and security officer.
Follow your organization’s procurement rules to ensure a fair bidding process. Include provisions for "off-ramps" in case you need to exit a vendor agreement due to performance issues or changing requirements. This strategy prevents vendor dependency and keeps your options open throughout the contract.
Set Timelines and Submission Protocols
Establish realistic deadlines that allow vendors enough time to craft quality proposals while keeping your project on schedule. Collaborate with your procurement specialist to outline key milestones, from the RFP release to contract signing. Confirm the availability of your evaluation committee by the bid closing date.
Set up electronic submission protocols for bid documents. Specify the required format, supporting documentation, and the process for vendors to submit questions during the RFP period. Ensure your evaluation team includes at least three members with technical expertise to guarantee a fair review and avoid delays. Keep detailed records of every step – from individual evaluations to vendor communications – to maintain transparency and prepare for potential audits.
Step 2: Define Helpdesk Requirements
Your RFP should clearly outline the functional features, technical specifications, and compliance standards necessary to support modern B2B support operations effectively.
Functional Requirements
Focus on specifying an AI-native architecture over outdated legacy systems. AI-native platforms directly connect to live data sources like Google Drive, SharePoint, and Confluence, enabling access to real-time information instead of relying on static Q&A libraries that demand constant manual updates.
Include a requirement for autonomous AI agents capable of handling tasks such as drafting responses, conducting competitor research, and analyzing customer data. For B2B environments, it’s also important to support multi-stakeholder workflows. Features like internal tagging, clear ownership of complex cases, and automated routing based on sentiment or custom rules are essential. The system should automatically pull customer context from your CRM, equipping agents with a complete relationship history before they respond.
For example, one case study found that AI-native systems reduced the time needed to complete a 100-question RFP from 17.5 hours to just 6 hours, with 84% of AI-generated responses accepted without edits.
Once you’ve established these functional needs, it’s time to define the technical infrastructure required to support them.
Technical Requirements
Your technical specifications should emphasize a cloud-based architecture to ensure scalability and ease of deployment. Include requirements for REST or SOAP APIs to enable seamless custom data integration. The system should support auto-scaling, load balancing, and maintain at least 99.9% uptime, while also integrating with your CRM, ERP, and productivity tools through documented APIs.
From a security standpoint, specify features like SSO/SAML integration, Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). Additionally, the platform should offer real-time dashboards, tools for building custom reports, and predictive analytics to enhance decision-making capabilities.
U.S. Compliance Considerations
For organizations working under federal contracting requirements, your RFP should address compliance with the Privacy Act of 1974 and relevant FAR clauses such as 52.224-1 and 52.224-2. These ensure contractors meet the same data safeguarding standards as federal employees. Require FIPS 140-2 compliant 256-bit AES encryption for data at rest and 128-bit encryption for data transfers to meet stringent security benchmarks.
If your organization operates in specific industries, include compliance mandates like HIPAA for handling patient data, GLBA for financial services, or FISMA for federal agency work. State-level privacy laws, such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (which imposes fines of up to $7,500 per willful violation) and the New York SHIELD Act (with penalties ranging from $500 to $3,000 per violation), should also be addressed.
To further ensure data security, mandate U.S. data residency, requiring that all data be stored on servers physically located within the United States. Prohibit vendors from using customer input or sensitive data to train their base AI models to prevent data leaks. Additionally, request SOC 2 Type II and ISO 27001 certifications as independent verification of the vendor’s security controls. The platform should also provide granular, time-stamped audit trails to support legal defensibility.
"The Privacy Act applies to federal government contractors who operate systems of records containing personal information." – GSA
sbb-itb-e60d259
Step 3: Evaluate Vendors Using Criteria and Process
Once you’ve clearly outlined your requirements, the next step is to systematically evaluate vendor proposals.
Start by organizing the proposals within a structured framework. This framework should clearly distinguish mandatory criteria (requirements that vendors must meet to be considered) from point-rated criteria, which assess technical strengths and added benefits. Vendors who fail to meet any mandatory criteria – such as data residency or compliance with local privacy laws – should be disqualified immediately, regardless of their pricing.
Vendor Evaluation Criteria
When assessing vendors, weighted categories can help balance technical capabilities with cost. For example, if you’re seeking a specialized helpdesk solution with AI-native features, you might allocate 80% of the weight to technical merit and 20% to price. This ensures that functionality and innovation are prioritized over simply choosing the lowest-cost option.
Within the technical merit category, break down your scoring into key areas such as:
- AI-native architecture and autonomous agent functionality
- Integration quality with your existing systems
- Strong security and compliance measures
- Vendor experience with similar B2B implementations
Set a minimum threshold for technical scores – such as 70% – to ensure vendors meet your standards. Vendors falling below this threshold should be excluded, even if they offer the lowest price. To maintain consistency, use a clear scoring system, like:
- 0 points: No demonstration of capability
- 5 points: Partial demonstration with gaps
- 10 points: Full demonstration with evidence
Form an evaluation committee of at least three members who are familiar with both the technical requirements and your operational needs. Each member should score proposals independently before coming together to discuss and reach a consensus.
| Selection Method | Description | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Lowest Price (Mandatory Only) | Focuses solely on price among vendors meeting all mandatory requirements | Basic helpdesk needs with minimal customization |
| Technical Merit & Price Weighted | Combines technical scoring (e.g., 80%) with price (e.g., 20%) | Complex B2B operations with AI-native needs |
| Lowest Price Per Point | Balances technical quality and cost; selects the lowest ratio | High technical standards with budget constraints |
Shortlist Vendors and Negotiate Contracts
After scoring, narrow your options to the top 3–5 vendors. Schedule live demos to test their performance in scenarios relevant to your needs. For example, ask vendors to showcase AI capabilities in real-world situations, such as managing multi-stakeholder escalations or integrating real-time customer data from your CRM.
Consider running a Best and Final Offer (BAFO) round with your finalists. This gives vendors a chance to adjust their proposals, potentially improving pricing or adding extra value. During contract negotiations, clarify pricing structures upfront. Opt for a firm price if your scope is well-defined, or a ceiling price if you anticipate potential growth in support volume.
Step 4: Use a Customizable RFP Scorecard
A well-designed scorecard takes the guesswork out of evaluating vendors. By applying consistent standards to every proposal, your team can make decisions that are easier to explain to stakeholders and leadership.
Design Your Scorecard
A scorecard builds on your vendor evaluation framework, helping you narrow down your options. Start by categorizing your criteria into mandatory and point-rated sections. Mandatory criteria – like compliance with privacy regulations or data residency – should be assessed on a pass/fail basis. If a vendor fails even one mandatory requirement, they’re automatically out of the running.
For point-rated criteria, use a 0-5-10 scale:
- 0 points for no evidence of meeting the requirement
- 5 points for partial fulfillment
- 10 points for full compliance with supporting proof
Assign weights to each category based on your priorities. For instance, if technical capabilities are your top concern, you might allocate 40% to technical merit, 30% to security and compliance, 20% to price, and 10% to vendor experience.
| Criterion Type | Scoring Method | Weight Example |
|---|---|---|
| Mandatory | Pass/Fail | N/A (Disqualifies if failed) |
| Technical Merit | Point-rated (0-100) | 40% |
| Security & Compliance | Point-rated (0-100) | 30% |
| Price | Weighted Price Score | 20% |
| Vendor Experience | Point-rated (0-100) | 10% |
Score Vendors and Make Your Final Selection
Once your scorecard is ready, use it to evaluate vendors. Each committee member should independently review the proposals and assign scores before coming together to discuss and finalize the results. This collaborative approach minimizes bias and incorporates diverse perspectives.
Keep detailed records of each score and the reasoning behind it. This documentation will come in handy if you need to justify your decision to procurement teams or other stakeholders.
After tallying the scores, your top vendor should stand out. If two vendors are neck and neck, revisit their demos and reference checks to make the final call. The scorecard provides the data, but your team’s judgment seals the decision.
Conclusion
Running a successful helpdesk RFP hinges on a clear structure, organized planning, and impartial evaluation. Start by defining your objectives, involving key stakeholders, and establishing firm timelines. This keeps your process on track and ensures vendors stay focused. By clearly outlining your functional, technical, and compliance needs, you can quickly identify vendors capable of meeting your core requirements.
To streamline evaluation, separate your criteria into two categories: mandatory and point-rated. Mandatory criteria act as a pass/fail filter, helping you eliminate unsuitable vendors early. Point-rated criteria, on the other hand, allow you to assess technical strengths and additional benefits using a consistent scoring system.
A well-designed scorecard is essential. Weighted criteria aligned with your priorities help quantify vendor capabilities, ensuring transparency and fairness in your decision-making. Independent scoring, followed by team discussions, creates a documented and defensible selection process.
Thorough documentation is crucial throughout the RFP lifecycle. Keeping detailed records – such as scores, justifications, and vendor communications – not only supports your final decision but also helps avoid compliance issues. In fact, incomplete records can lead to significant non-conformance findings.
Ultimately, selecting the right helpdesk solution through this structured process ensures your choice aligns with your long-term goals. This approach not only promotes operational efficiency but also supports compliance and sustained growth.
FAQs
What compliance standards should Canadian organizations consider when creating a helpdesk RFP?
When drafting a helpdesk RFP, Canadian organizations need to focus on meeting strict standards for privacy, security, and transparency. A crucial step is complying with federal and provincial privacy laws, which often involves conducting a Privacy Impact Assessment (PIA). This assessment ensures that personal data is managed responsibly and helps identify potential privacy risks, especially when outsourcing customer support services.
It’s also essential to establish well-defined evaluation criteria, security protocols, and contractual terms that align with government procurement guidelines. These typically include requirements like data residency, security clearances, and confidentiality agreements to safeguard sensitive information. By adhering to these standards, organizations not only protect their data but also ensure a fair and transparent vendor selection process.
How can I prioritize technical quality over cost when evaluating vendors?
When selecting a vendor, it’s important to focus on their ability to meet your organization’s specific needs rather than just their pricing. One effective way to do this is by assigning more weight to technical criteria – like experience, compliance, and innovation – while reducing the emphasis on cost. For instance, you might allocate 75% of the total score to technical merit, leaving the remaining 25% for cost considerations.
A structured scoring matrix can help you objectively evaluate proposals. Start by assessing mandatory requirements on a pass/fail basis to eliminate vendors who don’t meet your baseline needs. Then, use a point system to score technical aspects, ensuring the most capable vendors stand out. This method allows you to select a vendor who can deliver a high-quality, AI-driven solution that aligns with your goals, rather than defaulting to the lowest-cost option.
What are the advantages of using an AI-powered helpdesk system?
Using an AI-powered helpdesk system comes with several advantages that can make a big difference in customer support. First, it improves the customer experience by delivering faster, more personalized, and context-aware assistance. AI can handle customer inquiries naturally, offering intelligent, real-time responses that lead to quicker resolutions and happier customers.
Second, these systems take care of routine tasks like summarizing activities and generating responses automatically. This reduces the burden on support teams, freeing them up to tackle more complex or critical issues.
On top of that, AI platforms boost efficiency by streamlining workflows and centralizing support across multiple channels. This ensures consistent service quality while simplifying operations. They also provide advanced data analysis, allowing businesses to spot trends and refine their support strategies over time. For companies looking to modernize their helpdesk, AI-driven solutions offer a scalable and cost-conscious way to meet growing customer expectations while staying compliant with industry standards.
Related Blog Posts
- What are the best non-US helpdesk platforms for Canadian companies in 2026?
- How do Canadian data residency requirements affect helpdesk selection?
- What does “Buy Canadian” mean for software and SaaS procurement in Canada?
- Which helpdesks offer Canadian hosting – and what questions should you ask vendors?