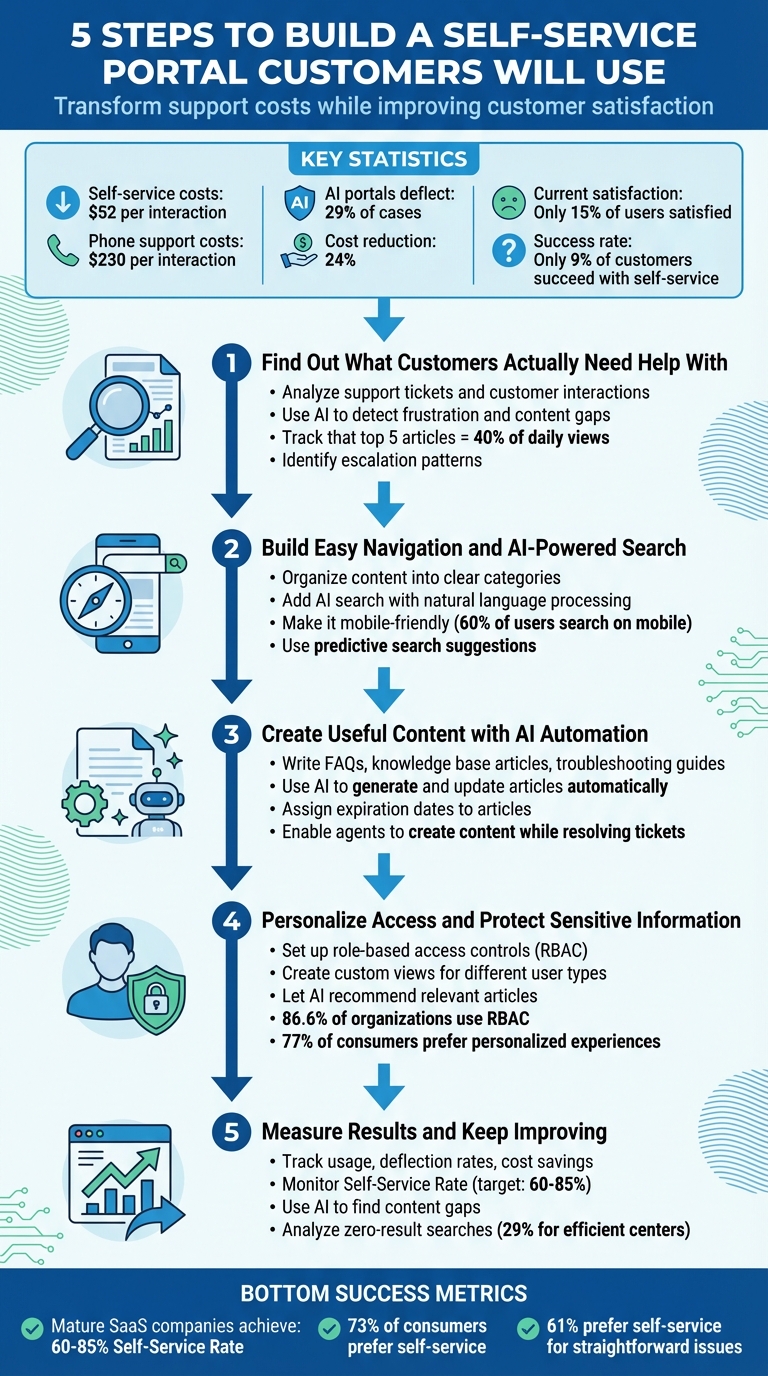
Most self-serve portals fail because they’re hard to use, outdated, or poorly designed. But a great portal can save money and improve customer satisfaction. Here’s how to build one that works:
- Understand Customer Needs: Use support data to identify common issues and create content that solves real problems.
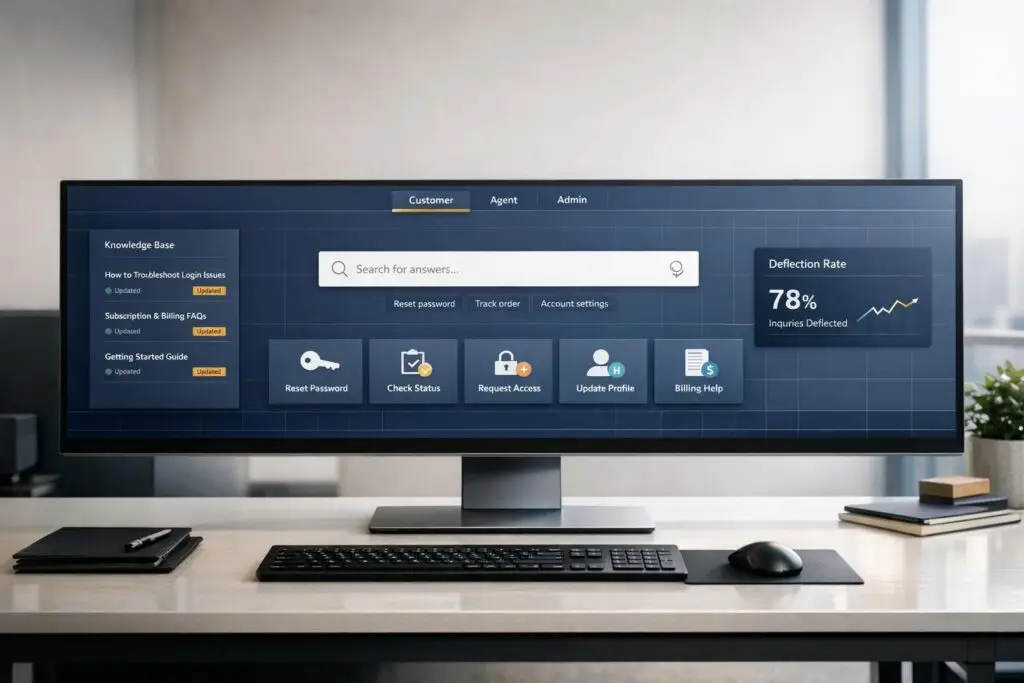
- Simplify Navigation: Organize content by tasks, not departments. Ensure mobile-friendliness and avoid confusing layouts.
- Use AI-Powered Search: Enable natural language search that handles typos and suggests relevant solutions.
- Create Reliable Content: Regularly update articles with clear instructions, visuals, and AI-driven automation.
- Personalize Access: Use role-based controls to show users only what’s relevant to them.
- Measure and Improve: Track metrics like deflection rates, search success, and cost savings to refine your portal over time.
Key Stats:
- Self-service costs $52 per interaction vs. $230 for phone support.
- AI portals can deflect 29% of cases and cut costs by 24%.
- Only 15% of users are satisfied with current self-serve options.
A successful portal combines smart design, useful content, and AI tools to deliver fast, effective support while reducing costs.
5 Steps to Build a Self-Service Portal Customers Will Use
Why Most Self-Serve Portals Don’t Get Used
Many self-serve portals fail to truly connect with users. In fact, only about 9% of customers who try to solve issues on their own actually succeed. This disconnect often boils down to three main problems: confusing design, outdated content, and poor search functionality. These shortcomings keep portals from delivering the support customers need.
Confusing Navigation and Poor Mobile Access
Portals often reflect a company’s internal structure instead of how customers think. For example, menus labeled by departments like "Finance Team" or "Product Engineering" leave users scratching their heads. Customers don’t think in terms of departments – they think in terms of tasks, like "Billing & Invoices" or "Troubleshooting." This mismatch leads to frustration and, eventually, abandonment of the portal.
The situation gets worse on mobile devices. With over 60% of users turning to their smartphones first for help, portals that aren’t mobile-friendly create unnecessary barriers. Non-responsive designs that require endless zooming or scrolling, or pages filled with hard-to-read text blocks, make solving problems on a small screen nearly impossible.
"If your grandmother needs a manual to use your portal, you’ve already failed." – Hexus.ai
Outdated or Missing Content
Nothing erodes trust faster than stale or incomplete information. Imagine clicking on an article only to find screenshots that don’t match the current product or no indication of when the content was last updated. It’s frustrating, and worse, it makes users question whether the company even cares about accuracy.
This lack of trust doesn’t just affect the portal – it can hurt the company’s reputation. Customers who can’t find reliable answers often move away from self-serve options, forcing them to rely on more expensive support channels. Additionally, outdated content creates problems for modern AI tools, which need current, accurate data to deliver helpful responses. Without it, even advanced AI features can fall flat.
"A findable article that doesn’t solve the problem is still failure." – Yulia Bondarenko, CS Lead, GrowthMate
Weak Search Functionality
Search is the backbone of any self-serve portal, but many fall short. Basic keyword searches can’t handle typos, synonyms (like "SSO" vs. "Single Sign-On"), or offer alternative suggestions. When users can’t quickly find what they need, frustration builds, and the portal loses its purpose.
The problem grows when portals bury or hide escalation options. If customers feel "trapped" without a clear way to reach live support, it damages their overall experience. This not only leads to portal abandonment but also drives up support costs as users turn to more resource-intensive channels for help.
Step 1: Find Out What Customers Actually Need Help With
When creating self-serve portals, base your decisions on actual support data – not guesses. Understanding where customers face challenges ensures your portal addresses real issues, cuts support costs, and encourages adoption. These are essential for efficient, AI-driven support systems.
Analyze Support Tickets and Customer Interactions
Digging into your existing support channels can uncover frequent issues and content gaps. For instance, 40% of daily help center views come from just the top five articles, and the top three in each category account for 50% of views. Pay attention to escalation patterns where searches fail to resolve issues – this often points to missing or unclear content. Comments and follow-up questions on articles also shed light on areas where documentation might be confusing or incomplete.
Consider adopting a Knowledge-Centered Service approach. In this model, support agents flag gaps or even draft articles based on the tickets they handle. Since your team is already familiar with customer pain points, they’re in the best position to ensure your knowledge base stays relevant and useful. These insights will also be crucial for improving portal navigation and search capabilities – something we’ll explore next.
Use AI to Detect Frustration and Content Gaps
AI can take things further by clustering tickets to spot emerging trends and unresolved issues. Automated tools can flag search queries that return no results or lead directly to escalations, helping you address gaps before they become widespread problems.
Sentiment analysis is another powerful tool. It identifies frustration in customer interactions, pointing to areas that may need more detailed troubleshooting guides. AI can also scan ticket descriptions during submission to suggest relevant articles, highlighting where your current content isn’t effective at deflecting cases. These insights will guide your content updates and portal improvements in the following steps.
The next step? Use this data to design navigation that works seamlessly for your users.
Step 2: Build Easy Navigation and AI-Powered Search
To address customer pain points effectively, your portal’s design should make it easy for users to find the right solutions. Even if your content is excellent, poor navigation can derail the user experience. The goal is simple: make finding answers as straightforward as possible. Once this foundation is in place, you can seamlessly integrate AI-powered search features to enhance usability.
Organize Content into Clear Categories
A good starting point? Ensure your self-service portal is no more than one click away from your main website. Adding a clearly labeled "Product Support" tab to your site’s header is a simple yet impactful step that many portals overlook.
Within the portal, opt for tab-based navigation to eliminate endless scrolling. Horizontal scrolling, in particular, should be avoided – it’s confusing, especially for mobile users. Arrange content in a clear hierarchy (e.g., Product > Category > Specific Task) so even users unfamiliar with technical jargon can locate what they need. You can also dynamically highlight trending articles based on recent searches and user activity to guide users toward popular solutions.
Add AI Search That Understands Questions
Traditional keyword searches often frustrate users, especially when they don’t know the exact technical terms. AI-powered search, using natural language processing, solves this problem by understanding the intent behind user queries. For example, if someone types, "why isn’t my payment going through", the AI can recognize this as a billing issue, even if the relevant article has a different title.
To make your search feature even more effective, implement unified indexing. This allows the system to pull results from your entire content library, including knowledge base articles, community forums, product manuals, and release notes, breaking down content silos. Predictive, search-as-you-type suggestions can further streamline the process, especially for mobile users who may find typing cumbersome. Additionally, integrating AI search into ticket creation can provide real-time article suggestions, helping reduce support costs by deflecting unnecessary tickets.
Your AI search should continuously improve based on user behavior. For instance, if most users click the third result for a specific query, the system should adjust rankings accordingly. Regularly reviewing search logs can also reveal content gaps, such as frequent null results or repeated escalations. By addressing these gaps, you ensure your search feature remains intuitive and effective.
Make It Work on Mobile and Match Your Brand
Responsive design is non-negotiable. Your portal should automatically adjust to any screen size without losing functionality. Use large, easy-to-tap buttons for common actions like "Reset Password" or "Track Order", and keep your search bar prominent with predictive suggestions to save users time.
Brand consistency is equally important. Align your portal’s design with your main website by using the same fonts, colors, headers, and footers. This not only creates a cohesive experience but also reinforces trust. As Ragsdale explains:
"Consistency offers a streamlined user experience, but you are also sending a subtle message that the company embraces customers and support is a core competency of the brand".
Avoid placing essential content "below the fold" on mobile screens, where it might go unnoticed. Focus on functionality over flashy design elements to ensure users can quickly find what they need. Lastly, include clear escalation options – like links to email, chat, or phone support – in the portal footer. This reassures users that help is available if self-service doesn’t resolve their issue.
With intuitive navigation and smart search in place, you’re well-positioned to deliver a support experience that’s both efficient and user-friendly.
Step 3: Create Useful Content with AI Automation
Great navigation and search features are meaningless without solid content to back them up. The challenge isn’t just creating content – it’s producing enough of it, keeping it relevant, and making sure it directly addresses customer needs. This is where AI automation steps in, turning content creation into a scalable, streamlined process. Building on the foundation of effective navigation and search, this step ensures your content aligns perfectly with what your customers are looking for.
Write FAQs, Knowledge Base Articles, and Troubleshooting Guides
One of the best ways to create customer-focused content is by mining insights from resolved support tickets. These tickets are a goldmine of real-world problems and solutions, which can be transformed into actionable resources.
When creating content, structure it with concise, keyword-rich titles that match the way customers search. For instance, instead of a generic title like "Payment Processing Overview", go for something specific like "Why isn’t my payment going through?" Use clear headers, step-by-step instructions, and visual aids like screenshots or videos to make the information easy to follow. As Elizabeth Williams from Zendesk’s Documentation Team puts it:
"A strong knowledge base is even more critical [when using AI], as it will improve the quality and accuracy of automated responses".
Keep the language simple and avoid unnecessary technical jargon unless your audience expects it. Imagine you’re explaining the solution to a colleague who isn’t familiar with the technical details – be clear, direct, and actionable.
Use AI to Generate and Update Articles Automatically
Once you’ve established the basics of your knowledge base, AI can take over to help you scale and maintain it. AI tools can analyze resolved cases, internal notes, PDFs, and past conversations to draft new articles automatically. For example, if a complex billing issue is resolved, AI can process the details and generate an article with a clear problem description, step-by-step solution, and relevant keywords.
AI also shines at identifying content gaps. By tracking searches that return no results and monitoring where AI agents struggle to answer queries, it creates a prioritized list of missing topics. This ensures you’re building content based on real customer needs rather than guesswork.
Beyond creating new articles, AI keeps your knowledge base up to date. It suggests updates for outdated information, refreshes guides automatically, and even handles translations for a global audience. Lauren Hakim, Director of Product Marketing at Zendesk, highlights this benefit:
"AI can help your team scale help center content without sacrificing quality. It can surface content gaps, suggest new topics, and assist with drafting or updating articles".
To keep your knowledge base fresh, adopt Knowledge-Centered Service (KCS) practices. This means empowering support agents to create or update articles directly while resolving tickets. This approach ensures that new solutions are added to your knowledge base in real time.
A practical tip: assign expiration dates to articles, especially those with product screenshots or version-specific instructions. This prompts regular reviews and prevents customers from following outdated guidance. Additionally, use AI-powered dashboards to monitor which articles perform well and identify those that need updates based on user behavior and resolution rates.
sbb-itb-e60d259
Step 4: Personalize Access and Protect Sensitive Information
Once your portal is packed with valuable content, the next step is making sure each user sees only what’s relevant to them while safeguarding sensitive information. Different customers, subscription levels, and security requirements call for a tailored approach. The challenge? Striking the right balance between personalization and protection. Tools like role-based access controls (RBAC) and AI-driven recommendations can help create an intuitive experience that feels custom while keeping confidential data secure.
Set Up Role-Based Access and Custom Views
At the heart of a secure and personalized portal is role-based access control (RBAC). Instead of assigning permissions to individual users, RBAC grants access based on roles tied to job functions or customer types. This simplifies managing who can view what. For instance, free-tier customers shouldn’t see enterprise-level documentation, and internal troubleshooting guides should remain off-limits to end users.
Customizing views is equally important. Admins need access to governance tools, free-tier users should see only basic content, and new users benefit from Getting Started guides. Meanwhile, experienced users can dive into advanced troubleshooting. This tailored approach not only reduces confusion but also ensures users aren’t overwhelmed with irrelevant information.
To make RBAC work effectively, stick to the principle of least privilege (PoLP) – grant users only the minimum access necessary to complete their tasks. Structuring roles hierarchically also helps. For example, a "Manager" role can inherit permissions from an "Employee" role, cutting down on redundant configurations. For added security, link your portal to a central identity management system like LDAP or Active Directory. This ensures access is automatically revoked when someone leaves the organization. Regular audits, ideally every quarter, can help catch "privilege creep", where users accumulate more permissions than they should.
RBAC is widely adopted for good reason. As of 2025, 86.6% of organizations use RBAC as their primary access control model. It’s scalable, efficient, and simplifies administration. To get started, carefully define administrative groups and roles before enabling RBAC.
Once access is secure, AI can take personalization to the next level by delivering relevant content and simplifying escalations.
Let AI Recommend Relevant Articles and Escalate When Needed
While RBAC controls what users can see, AI steps in to decide what they should see. By analyzing user behavior – like search history, past interactions, and case records – AI can recommend content that feels tailored to each individual. For example, someone frequently searching for billing topics might see articles about payment methods, invoicing, or subscription adjustments before they even ask.
AI also adapts content to different user types. A first-time visitor might get onboarding guides and FAQs, while a returning customer with a track record of complex issues could be shown advanced troubleshooting steps. This context-aware approach anticipates user needs, making the experience feel more relevant and satisfying.
When self-service falls short, AI ensures smooth context-preserving escalation. Instead of forcing users to re-enter their information, AI creates a support ticket that includes their entire session history – what they searched for, which articles they viewed, and where they got stuck. This seamless handoff to live chat or email support saves time for both the user and your team. AI can even prioritize tickets based on urgency or topic, ensuring critical issues are routed to senior agents.
The benefits of this approach are clear. Studies show that 77% of consumers are willing to choose or spend more on brands offering personalized experiences. Additionally, 61% of customers prefer self-service for resolving straightforward issues. By combining RBAC with AI-driven recommendations, you can build a portal that feels tailor-made for each user while keeping sensitive data secure and protected.
Step 5: Measure Results and Keep Improving
Launching your self-serve portal is just the beginning. To make sure it meets customer needs over time, it’s crucial to track key performance metrics and make ongoing improvements. By keeping an eye on these numbers, you can ensure your portal stays effective and relevant.
Track Usage, Deflection Rates, and Cost Savings
Start by focusing on metrics that give you a clear picture of your portal’s performance. The Self-Service Rate (SSR) measures how many customers solve their issues independently instead of reaching out to support. For reference, mature SaaS companies often achieve SSRs between 60% and 85%. Another important metric, the Ticket Deflection Rate, shows the percentage of users who intended to contact support but found their answer in the portal instead. This has a direct impact on cost savings, as phone support averages $230 per call compared to just $52 for self-service interactions.
Other metrics to monitor include:
- Search Success Rate: Tracks how often a search leads to a clicked article with high dwell time and no follow-up ticket. If users leave quickly after clicking, it’s a sign the content didn’t address their issue.
- Article Helpfulness Score: Calculated by dividing upvotes by total votes, this highlights which articles may need improvement.
- Resolution Time: Measures how long users take to find answers. Shorter times often lead to better satisfaction and retention.
Pay close attention to "no results" searches. Efficient help centers report zero-result searches about 29% of the time, while outdated ones see rates over 40%. Each zero-result search points to a content gap. For example, Riot Games, which handles over 3 million tickets annually, uses collaborative knowledge creation – averaging 5.6 agents per article – and automation to deflect tickets and reduce wait times significantly.
Once you’ve established these metrics, you can take things a step further by leveraging AI to refine your content and predict future needs.
Use AI to Find Content Gaps and Predict Customer Needs
AI tools can go beyond basic reporting by identifying patterns you might miss otherwise. Machine learning, for example, can analyze support tickets to uncover topics that lack adequate knowledge base articles. Microsoft uses this approach to refine its self-service tools and search algorithms in real-time, analyzing millions of support interactions. Companies that regularly update their content – sometimes called "Agile Improvers" – achieve a median Self-Service Ratio of 4.4, compared to just 2.4 for those that neglect regular updates.
Predictive AI can also analyze historical data to forecast future customer needs. Additionally, it automates routine content maintenance tasks like summarizing long articles, updating outdated information, and translating content for international users. This is particularly important since the top five articles in a help center often account for about 40% of daily views.
"If you’re using AI-powered features that draw information from your help center content, a strong knowledge base is even more critical, as it will improve the quality and accuracy of automated responses." – Elizabeth Williams, Zendesk Documentation Team
Conclusion
Creating a self-serve portal that truly delivers involves five key steps: understanding customer needs, designing user-friendly AI-driven navigation, automating high-quality content, tailoring access with role-based controls, and consistently improving performance. Each step builds on the last, with AI acting as the glue that connects and enhances the entire process. AI identifies gaps, fine-tunes content, and anticipates future demands, ensuring the portal evolves with its users.
The financial payoff is undeniable. With 73% of consumers preferring to resolve issues independently, a well-designed portal not only reduces costs but also aligns with customer preferences. Companies with advanced self-service portals report success rates between 60% and 85%, significantly reducing support tickets and allowing agents to focus on complex, high-value tasks. This approach doesn’t just streamline support – it drives measurable business outcomes.
"A well-executed self-service portal is far more than a cost-cutting measure – it’s a strategic asset that can transform the way you engage with your customers." – Hexus.ai
AI plays a pivotal role in every stage, from predicting customer needs and updating content automatically to improving escalation processes. But the key to AI’s success lies in maintaining accurate, up-to-date content. Without ongoing updates and refinements, even the smartest AI can’t deliver the results customers expect.
Continuous optimization is essential. Regularly auditing content, analyzing failed searches, and tracking metrics like resolution times and ticket deflection rates ensure your portal stays relevant. A well-maintained self-serve portal not only reduces costs but also enhances customer satisfaction and grows alongside your business.
FAQs
How can AI make self-serve portal searches more effective?
AI makes the search functionality of a self-serve portal smarter, faster, and easier to use. With natural language processing (NLP), it can understand the intent and context behind user queries – even if those queries are phrased conversationally. This means users get results that are more accurate and relevant, rather than just a list of keyword matches.
It also enhances the search experience with tools like auto-complete, smart suggestions, and relevance ranking, helping users find what they need in less time. Plus, AI continuously learns from user behavior and search trends. This allows it to fine-tune its algorithms, spot missing content, and keep the knowledge base current. The result? A self-serve portal that feels intuitive and reliable, improving both customer satisfaction and the overall self-service experience.
How can customer data improve the design of a self-serve portal?
Customer data plays a key role in building a self-serve portal that genuinely addresses user needs. By examining details like common challenges, frequently asked questions, and usage trends, support teams can craft resources that resonate with users – think FAQs, knowledge base articles, and troubleshooting guides. This approach ensures the portal aligns with what customers actually want, leading to higher adoption and satisfaction.
On top of that, keeping an eye on usage analytics and gathering customer feedback helps improve the portal over time. Understanding which resources users find most helpful, identifying content gaps, and analyzing how people navigate the portal can guide updates to its structure, search tools, and content quality. Using customer data in this way ensures the portal evolves alongside user needs, delivering a smoother experience and boosting engagement.
How can self-service portals help lower customer support costs?
Self-service portals are a smart way to lower customer support costs. How? They let customers handle common issues themselves, which means fewer support tickets for your team to manage. This frees up your staff to tackle more complex and urgent problems.
By offering resources like FAQs, troubleshooting guides, and knowledge base articles, you can address recurring customer concerns quickly and effectively. Over time, this approach doesn’t just save money – it also boosts customer satisfaction by providing fast and convenient solutions.