Inconsistent ticket categorization creates unreliable data, making it hard to track recurring issues, prioritize tasks, or share insights with other teams. The solution? A well-structured, standardized system that ensures every ticket is categorized accurately and consistently.
Here’s how to do it:
- Audit your current system: Identify redundant or vague tags and simplify your taxonomy.
- Create a hierarchy: Use 30–50 clear categories, organized into tiers (e.g., broad to specific).
- Train your team: Involve agents in the process, provide clear guidelines, and monitor usage.
- Leverage AI: Automate tagging to save time and improve accuracy.
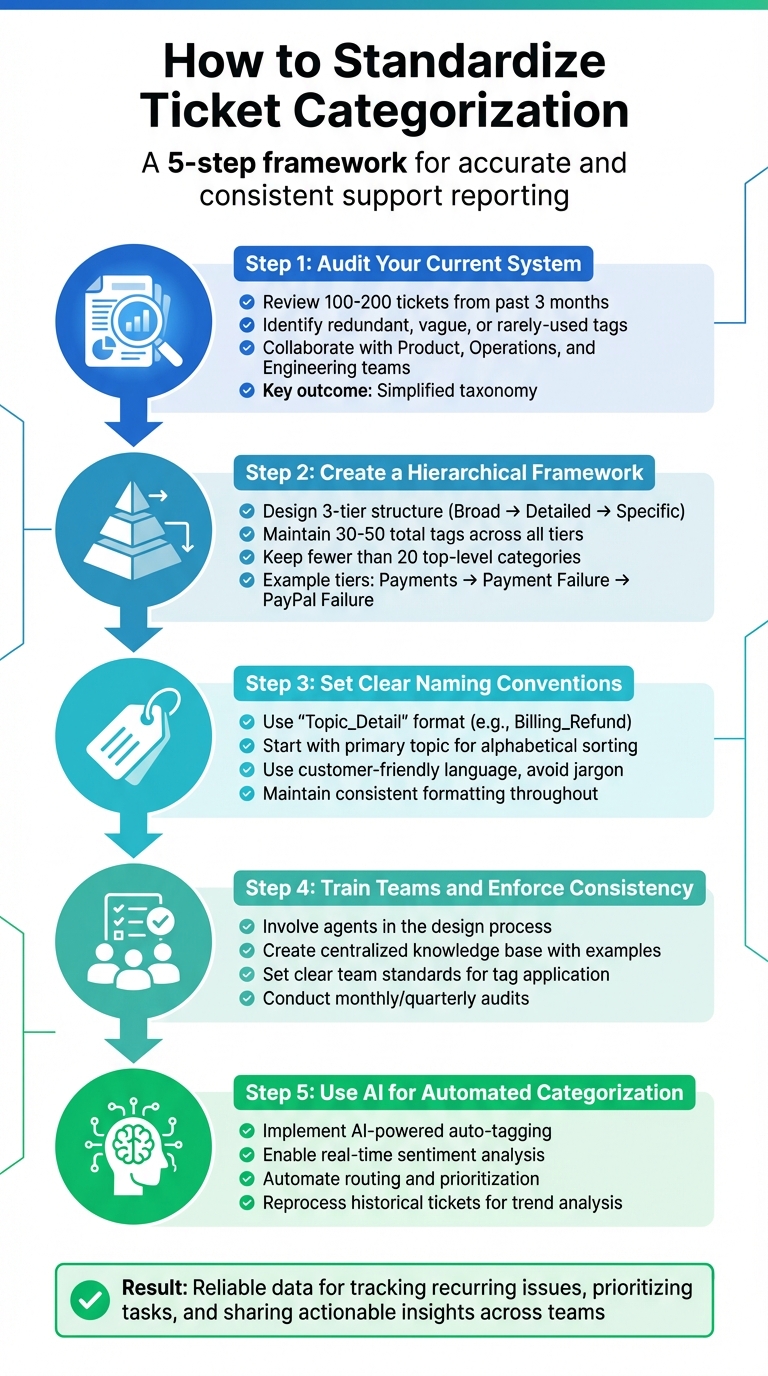
5-Step Process to Standardize Ticket Categorization for Accurate Support Reporting
Automatic classification of helpdesk tickets through Natural Language Processing techniques
Step 1: Audit Your Current Categorization System
Before making improvements to your categorization system, it’s essential to figure out what’s not working. Many support teams struggle with overly complex taxonomies that are hard for agents to navigate. When agents only have about three seconds to classify a ticket, they often pick the first tag that seems relevant instead of the most accurate one.
How to Conduct a Categorization Audit
Start by pulling a random sample of 100–200 completed tickets from the past three months. Print these tickets and have team members jot down key details on sticky notes. This hands-on exercise makes it easy to spot missing categories, overlapping tags, or ones that barely get used.
Next, dig into your system to identify tags that are rarely used or were created for one-off events – these are often called "chocolate teapot" tags. If a tag has only been used once or twice in the last year, it’s a good candidate for merging into a broader category. Also, check for inconsistencies, like agents using different tags for the same issue or manual entries leading to misspelled duplicates. These problems fragment your data and reduce its usefulness.
Don’t tackle the audit alone. Collaborate with teams like Product, Operations, and Engineering to understand what they need from your support data. For example, your CIO might require specific tags for high-level reporting, while your agents need categories that make routing tickets easier.
Simplify Categories for Better Results
After the audit, you’ll likely find opportunities to simplify your taxonomy. For most B2B support teams, a system with 30–50 tags strikes the right balance. It’s detailed enough to be actionable but not so overwhelming that it hinders agents or compromises data quality.
Begin by merging overlapping categories. For instance, if you have tags like "Customer how-to", "Help customer", and "User guidance", combine them into a single "How-To Question" category. Also, get rid of vague catch-all tags like "General Inquiry" or "Miscellaneous." These don’t provide much value and are often used as a default when agents are in a hurry. Finally, standardize naming conventions with clear, customer-friendly language. For example, a tag like "Payment_failed_paypal" is much more descriptive than an acronym like "FTLI" (first-time login issues).
Once your categories are streamlined, you’ll be ready to build a stronger hierarchical framework in Step 2.
Step 2: Create a Hierarchical Categorization Framework
Once you’ve streamlined your taxonomy, the next step is to organize it into a tiered system that can scale as your needs grow. A hierarchical framework arranges tags in levels, moving from broad categories at the top to more specific ones below. This structure avoids over-tagging and helps agents quickly locate the right label. It works hand-in-hand with your simplified taxonomy, ensuring tickets are categorized accurately and efficiently.
Design a Tiered Category Structure
A well-designed hierarchy typically includes three tiers. Here’s how it works:
- Tier 1: Broad categories like "Payments", "Technical Issues", or "Product Feedback" serve as the foundation.
- Tier 2: These break down into more detailed subcategories, such as "Payment Failure" or "API Issues."
- Tier 3: The final level pinpoints specific causes, like "PayPal failure" or "Documentation error".
This setup not only helps classify tickets but also uncovers patterns in customer interactions. For example, it can reveal which product features are mentioned most often in complaints, allowing operations teams to prioritize fixes and streamline customer experience improvements. To keep navigation simple, aim for fewer than 20 top-level categories, with a total of 30–50 tags across all tiers.
When building your tiers, involve stakeholders from across the company. Jenny Dempsey, CX Manager at Apeel, highlights the importance of collaboration:
"I typically start by talking to other teams to understand what needs to be measured outside of what I/my team want to measure. I learned early on that if I just measure what I want, I don’t have access to data that other teams need."
For instance, your CIO might need high-level categories for reporting, while your product team may prefer tags tied to specific features like "Analytics" or "Chatbot."
Compare Different Categorization Approaches
Not all categorization methods are created equal. Choosing the right approach depends on your support team’s goals and structure. Here’s a comparison of common methods:
| Approach | Advantages | Drawbacks | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Issue-Based | Great for root cause analysis and spotting product bugs. | Can become overly detailed if not carefully managed. | Ideal for product-driven teams focused on constant improvement. |
| Department-Based | Simplifies routing to specialized teams (e.g., Billing, Legal, Engineering). | Provides little insight into the reasons behind customer inquiries. | Best for large enterprises with distinct, siloed teams. |
| Product-Based | Directly aligns support data with product development roadmaps. | May confuse agents if product lines overlap. | Works well for SaaS companies with diverse features or modules. |
A hybrid approach often works best for B2B support teams. For example, you could use Tier 1 for product modules, Tier 2 for issue types (like Bug, Feature Request, or Question), and Tier 3 for specific root causes. This setup combines the routing benefits of department-based categorization with the actionable insights of issue-based analysis, giving you the best of both worlds.
Step 3: Set Clear Naming Conventions
A well-structured framework is only as effective as the labels it uses. Consistent naming conventions keep everything organized, helping agents quickly locate and apply the right tags without wasting time scrolling through a messy list. Using familiar and intuitive language for category names ensures they’re easy to recognize at a glance.
Best Practices for Naming Categories
When creating tags, always start with the primary topic. For instance, use Size_small instead of Small_size, or Billing_Refund instead of Refund_Billing. This approach makes alphabetically sorted lists easier to scan, speeding up the tagging process. Stick to a clear "Topic_Detail" format, using underscores or dashes as separators. Avoid spaces or inconsistent punctuation, as these can lead to duplicate entries or confusion.
Keep your framework manageable by adhering to the guideline of 30–50 tags overall, with fewer than 20 at the top level. This balance ensures efficiency without overwhelming your agents.
Also, align your naming conventions with the language your customers use. If customers frequently say, "I can’t check out", your tag should be Checkout_Failed instead of something overly technical like ECOM_ERR_003. This customer-focused approach not only shortens training time but also improves tagging accuracy across the team.
Finally, let’s look at some common mistakes that can disrupt your taxonomy and how to avoid them.
Common Categorization Mistakes to Avoid
Using acronyms or internal jargon can create unnecessary confusion. For example, a tag like FTLI for "First Time Login Issue" might be clear to your engineering team but could leave new agents scratching their heads, leading to tagging errors. Avoid department-specific shorthand and instead use straightforward, descriptive terms.
Inconsistent formatting is another common issue. Tags like "Customer how-to" and "Customer Howto" might seem similar but could be treated as separate categories by your reporting system. To prevent this, standardize your formatting – whether you choose lowercase, CamelCase, or Title Case – and stick to it across the board. Consistency is key to keeping your taxonomy clean and effective.
sbb-itb-e60d259
Step 4: Train Teams and Enforce Consistency
Even the most well-designed system can fall apart without consistent use. Standardized categorization only improves reporting and workflow efficiency when your team applies it correctly every single time.
Involve Teams in the Standardization Process
Consistency starts with team involvement. If agents are part of the design process, they’re more likely to see categorization as a helpful tool – not just another task to check off. Collaboration across departments ensures your taxonomy works for everyone, whether it’s Product teams tracking feature requests or Operations identifying recurring problems.
Here’s a practical idea: try a "Post-It" exercise with your team. Gather a random sample of past tickets, and ask agents to write down the key information they think should be captured for each one. This hands-on activity highlights which categories are useful and which ones might cause confusion or overlap. Testing your proposed structure against real tickets also helps uncover flaws you might miss on your own.
When agents understand why specific tags matter to teams like Product or Operations, they’re more motivated to use them correctly. Greg Rich, CEO of Vivantio, explains it well:
"The key to getting it right is involving people from all levels to make sure you address everyone’s core needs".
Once you’ve secured buy-in, the next step is training agents and ensuring they stick to the system.
Train Agents and Monitor Application
Involvement is the first step, but training and ongoing monitoring are what make the system stick. After finalizing your structure, create a centralized knowledge base that clearly defines each category. Include examples and screenshots showing when and how to use specific tags. A visual flowchart can also guide agents through the decision-making process as they get familiar with the system.
Set clear team standards. For instance, decide that a "refund" tag should only be applied when a refund is authorized, not just requested. To maintain consistency, limit who can create new tags – this avoids duplicates like "How-to" versus "Howto".
Regular reviews are essential. Schedule monthly or quarterly sessions to audit tagging accuracy, give feedback, and clean up any unnecessary tags that have crept in. Real-time dashboards can also help you spot inconsistencies early, before they become a bigger problem. And don’t underestimate the value of coaching – encourage agents to prioritize clarity over speed when tagging. This steady reinforcement keeps the system working as intended.
Step 5: Use AI for Automated Categorization
Manual tagging systems simply don’t hold up when scaled. Agents often spend just a few seconds picking from a long list of tags, sometimes choosing the first one that seems “close enough”. This can lead to inconsistent data, which erodes confidence in support reporting. AI steps in here, ensuring a standardized taxonomy is applied accurately and consistently across every ticket. This is where AI-driven solutions start to shine.
AI-Powered Auto-Tagging and Sentiment Analysis
With a refined taxonomy in place, AI takes over to deliver consistent, precise tagging. Machine learning algorithms are designed to understand both context and intent. For example, if a customer writes, "I don’t want a refund", traditional keyword tagging might misclassify this as a refund request. AI, however, identifies the negation and categorizes it correctly.
Supportbench’s AI automation goes even further, handling multiple aspects simultaneously. It can classify issue types (e.g., "Product Bug"), assign priorities (like "Critical"), and even assess customer sentiment in real time. A practical example of this is James Villas, a global holiday rental company, which used AI to auto-categorize and prioritize urgent tickets. The result? A 46% reduction in response time.
AI also reprocesses historical tickets, uncovering trends, assessing churn risks, and enabling root-cause analysis. Sharad Khandelwal, Founder and CEO of SentiSum, highlights the reliability of AI-driven tagging:
"Artificial intelligence-powered tagging doesn’t run into this issue [catch-all tags] because it never tires or rushes. As long the taxonomy is set up correctly, AI will apply tags consistently every time."
Integrate AI into Your Support Workflows
AI’s capabilities go beyond ticket tagging – it transforms workflows into smarter, more efficient systems. Once a ticket’s issue type and sentiment are identified, Supportbench can automatically assign it to the right team, suggest tailored response templates, or even flag emerging trends before they escalate.
AI integration also boosts overall workflow efficiency. Take Wolseley Canada, for instance. In 2025, they automated the routing of 7,000–8,000 monthly emails, significantly streamlining operations. Eilis Byrnes, Customer Service and Process Improvement Manager at Wolseley Canada, shared:
"The system promptly resolved overdue cases and enhanced staff efficiency."
To maximize AI’s impact, set up rules for critical scenarios like VIP escalations or product-specific issues. Establishing a feedback loop ensures the system continues to improve over time. Syncing historical data – ideally up to 50,000 tickets – allows the AI to quickly learn existing patterns, providing accurate results from the outset.
Conclusion
Standardized ticket categorization is the backbone of effective support strategy. Without it, you risk overlooking recurring issues, mishandling urgent priorities, and failing to provide actionable insights for decision-makers. A well-structured system transforms your support data into a powerful tool for driving improvements across your organization.
Key Takeaways for Standardization
To get started, evaluate your current system to identify and remove redundant tags and vague categories that don’t provide meaningful insights. Next, design a hierarchical framework with 30–50 clear and concise tags. This balance ensures enough detail to uncover root causes while remaining manageable for your team to use effectively.
Consistency is the key to success. Develop a tagging knowledge base that outlines when and how to use each category. Collaborate with teams from Product, Operations, and Engineering to align the system with organizational goals. Regular reviews – ideally every quarter – help keep the taxonomy relevant as your products and features evolve.
Lastly, consider leveraging AI to scale your categorization efforts. Automated tagging reduces human error, prevents fatigue, and brings in advanced tools like real-time sentiment analysis and intelligent routing. With AI, your support data becomes a strategic asset, driving efficiency, improving customer satisfaction, and boosting your overall performance.
FAQs
How does AI help improve the accuracy of ticket categorization?
AI enhances ticket categorization by leveraging machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) to analyze the content of support tickets. These tools enable automated assignment of the most appropriate categories, ensuring consistent and accurate tagging while minimizing human errors.
Over time, AI systems improve by learning from new data, making it possible to identify emerging trends and stay aligned with evolving customer needs. Automating this process not only saves time but also boosts the accuracy of reports, streamlines operations, and improves data quality – providing a stronger foundation for informed decision-making.
What are the most common mistakes in ticket categorization, and how can they be avoided?
Ticket categorization often goes off track due to a lack of structure and consistency. One common issue is using vague or overly broad categories, which can make it tough to route tickets efficiently or produce useful reports. Another problem? Skipping input from key stakeholders – like support agents and team leads – during the setup process. This oversight often leads to categories that don’t match actual workflows or meet customer needs.
Inconsistent category usage by support agents is another frequent challenge. This usually happens when guidelines are unclear or training is inadequate, resulting in unreliable data and reporting errors. On top of that, relying solely on manual categorization invites human error, especially as ticket volumes increase.
To tackle these problems, consider leveraging AI tools for automated tagging. These tools can help reduce errors and save time. It’s also a good idea to regularly review and update your categorization system to keep it aligned with customer trends and business goals.
Focusing on clear guidelines, consistent practices, and periodic updates can help you build a system that not only boosts reporting accuracy but also streamlines operations.
Why is it important to use a structured framework for ticket categorization?
A structured categorization framework plays a key role in maintaining clarity, consistency, and efficiency in customer support operations. It simplifies processes like ticket routing, prioritization, and escalation, while also providing the foundation for accurate trend analysis and reporting.
As ticket volumes increase, a well-defined hierarchy becomes even more important. It helps avoid confusion and ensures data is organized to support smarter decision-making. This kind of standardization not only boosts operational efficiency but also contributes to a smoother, more satisfying experience for customers.