Each executive spends a part of the day trying to figure out how to make their products and services stand out while still making money. That’s what every company is trying to do: Make great products and a lot of money.
It seems so simple yet so hard to do. What makes some companies successful while others fail? There are many various reasons why companies fail or succeed, but perhaps one of the main ones is their competitive edge.
A value chain can be thought of as a model that helps organizations identify their competitive advantage and improve their operations for better efficiency and increased profits. Read on to learn more about value chains, models, and examples.
What is a Value Chain?
The value chain is a business model that examines all the steps a company takes to turn an idea into a product for sale. Companies can use this model to improve their perspective, increase profits, and lower costs.
There are two main ways to add value to your value chain:
- First, enhance the social value of your products by improving quality and building brand trust, which can lead to more sales.
- Second, lower production costs to encourage more purchases and increase profit margins.
You can also analyze the value chain to find ways to improve specific sales and production activities. By increasing value or cutting costs, you can gain a competitive edge in the market and refine your sales strategies.
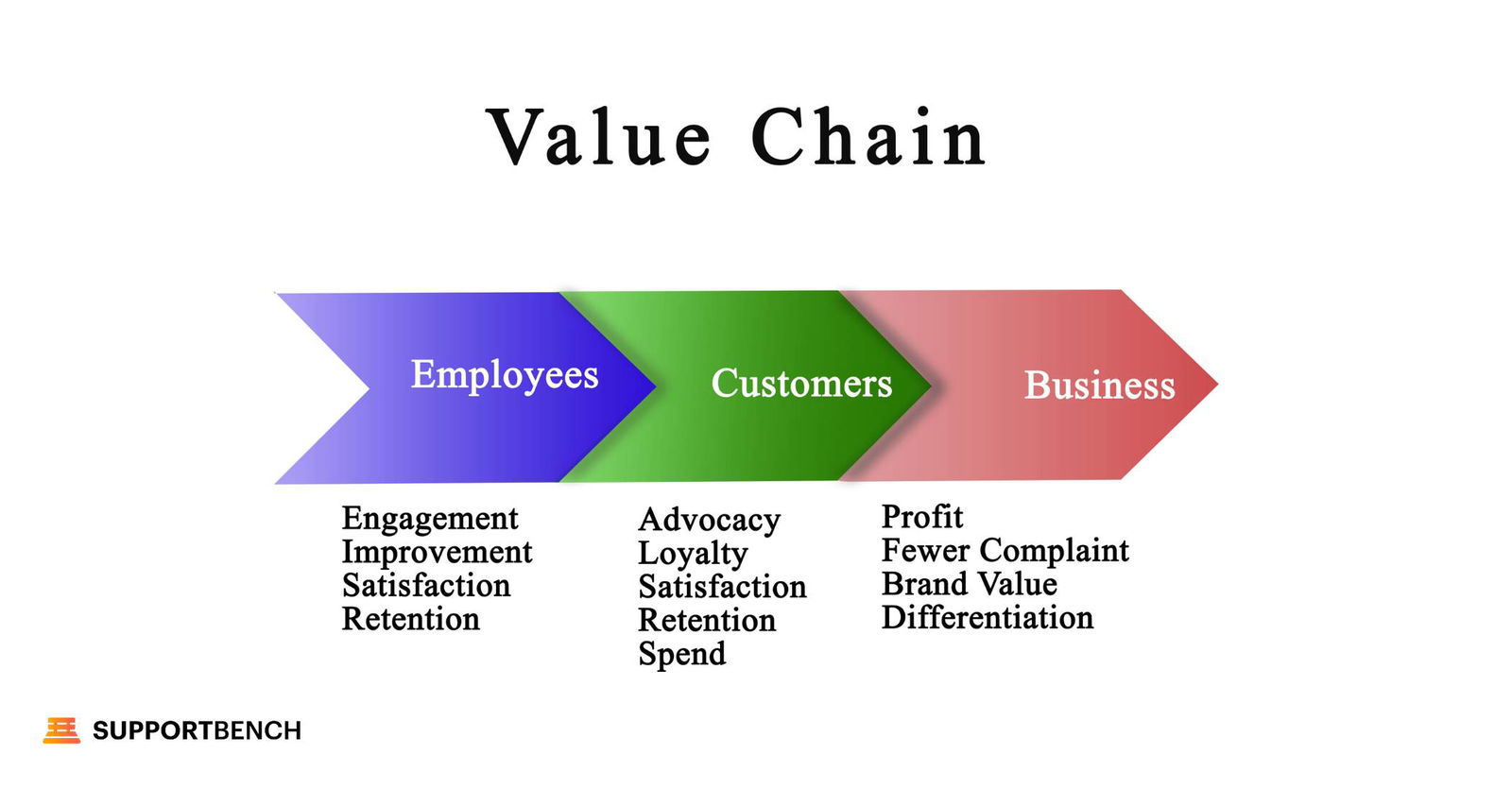
Components of a Value Chain
Company activities are divided into two main types: primary activities and support activities. Each category has specific tasks that may differ depending on the industry.
Primary Activities
Primary activities are those that add value and provide a competitive advantage. They are generally:
- Inbound Logistics: Receiving, storing, and controlling inventory.
- Operations: Converting the raw material to the final product.
- Outbound Logistics: Delivering the final product to the customer.
- Marketing and Sales: Strategies to promote products and reach customers, including advertising and pricing.
- Service: Programs to support products and improve customer experience, like customer service and repairs.
Support Activities
Support activities help improve the efficiency of primary activities. Enhancing any support activity benefits at least one primary activity. These activities usually appear as overhead costs in a company’s income statement:
- Procurement: How a company obtains raw materials.
- Technological Development: Research and development related to designing and improving manufacturing processes.
- Human Resources Management (HRM): Hiring and keeping employees who can help the company pursue its strategy and product development.
- Infrastructure: Company systems and management structure include planning, finance, and quality control.
Benefits of Value Chains
The value chain framework helps the organization to find sources of their positive or negative cost efficiency. Value chain analysis can support businesses in the following ways:
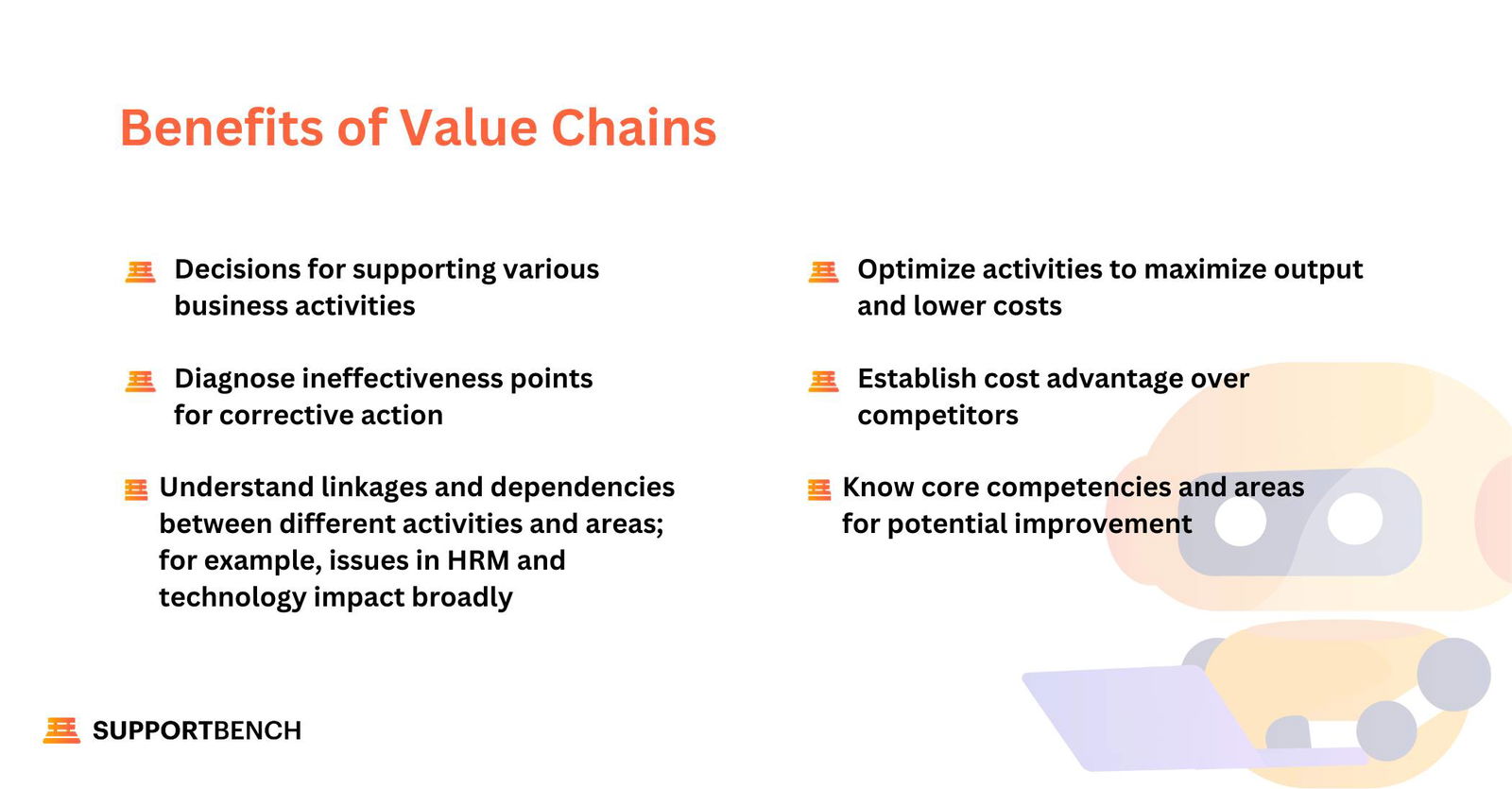
- Decisions for supporting various company activities
- Diagnose ineffectiveness points for corrective action
- Understand linkages and dependencies between different activities and areas; for example, issues in HRM and technology impact broadly
- Optimize activities to maximize output and lower costs
- Establish cost advantage over competitors
- Know core competencies and areas for potential improvement
While value chain analysis is extremely useful, it is even more important when a high level of emphasis is placed on granular process details in a value chain to continue supporting an organization’s larger strategy.
How to Conduct a Value Chain Analysis?
Companies should not view the value chain analysis as a completed frame or linear process. To gain a deeper understanding of their value chains, companies can follow these steps:
- Split each primary and secondary activity into sub-activities: By analyzing each function in more detail, they can better evaluate its return on investment.
- Identify connections between sub-activities: Inefficiencies in one area are often tied to others. For example, a poor HR hire might create issues across departments. Similarly, technology and inbound operations can have far-reaching effects.
- Diagnose areas for improvement: Look for trends and patterns within sub-activities and their connections and assess where specific improvements can be made.

Value Chain Example
Let’s simplify the value chain example for Apple, Inc. and its main activities:
Inbound Logistics
Apple works with about 200 suppliers, which it reviews yearly to improve efficiency. These suppliers provide around 98% of the materials needed for production and assembly.
Operations
Through outsourcing, Apple manufactures its products in Japan and China, which helps keep labor and materials costs low.
Outbound Logistics
Customers can buy Apple products online, in Apple stores, or through distributors like Best Buy. Distributors who prominently display Apple products receive a 25% discount.
Sales and Marketing
Apple focuses its sales and marketing on design and brand reputation. Its target customers are anyone who can afford to buy an Apple product.
Service
Apple provides long warranties, the Genius Bar, and trained technicians in stores. The company prioritizes customer service with each new product release to enhance the buying experience.
Enhance Your Value Chain and Customer Service with Supportbench
Effective customer interaction management has become significant for any business looking to optimize its value chain and gain a competitive edge. Supportbench offers a customer support platform that streamlines ticket management, workflow automation, and customer management processes.
Furthermore, with features like SLA management, escalation handling, and detailed analytics, Supportbench helps support teams operate more efficiently.
Whether you’re a large enterprise or a small-to-medium-sized business, the customizable portals, multi-channel communication, and integrations with various business tools truly elevate customer service.
Get started with Supportbench to help your organization reduce costs while improving customer satisfaction at every touchpoint in the value chain.
Conclusion
Today’s market is competitive, and no organization alone can come out on top without understanding and improving its value chain. By analyzing each part of the value chain, companies can work more efficiently, cut costs, and gain an edge over competitors.
Tools like Supportbench help companies enhance customer interaction, which is one of the significant parts of the value chain. Whether improving customer service, reducing costs, or strengthening brand reputation, careful value chain analysis and using tools like Supportbench can lead to higher profits and long-term success.
FAQs
1- What are the five value chains?
The value chain framework includes five main activities: inbound operations, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service.
It also has four support activities: procurement, human resource management, technological development, and company infrastructure.
2- What is the primary purpose of the value chain?
Value chain analysis helps your company make more money. By knowing the value you provide to your audience, you can create a better sales plan and change your activities to increase revenue.
3- What is the CRM value chain?
The Customer Relationship Management Value Chain (CRM VC) shows how we view CRM today. It includes management practices that aim to increase profits. The CRM VC focuses on making customers profitable rather than just improving brand performance or gross margins.















